Human Resources (HR) plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s culture, driving engagement, and ensuring growth. While some traditional Human Resources Roles remain fundamental, essential Human Resources roles have evolved to include specialized positions and advanced skills that support the needs of a dynamic, hybrid workforce. From recruitment to employee wellbeing, modern HR functions are diverse and essential for creating a resilient, adaptable workplace.
Key Functions of Human Resource Management
HR’s primary functions are critical to managing and supporting employees effectively, whether they are on-site, remote, or part of a hybrid workforce.
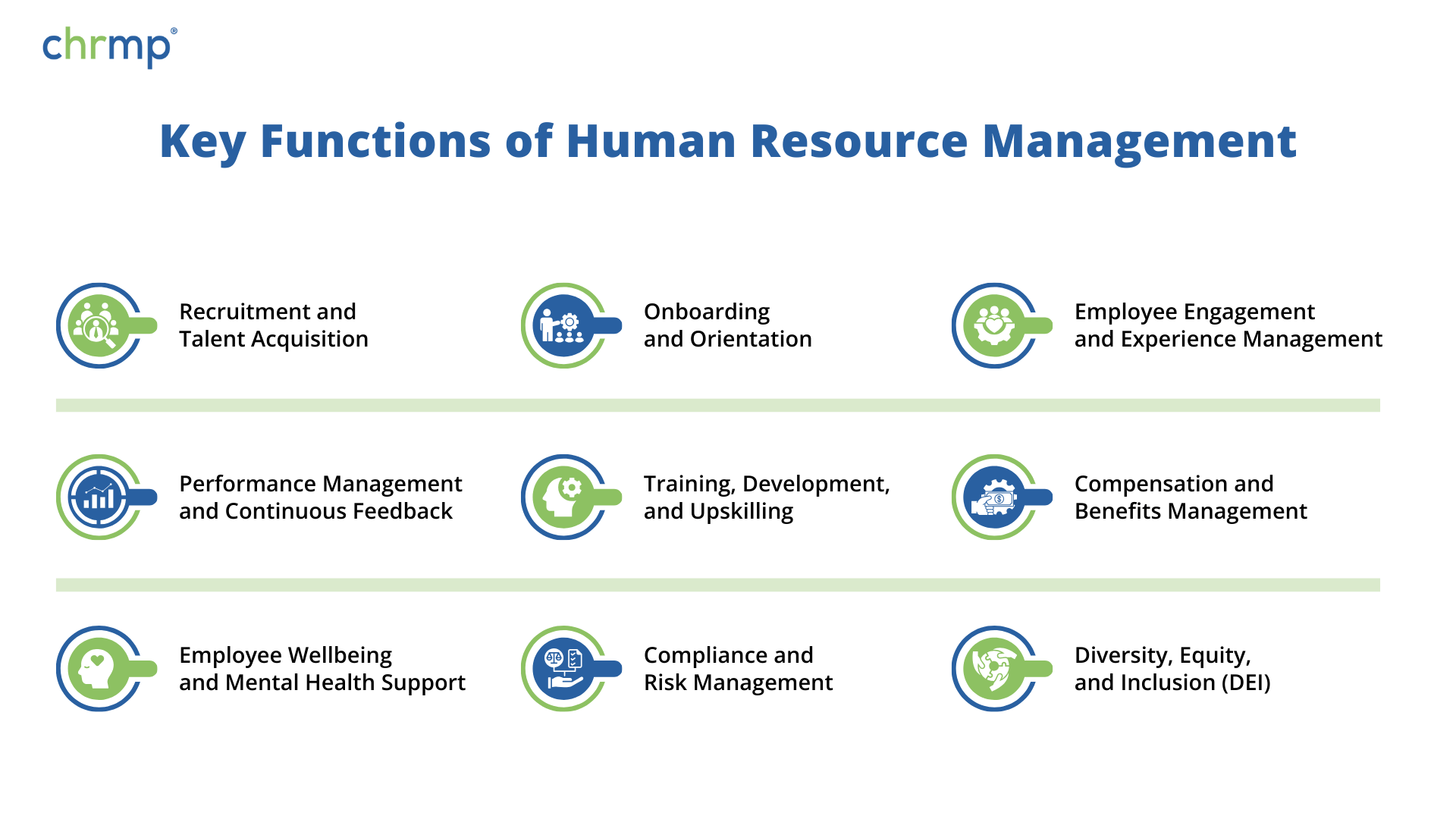
1. Recruitment and Talent Acquisition
Recruitment remains a core HR function, focusing on sourcing, screening, and hiring candidates who align with the company’s values and goals. Today, this function is enhanced with digital tools, employer branding, and diversity-focused hiring strategies.
Responsibilities: Developing job descriptions, sourcing candidates, managing interviews, and building a positive candidate experience.
Skills Needed: Strong communication, technical skills in Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), and brand management.
Example: HubSpot’s recruitment team uses social media to showcase their culture and engage potential candidates, helping them attract diverse, value-aligned talent.
2. Onboarding and Orientation
Onboarding goes beyond initial orientation, welcoming employees to the team and setting them up for success. With remote and hybrid roles becoming more common, onboarding now often includes digital orientation to help new hires integrate smoothly.
Responsibilities: Organizing orientation sessions, providing resources, and pairing new hires with mentors.
Skills Needed: Organization, empathy, and digital communication.
Use Case: Dropbox’s “Virtual First” onboarding provides virtual tours, tool training, and team introductions to create an inclusive remote onboarding experience.
3. Employee Engagement and Experience Management
Employee engagement ensures that employees feel valued and motivated, which directly impacts retention. Today, HR teams focus on building a positive employee experience (EX) that promotes work-life balance, mental wellbeing, and career growth.
Responsibilities: Conducting engagement surveys, developing recognition programs, and implementing flexible work policies.
Skills Needed: Emotional intelligence, data analysis, and creativity.
Example: Microsoft’s “Growth Mindset” initiative encourages continuous feedback and employee learning, creating a culture where employees feel supported and valued.
4. Performance Management and Continuous Feedback
Performance management has shifted from annual reviews to a continuous feedback approach, helping employees stay aligned with goals and develop in real time. This ongoing model promotes engagement and helps employees achieve their potential.
Responsibilities: Setting performance metrics, creating feedback systems, and coaching managers.
Skills Needed: Analytical thinking, coaching, and goal-setting.
Use Case: Adobe’s “Check-In” system replaced annual reviews with regular feedback sessions, leading to improved engagement and productivity.
5. Training, Development, and Upskilling
Learning and development (L&D) is essential to employee satisfaction and organizational growth. HR designs training programs that help employees build skills, advance their careers, and stay relevant in a fast-changing world.
Responsibilities: Assessing skill gaps, providing training resources, and promoting continuous learning.
Skills Needed: Instructional design, strategic thinking, and adaptability.
Example: Amazon’s Career Choice Program funds employees’ learning to gain skills, showing a commitment to their long-term growth.
6. Compensation and Benefits Management
Managing compensation and benefits ensures employees feel valued and financially secure. This includes competitive salaries, comprehensive health benefits, retirement plans, and modern wellness perks.
Responsibilities: Creating compensation structures, evaluating benefits packages, and ensuring fair pay practices.
Skills Needed: Financial knowledge, negotiation, and benefits management.
Example: Patagonia’s unique benefits, including time off for volunteering, attract socially conscious employees who appreciate the company’s values.
7. Employee Wellbeing and Mental Health Support
Wellbeing now includes physical, mental, and financial health. HR creates wellness programs and provides resources to support employees’ overall wellbeing, fostering resilience and reducing burnout.
Responsibilities: Developing mental health programs, providing access to wellness resources, and promoting a balanced work culture.
Skills Needed: Empathy, wellness knowledge, and problem-solving.
Example: Salesforce provides comprehensive mental health support, including reimbursements for therapy, to support employees’ holistic health.
8. Compliance and Risk Management
HR ensures that organizations adhere to labor laws, health and safety standards, and cybersecurity regulations. This function is especially important in a hybrid work environment, where compliance must be maintained across diverse locations.
- Responsibilities: Developing policies, conducting audits, and ensuring workplace safety.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of labor laws, regulatory awareness, and attention to detail.
- Use Case: Twitter’s “Remote Work Playbook” offers remote security and compliance guidelines to support its remote-first policy.
9. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
DEI programs are crucial to fostering a culture of belonging and respect. HR teams are responsible for building strategies that promote inclusivity, address biases, and create equal opportunities for all employees.
Responsibilities: Implementing DEI initiatives, conducting bias training, and tracking diversity metrics.
Skills Needed: Cultural competence, inclusivity, and leadership.
Example: Nike sets specific DEI targets and publishes progress reports to promote accountability and transparency in its DEI goals.
Traditional and New Human Resources Roles for a Modern Workplace
The HR function has diversified, with traditional roles still essential and new roles emerging to meet modern workplace demands. Below are the key Human Resources Roles, both foundational and specialized, each addressing specific organizational needs.
Traditional Human Resources Roles
1. HR Executive
- Responsibilities: Manages essential HR operations, such as payroll, benefits, and documentation. Supports HR Managers by handling daily administrative tasks.
- Skills Needed: Organizational skills, multitasking, and familiarity with HR software.
- Example: An HR Executive might ensure new hire paperwork is processed smoothly, ensuring compliance and a positive experience.
2. HR Manager
- Responsibilities: Manages HR team, oversees employee relations, and develops policies. HR Managers bridge strategic and operational functions.
- Skills Needed: Leadership, decision-making, and conflict resolution.
- Example: An HR Manager might implement company-wide engagement programs, enhancing employee satisfaction and loyalty.
3. HR Director
- Responsibilities: Shapes HR strategy, oversees budgeting, and ensures HR practices align with company goals. Collaborates with executives to address workforce challenges.
- Skills Needed: Strategic planning, data analysis, and cross-functional leadership.
- Example: At Google, HR Directors leverage people analytics to optimize team performance and identify trends in engagement and retention.
4. Recruitment Specialist
- Responsibilities: Focuses on candidate sourcing, conducting interviews, and managing recruitment processes.
- Skills Needed: Digital recruitment, relationship-building, and negotiation.
- Example: A Recruitment Specialist at Netflix assesses cultural fit to ensure that new hires align with the company’s values
New Human Resources Roles adopted by organizations worldwide
1. Employee Experience (EX) Manager
- Responsibilities: Focuses on creating a positive journey for employees from onboarding to career development, improving engagement and satisfaction.
- Skills Needed: Project management, empathy, and knowledge of engagement strategies.
- Example: Airbnb’s EX Managers organize virtual team-building events and wellness sessions, helping remote employees feel connected.
2. Compensation and Benefits Specialist
- Responsibilities: Designs competitive pay structures, manages benefit programs, and tracks compensation trends.
- Skills Needed: Financial planning, negotiation, and knowledge of market trends.
- Example: At companies like Salesforce, Compensation Specialists ensure benefit packages align with employee needs, supporting retention.
3. Learning and Development (L&D) Specialist
- Responsibilities: Develops training programs, identifies skill gaps, and supports employee growth.
- Skills Needed: Instructional design, adaptability, and strategic planning.
- Example: Amazon’s L&D Specialists create programs for technical upskilling, which keeps their workforce agile and competitive.
4. Employee Relations Specialist
- Responsibilities: Manages workplace grievances, resolves conflicts, and ensures a positive work environment.
- Skills Needed: Conflict resolution, active listening, and empathy.
- Example: An Employee Relations Specialist might mediate disputes, creating a fair and respectful workplace culture.
5. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Officer
- Responsibilities: Promotes inclusivity, implements DEI policies, and monitors diversity metrics.
- Skills Needed: Cultural awareness, empathy, and leadership.
- Example: DEI Officers at companies like Nike set diversity hiring goals and provide unconscious bias training to foster inclusion.
6. HR Data Analyst
- Responsibilities: Analyzes workforce data, tracks engagement metrics, and informs HR strategies with insights.
- Skills Needed: Data analysis, reporting, and critical thinking.
- Example: At IBM, HR Data Analysts use analytics to optimize hiring, reduce turnover, and enhance productivity.
7. Human Resources Business Partner (HRBP)
- Responsibilities: Acts as a strategic consultant, aligning HR initiatives with departmental goals.
- Skills Needed: Business acumen, relationship-building, and strategic thinking.
- Example: An HRBP at Facebook advises department heads on talent strategies, ensuring alignment with broader company objectives.
8. Change Management Specialist
- Responsibilities: Leads organizational change initiatives, such as restructuring or technology adoption, and supports employees through transitions.
- Skills Needed: Project management, communication, and problem-solving.
- Example: During digital transformations, Change Management Specialists at companies like Microsoft ensure employees are well-prepared and supported.
9. Talent Management Specialist
- Responsibilities: Manages career development, succession planning, and helps employees identify growth opportunities.
- Skills Needed: Mentorship, planning, and leadership.
- Example: A Talent Management Specialist might create development plans for high-potential employees, helping prepare future leaders.
Emerging Human Resources Roles in the Modern Workplace
In recent years, HR has expanded significantly to meet the changing needs of the modern workplace. Driven by digital transformation, a growing emphasis on diversity, and a focus on employee wellbeing, a range of new Human Resources roles has emerged. Here are some of the most prominent roles shaping today’s HR landscape.
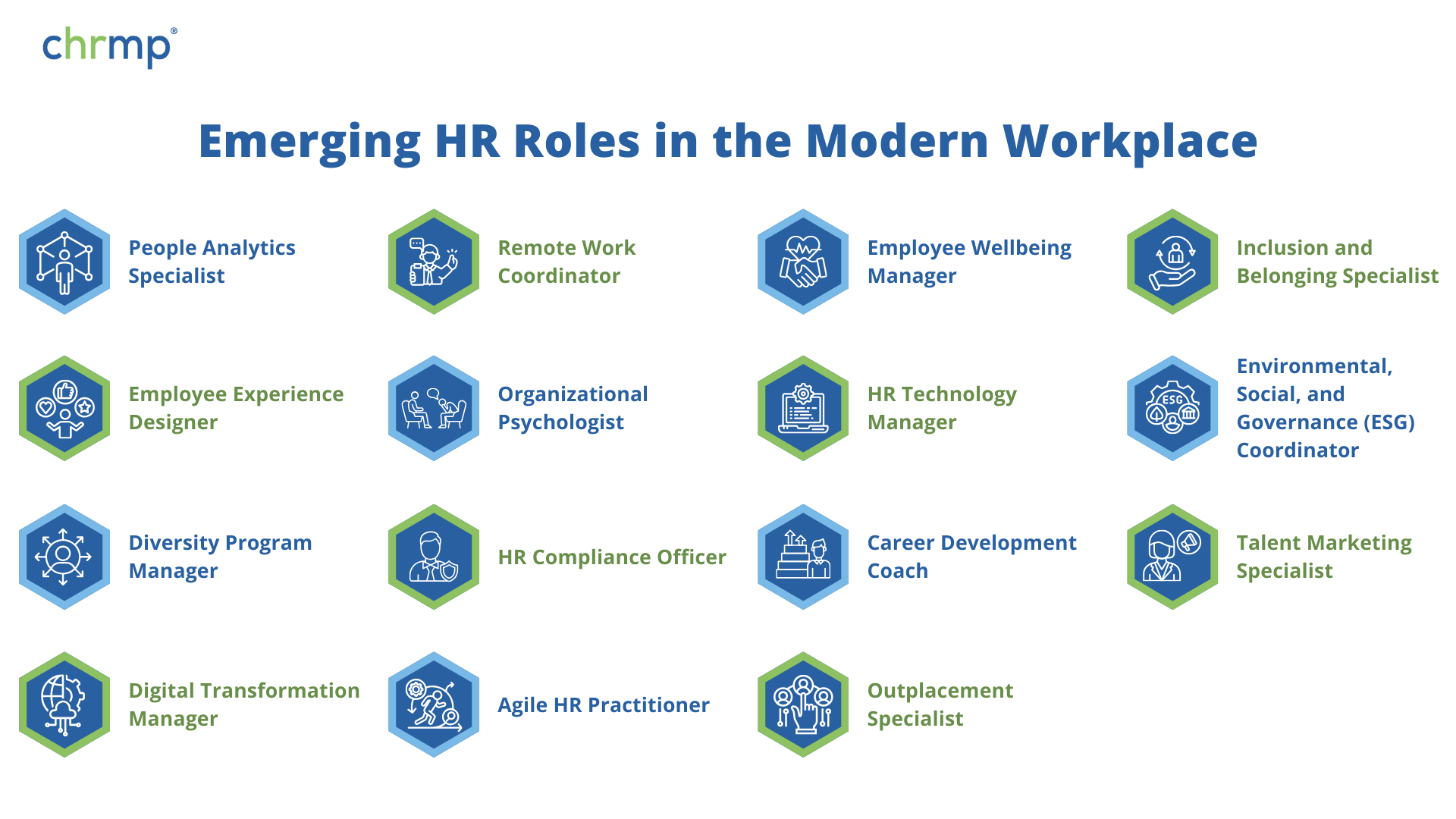
In recent years, Human Resources has expanded significantly to meet the changing needs of the modern workplace. Driven by digital transformation, a growing emphasis on diversity, and a focus on employee wellbeing, a range of new Human Resources roles has emerged. Here are some of the most prominent roles shaping today’s HR landscape:
1. People Analytics Specialist
- Description: People Analytics Specialists focus on using data to understand workforce trends, improve HR strategies, and drive decision-making. By analyzing data on employee performance, retention, and engagement, they provide insights to optimize HR practices.
- Skills Needed: Data analysis, predictive analytics, understanding of HR metrics, and proficiency in analytics software (e.g., Power BI, Tableau).
2. Remote Work Coordinator
- Description: With the rise of remote and hybrid work, Remote Work Coordinators ensure remote employees have the resources, support, and structure they need to thrive. They manage remote work policies, coordinate virtual team-building activities, and address remote-specific challenges.
- Skills Needed: Strong organizational skills, remote team management, digital communication, and knowledge of remote work technologies.
3. Employee Wellbeing Manager
- Description: Focused exclusively on employee wellness, this role develops and oversees wellbeing initiatives, from mental health programs to physical wellness challenges. The goal is to reduce burnout, support employee resilience, and create a healthier workplace.
- Skills Needed: Background in health and wellness, program management, mental health awareness, and empathy.
4. Inclusion and Belonging Specialist
- Description: Beyond diversity and equity, Inclusion and Belonging Specialists focus on creating a sense of belonging within the organization. They design programs to ensure that every employee feels valued, included, and connected, regardless of their background.
- Skills Needed: Cultural awareness, emotional intelligence, communication skills, and experience with DEI initiatives.
5. Employee Experience Designer
- Description: This role combines elements of human-centered design and HR to shape every step of the employee journey, from onboarding to exit. Employee Experience Designers work to make each interaction meaningful, engaging, and aligned with company culture.
- Skills Needed: Design thinking, empathy, communication, and project management.
6. Organizational Psychologist
- Description: Organizational Psychologists apply principles of psychology to improve workplace culture, address productivity issues, and enhance employee satisfaction. They might conduct assessments, provide counseling, or offer insights on team dynamics.
- Skills Needed: Psychology background, interpersonal skills, analytical skills, and an understanding of organizational behavior.
7. HR Technology Manager
- Description: As HR technology becomes essential, HR Technology Managers oversee HR software implementations, integrate digital tools, and ensure data security. They evaluate HR technology needs, provide tech support, and manage vendor relationships.
- Skills Needed: Technical proficiency, understanding of HRIS systems, project management, and vendor negotiation skills.
8. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Coordinator
- Description: ESG Coordinators focus on building sustainable practices within the organization. They may collaborate with HR to ensure environmental responsibility, promote social initiatives, and maintain ethical governance practices aligned with corporate values.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of sustainability practices, corporate social responsibility, communication, and project coordination.
9. Diversity Program Manager
- Description: While DEI has been a priority, the Diversity Program Manager role specifically develops and oversees diversity-focused initiatives. This can include recruitment programs, mentorship opportunities, and partnerships with diverse organizations.
- Skills Needed: DEI expertise, program management, cultural competence, and stakeholder engagement.
10. HR Compliance Officer
- Description: With ever-changing labor laws and workplace regulations, HR Compliance Officers ensure that company policies meet all legal requirements. They conduct audits, manage risk, and implement policies that protect both the company and employees.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of employment law, attention to detail, policy development, and auditing.
11. Career Development Coach
- Description: Career Development Coaches work with employees to map out career paths, identify growth opportunities, and set achievable goals within the organization. They focus on skill-building, internal mobility, and personalized development plans.
- Skills Needed: Coaching, mentorship, career counseling, and knowledge of talent management.
12. Talent Marketing Specialist
- Description: Also known as Employer Branding Specialists, Talent Marketing Specialists promote the company’s employer brand, showcasing company culture to attract top talent. They manage social media campaigns, create content, and work with marketing to build a strong employer brand.
- Skills Needed: Marketing knowledge, social media strategy, content creation, and brand management.
13. Digital Transformation Manager
- Description: This role bridges Human Resources and IT, guiding HR through digital transformation projects such as implementing new technologies or reengineering workflows for greater efficiency.
- Skills Needed: Project management, tech proficiency, change management, and strong problem-solving skills.
14. Agile Human Resources Practitioner
- Description: Agile HR Practitioners apply Agile methodologies to HR practices, focusing on flexibility, collaboration, and iterative improvement. This role often involves working in sprints, prioritizing tasks, and continuously adapting HR practices to meet evolving needs.
- Skills Needed: Understanding of Agile methodologies, project management, adaptability, and collaborative skills.
15. Outplacement Specialist
- Description: Outplacement Specialists support employees transitioning out of the company, helping them find new roles and providing career counseling. They ensure employees have a positive exit experience and that the company maintains a strong reputation.
- Skills Needed: Career counseling, empathy, relationship-building, and job market knowledge.
These emerging roles reflect HR’s expanding focus on supporting a holistic employee experience, enhancing workplace culture, and aligning HR practices with technological advances and societal expectations. Each of these roles contributes to creating a resilient, agile, and inclusive organization that meets the needs of today’s workforce.
Key Skills for Human Resources Professionals in Today’s Workplace
To succeed in today’s diverse, hybrid, and digital workplace, HR professionals must cultivate a blend of technical and interpersonal skills:
- Digital Literacy and Data Analysis: Using Human Resources technology and data analytics to inform recruitment, engagement, and DEI strategies.
- Change Management: Supporting employees through organizational change and adapting to shifting work structures.
- Emotional Intelligence (EI): Essential for understanding and supporting employee needs, managing conflicts, and fostering trust.
- Cultural Competence: Valuing diversity and fostering an inclusive work environment.
Conclusion | Human Resources Roles
Human Resources is more diverse, specialized, and essential than ever. From traditional roles like HR Managers and Recruitment Specialists to emerging roles like DEI Officers and HR Data Analysts, today’s HR professionals are instrumental in creating engaging, inclusive, and resilient workplaces. By mastering the **key functions of human resource management** and the essential skills of modern HR, organizations can build a supportive culture where employees thrive, innovate, and drive long-term success.





