

In today’s competitive environment, strategic compensation planning is a critical part of aligning HR practices with broader organizational goals. But what is compensation planning exactly? Essentially, it’s a systematic approach to determining and managing the types of compensation plans that will both attract and retain talent while also motivating high performance across the organization.
In compensation planning in HRM, creating a structured, equitable system of rewards goes beyond setting a simple pay scale; it’s about aligning compensation with business objectives. By clearly defining a compensation plan in HRM, organizations can ensure that employees feel valued, fairly rewarded, and motivated to contribute to the company’s success. This guide will introduce you to each essential element of compensation planning, providing the foundation you need to craft a robust strategy.
The importance of compensation planning can’t be overstated—it impacts employee satisfaction, productivity, and ultimately, the company’s bottom line. Effective employee compensation management gives HR professionals the tools to design packages that are competitive and compliant, yet flexible enough to evolve with organizational growth. We’ll cover everything from understanding compensation plan meaning to the key types of compensation involved in today’s market.
Why is strategic compensation planning so essential in today’s fast-changing labor market? With the rise of remote work, evolving skill requirements, and increased demand for pay transparency, having a well-structured compensation plan in HRM is more crucial than ever. Effective compensation planning allows organizations to keep pace with industry trends, adjust to market shifts, and provide clear, competitive rewards that resonate with current and prospective employees.
A well-designed compensation plan meaning more than just a salary range; it encompasses an entire rewards system, including benefits and performance-based incentives, ensuring employees feel fairly compensated for their contributions. This approach to compensation planning in HRM enables companies to attract top talent, retain valuable employees, and boost overall job satisfaction.
A case in point: organizations that prioritize job evaluation in compensation management and regularly adjust pay based on market benchmarks often see better retention rates and enhanced employee engagement. Such companies show their commitment to fair employee compensation, reflecting the organization’s values and long-term goals.
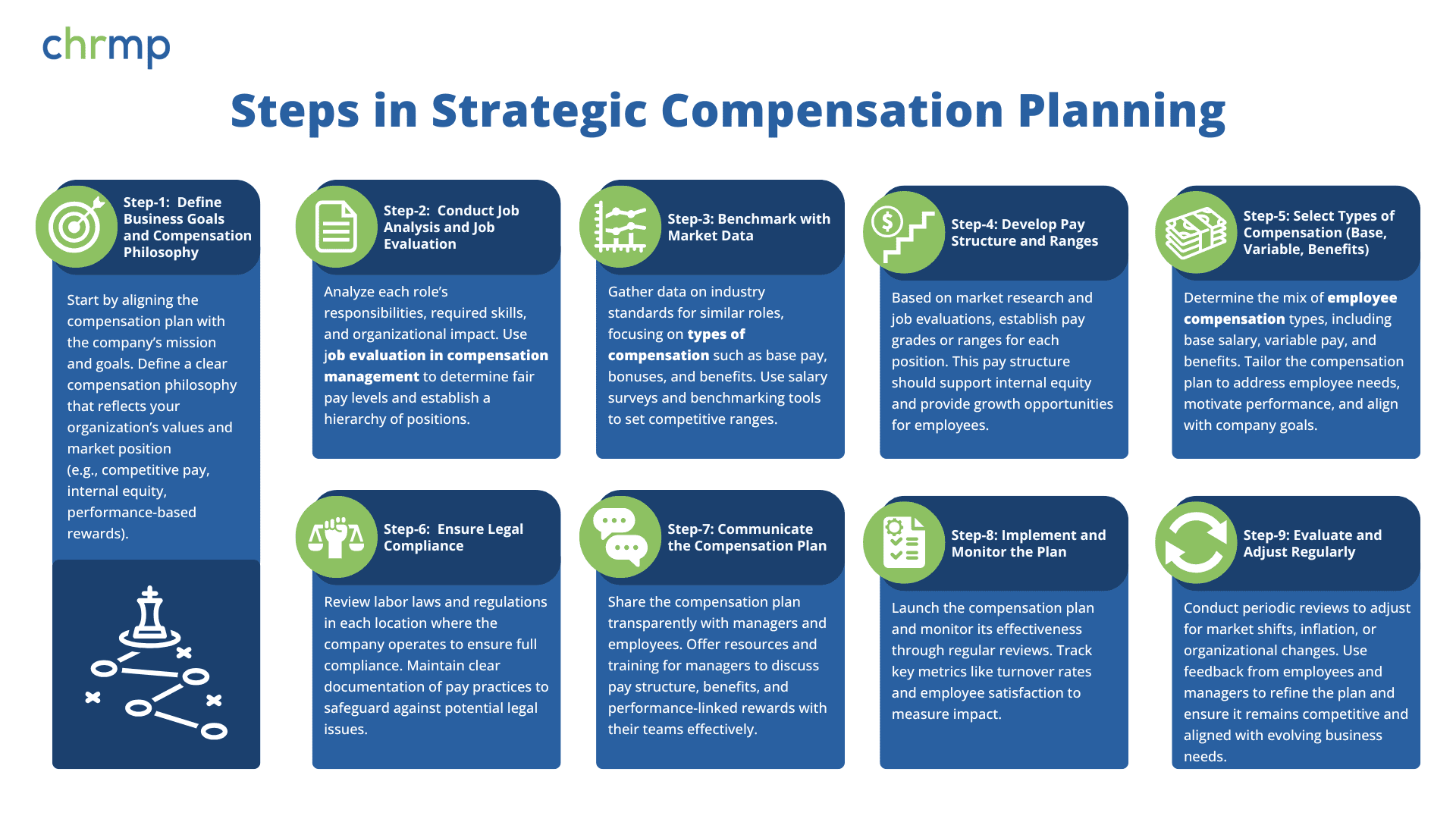
Building a strategic compensation plan starts with a firm foundation in understanding the types of compensation plans available, as well as their intended impact on employee behavior and organizational success. Here are the key components HR professionals must prioritize to create an effective compensation plan:
Understanding compensation types within this framework allows HR professionals to build packages that align with business goals and reflect current market standards. By laying this foundation, organizations can ensure their compensation planning practices are robust, fair, and responsive to both organizational needs and employee expectations.
Defining the Types of Compensation: Base Pay, Variable Pay, and Benefits
In strategic compensation planning, understanding and effectively integrating different types of compensation is critical for addressing diverse employee needs and aligning rewards with company objectives. Each type of compensation serves unique motivational purposes and together form a cohesive compensation plan in HRM.
Base pay is the fixed compensation provided to employees in the form of a salary or hourly wage. It’s often the largest and most predictable component of employee compensation, setting the baseline for how employees are rewarded. Job evaluation in compensation management is used to determine appropriate base pay by assessing job responsibilities, skill requirements, and market value to ensure pay equity across roles.
Example: In a tech company, a software engineer’s base pay might be determined by industry standards, skill requirements, and internal job evaluations. If the market rate for this role is $80,000, the company may set a range from $75,000 to $85,000 based on experience and performance.
Variable pay is a performance-based component that fluctuates according to the achievement of specific goals. Unlike base pay, it’s directly tied to an employee’s or team’s performance, creating a powerful incentive for achieving high performance and aligning employee contributions with business goals.
Example: A sales team might have a commission-based structure where members earn a percentage of their total sales in addition to a base salary. For instance, if a sales representative has a base pay of $50,000 and a 5% commission, they stand to earn additional compensation based on their sales performance.
Benefits are non-cash compensation elements that contribute significantly to the overall employee compensation package. They’re designed to address broader employee needs, enhance job satisfaction, and support employee well-being. Health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and wellness programs are all standard benefits that demonstrate the employer’s investment in their workforce beyond salary.
Example: A manufacturing firm might offer employees comprehensive health insurance, retirement matching, and paid leave, which enhances job satisfaction and attracts long-term, committed employees.
Aligning compensation with business objectives is key in ensuring the compensation structure contributes meaningfully to organizational success. A strategic compensation plan should not only meet employee needs but also drive behaviors that support company objectives. Below are three main steps HR professionals should follow:
Benchmarking and market research form the backbone of competitive compensation planning, ensuring that the organization’s compensation packages meet market standards and support recruitment and retention.
Staying compliant with labor laws and regulations is fundamental to effective compensation planning in HRM. Navigating complex legal requirements ensures that the organization’s employee compensation practices are fair, non-discriminatory, and legally defensible.
A well-designed compensation plan is only as effective as its communication strategy. Transparency in employee compensation builds trust and ensures that employees understand how their pay is structured and why.
Compensation needs to remain responsive to evolving business and market conditions. Regular evaluation and adjustments ensure the compensation plan in HRM remains competitive and aligned with the company’s goals.
Mastering the essentials of strategic compensation planning is crucial for HR professionals aiming to attract, motivate, and retain top talent in an ever-evolving market. From understanding compensation plan meaning and evaluating compensation types to aligning rewards with business goals and ensuring compliance, each component plays a vital role in creating a robust compensation plan in HRM.
By grounding the plan in thorough job evaluation in compensation management and benchmarking with industry standards, HR can ensure that employee compensation is both competitive and fair. A clear compensation philosophy, proactive communication strategies, and periodic evaluations help establish transparency, enhance employee satisfaction, and build trust.

© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited
