Have you ever wondered why some teams break performance records every quarter while others struggle to meet even basic goals—even when both have talented people on board? This blog will unpack what is performance management, why it’s crucial for organizational success, and how you can overcome common PM challenges in your own workplace.
In many cases, the answer lies in performance management practices.
When performance management is done effectively, it helps employees understand expectations, receive timely feedback, and continuously develop their skills. However, if it’s neglected or overly complex, it can stifle growth and leave employees feeling unmotivated.
What Is Performance Management?
To begin, let’s clarify the performance management definition. Performance management is a systematic, ongoing process that aligns employees’ daily activities and long-term career goals with the broader strategy of an organization. Although PM basics certainly include tasks like evaluating performance and giving feedback, modern performance management is much more than an annual formality. Think of it as a perpetual cycle of goal setting, coaching, and assessing progress, designed to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
So, what is performance management in practical terms?
Picture a manager and an employee setting clear objectives at the start of each quarter. They hold brief check-ins every few weeks, discussing challenges and celebrating wins. The employee knows how their work contributes to the company’s overarching mission, and they have a detailed plan for honing new skills. At the end of the quarter, they review progress, gather feedback from multiple sources, and plan for the upcoming cycle. This ongoing rhythm helps the individual grow, while also boosting employee performance and overall organizational success.
Why Is Performance Management Important?
To understand the importance of performance management, consider the broad impact it has on employee performance at every level. Effective performance management systems don’t just measure results—they actively nurture the conditions under which employees can thrive. This, in turn, propels organizational success.
According to Harvard Business Review, companies with an effective performance management system typically see better overall results. A separate review highlights Netflix as an example: instead of traditional reviews, Netflix focuses on ongoing feedback and employee autonomy. By giving employees more freedom and responsibility, Netflix has fostered higher engagement and stronger retention—employees feel both trusted and empowered in their roles.
- Enhances Employee Engagement and Motivation
Engaged employees are often the lifeblood of a thriving organization. According to a Gallup study, highly engaged teams have 21% greater profitability and 41% fewer quality defects. Clear goals, meaningful feedback, and fair recognition are core elements of a strong performance management framework that helps individuals stay motivated and committed to their roles.
- Encourages Continuous Improvement and Accountability
When employees understand that performance is reviewed regularly—not just once a year—they tend to take greater ownership of their tasks. This culture of continuous improvement nurtures accountability and helps detect performance issues before they become overwhelming.
- Strengthens Organizational Culture and Values
Performance management can serve as a powerful tool to reinforce core organizational values. For instance, if collaboration is part of your corporate identity, managers can include peer feedback in reviews and applaud cross-functional initiatives. By celebrating such values within your performance management practices, you weave them into day-to-day operations.
- Links Individual Goals to Organizational Objectives
It’s not enough to have great individual performers if their efforts don’t contribute to the bigger picture. An effective performance management system will map out how each employee’s goals tie into overarching strategic objectives. This alignment ensures everyone moves in the same direction, which amplifies collective impact.
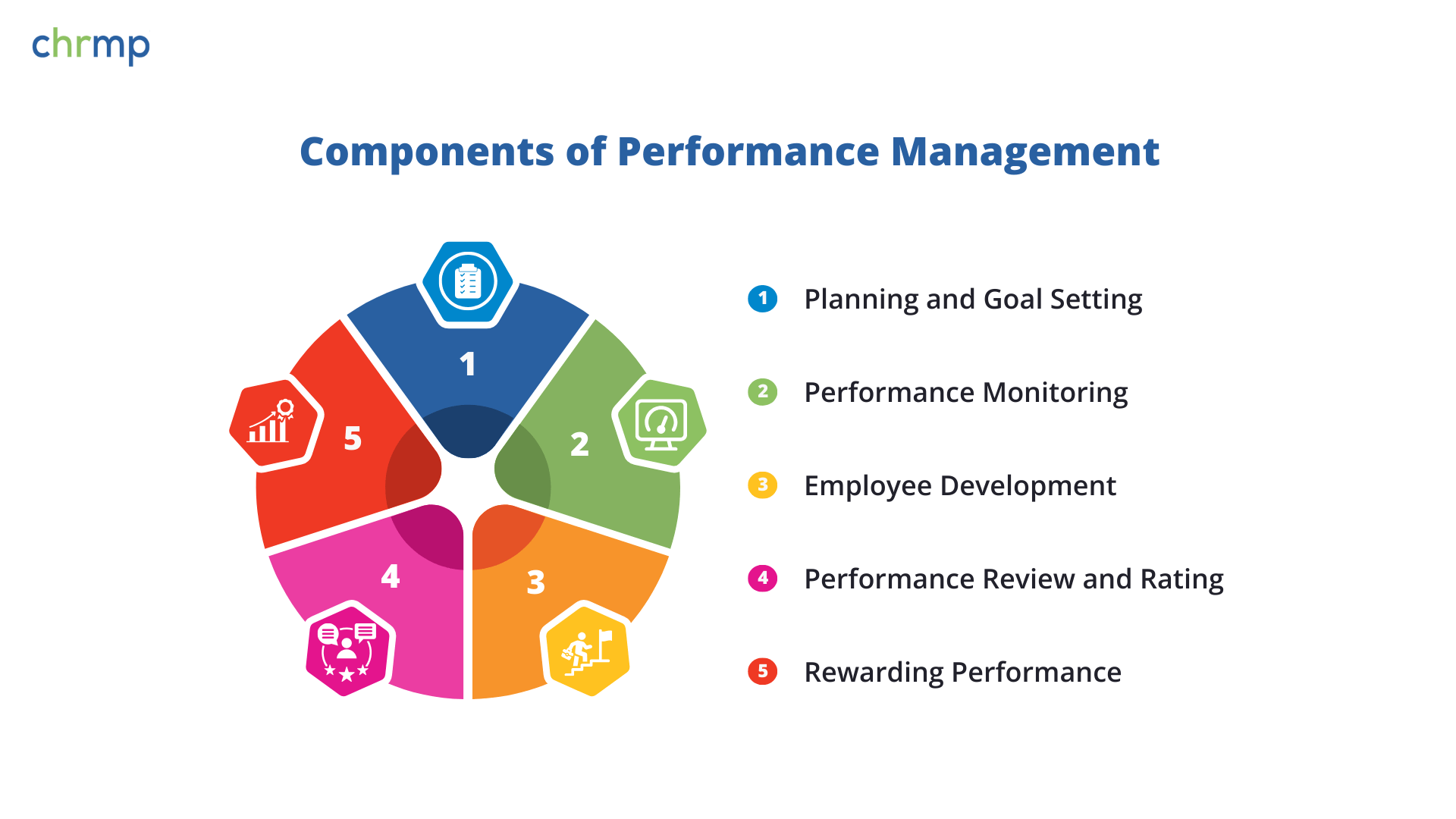
Components of Performance Management
Even though different organizations may tailor performance management differently, there are some universal components:
- Planning and Goal Setting
Planning and goal setting lay the foundation for effective performance management. This step involves identifying organizational objectives and translating them into clear, measurable targets for each employee. By setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals and adopting frameworks like OKRs (Objectives and Key Results), you establish a roadmap that aligns individual contributions with the company’s broader mission. OKRs, in particular, help teams link daily tasks to overarching organizational goals by focusing on measurable outcomes. Well-defined plans also create a shared understanding of responsibilities, reducing ambiguity and setting the stage for meaningful feedback discussions down the line.
- Performance Monitoring
Once goals are established, performance monitoring ensures progress stays on track. Regular check-ins, one-on-one meetings, and data-driven insights help managers and employees identify potential obstacles early. By addressing issues in real time, teams can make immediate adjustments to tasks or timelines, preventing minor roadblocks from escalating into major setbacks. This proactive approach fosters open communication and provides frequent opportunities for feedback that supports continuous improvement.
- Employee Development
A thriving performance management system goes beyond evaluations to support employee development. This includes identifying skill gaps, offering relevant training, and crafting tailored development planning paths for each team member. By investing in professional growth—through workshops, mentoring, or online courses—organizations nurture a culture where employees are motivated to learn and excel. Over time, this approach not only boosts individual capabilities but also drives overall business performance.
- Performance Review and Rating
Formal performance appraisal processes remain vital for documenting achievements and setting future expectations. During performance review discussions, managers assess employees’ successes, challenges, and overall progress against their goals. Ratings or qualitative assessments provide a structured snapshot of performance and can inform decisions related to promotions, compensation, or further development. Conducted fairly and transparently, a well-managed performance review reinforces accountability and underscores the organization’s commitment to supporting every employee’s growth.
- Rewarding Performance
Finally, recognizing and rewarding performance is essential for sustaining motivation and engagement. This step may involve monetary incentives, promotions, or even non-financial rewards like public recognition, extra paid leave, or career advancement opportunities. Tying rewards to goal attainment and positive behavior ensures that high achievers feel valued, while others see a clear path for what’s expected. In turn, this cycle of recognition and encouragement cements a high-performance culture across the organization.
- Modern Trends in Performance Management
The days of relying solely on annual reviews are fading fast. Organizations now recognize that to remain agile and competitive, they need to adopt more dynamic and data-driven approaches.
- Continuous Feedback over Annual Reviews
The shift to continuous feedback allows for more frequent, bite-sized coaching. This approach reduces anxiety and surprises in annual reviews, and it enables employees to correct course long before a small problem becomes a major concern.
- Real-Time Performance Reviews
Building on continuous feedback, many companies incorporate real-time performance reviews—quick evaluations or check-ins that might happen after a key project wraps up or when new responsibilities are assigned. This ensures that feedback is always current and relevant, rather than a retroactive look at events from months ago.
- Performance Analytics
Thanks to advancements in HR tools, organizations can now track performance data in real time. Performance analytics can highlight trends such as which teams might benefit from additional training or which department has the highest engagement levels. Using this data, HR professionals can proactively address issues like skill shortages or burnout before they become systemic problems.
- Emphasis on Employee Well-Being
In recent years, companies have recognized that employee engagement and performance hinge not only on targets and data but also on well-being. As a result, elements like mental health support, flexible working arrangements, and clear work-life boundaries have become integral to modern performance management. Happier, healthier employees typically contribute more effectively to organizational success.
Key Differences Between Performance Management and Performance Appraisal
While the terms performance management and performance appraisal are often used interchangeably, they actually serve different yet complementary roles in an organization’s talent strategy.
Performance management is a dynamic, ongoing process that aligns individual goals with overall business objectives, emphasizing continuous feedback, coaching, and employee development. Performance appraisal, on the other hand, typically involves a formal, periodic evaluation of an employee’s performance, focusing on past achievements and outcomes.
Understanding these distinctions helps organizations create more holistic HR strategies—ones that not only measure success but also foster long-term growth and engagement.
| Aspect | Performance Management | Performance Appraisal |
| Definition | An ongoing, strategic process of aligning individual and organizational goals through continuous feedback, development, and support. | A formal, periodic evaluation of an employee’s performance, typically done annually. |
| Focus | Broader focus on overall employee development, goal alignment, and continuous improvement. | Narrow focus on measuring and documenting performance over a specific period. |
| Frequency | Ongoing and regular (weekly, monthly, or quarterly check-ins and reviews). | Conducted periodically (often annually or biannually). |
| Objective | To foster a culture of continuous feedback, coaching, and skill-building to improve long-term performance. | To assess past achievements, allocate rewards, and identify major performance gaps. |
| Scope | Considers employee strengths, career aspirations, and development opportunities in addition to performance metrics. | Primarily assesses the outcomes and results against predefined targets or criteria. |
| Approach | Collaborative and future-focused, with action plans aimed at growth and ongoing dialogue. | Manager-led and past-focused, evaluating prior achievements and results. |
| Outcome | Enhanced employee engagement, clearer goal alignment, and sustained organizational growth. | Provides official performance ratings, influencing compensation, promotions, and formal records. |
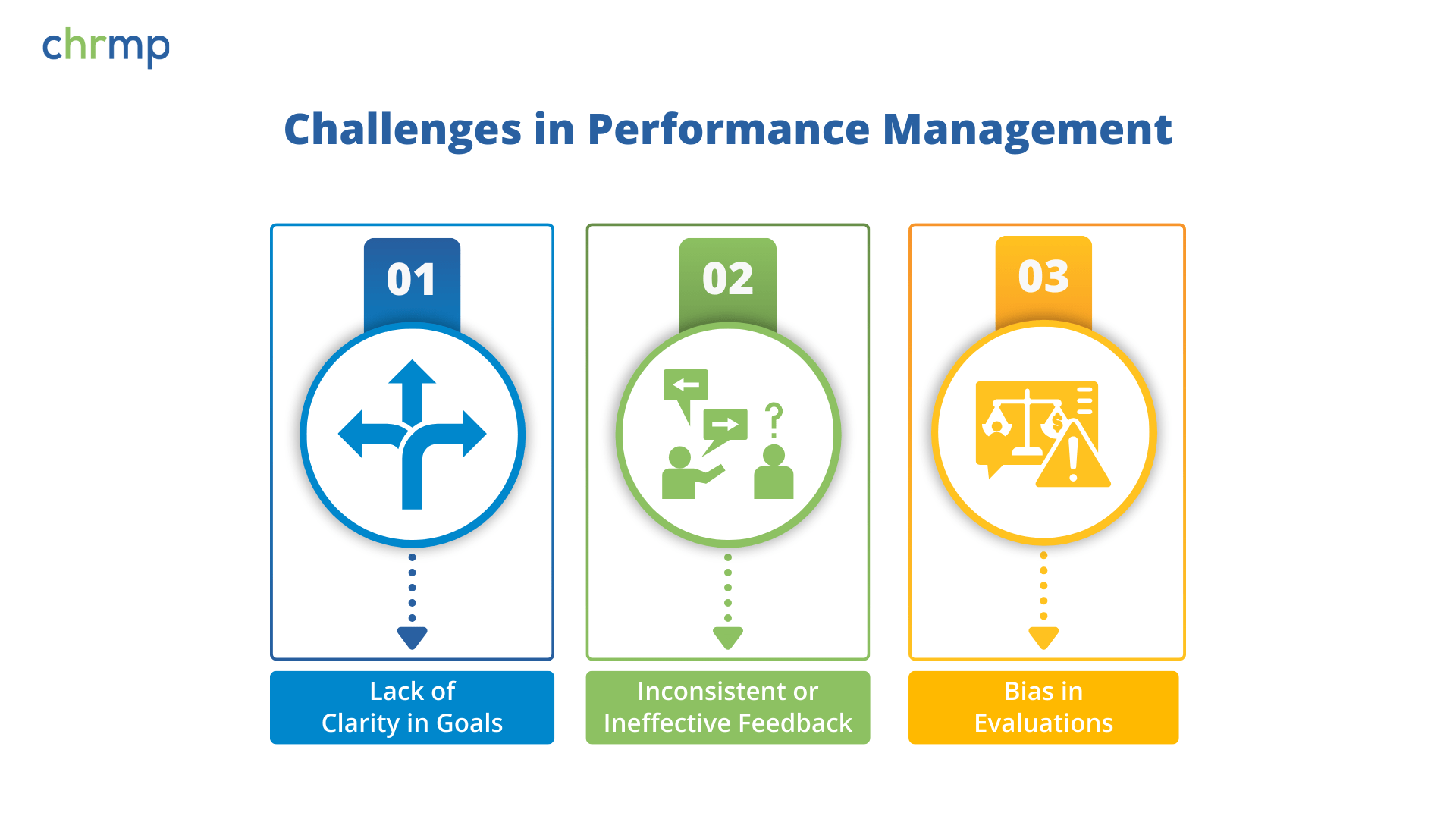
Challenges in Performance Management
Even with the best intentions, performance management can encounter hurdles. Understanding these PM challenges is the first step to overcoming them.
- Lack of Clarity in Goals
Without well-defined objectives, employees may feel uncertain about their priorities, leading to reduced employee engagement. Over time, this can foster a culture where people feel lost and unproductive.
- Inconsistent or Ineffective Feedback
If feedback is sporadic, vague, or overly critical without offering solutions, it can demotivate employees rather than helping them improve. High turnover often stems from a perceived lack of support in the feedback loop.
- Bias in Evaluations
Personal bias—conscious or unconscious—can color a manager’s assessment, making it less objective. Whether it’s the “halo effect” (overemphasizing one positive trait) or the “recency effect” (rating based on recent events), bias in evaluations undermines fairness and trust. This is especially problematic in diverse workplaces, where unchecked bias can derail DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) efforts.
Deloitte famously overhauled its performance management system to address issues of complexity and bias. Instead of lengthy annual reviews, the company implemented short “check-in” conversations focusing on what was done well and what could be improved in real time. This approach not only simplified the process but also increased the accuracy of evaluations. Deloitte reported that managers found more time to coach, resulting in higher levels of satisfaction among teams.
Real-World Success Stories in Performance Management
- Adobe
Adobe replaced its annual performance reviews with “Check-in,” a more flexible system that emphasizes frequent, informal feedback and ongoing performance conversations. This shift helped reduce voluntary turnover by over 30% and boosted productivity by encouraging open communication and accountability among employees.
- Cargill
Cargill introduced “Everyday Performance Management,” which focuses on daily feedback rather than once-a-year reviews. This approach encourages regular interactions between managers and employees, improving relationships and creating a culture of recognition. As a result, 69% of employees reported receiving useful guidance for their career growth, significantly raising morale and efficiency.
- Microsoft
Microsoft moved away from a competitive stack ranking system to a more collaborative approach called “Connects.” Every two months, employees and managers have structured check-ins for timely feedback on goals and skill-building. This change has led to higher engagement and motivation, fostering a more supportive workplace.
- Accenture
Accenture got rid of its annual reviews and stack rankings in 2015, turning its attention to continuous performance development. Employees now receive prompt, work-based feedback that supports a fairer rewards process. The transformation has been popular, leading to greater job satisfaction and better performance across the organization.
- Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs overhauled its performance management by eliminating traditional rating-based reviews and introducing frequent feedback sessions. A web-based platform for informal performance discussions helps employees and managers communicate more easily, leading to improved engagement and clearer performance expectations.
How CHRMP.com Helps with Performance Management
CHRMP.com stands out as a go-to resource for HR professionals seeking to refine or revamp their performance management systems. Here’s how:
CHRMP Certifications
- Targeted Curriculum: CHRMP certifications ensure that HR professionals gain a deep understanding of both PM basics and advanced methods like real-time performance reviews and performance analytics.
- Industry Recognition: Being certified through CHRMP.com lends credibility, demonstrating that you’re equipped with modern, evidence-based practices.
Performance Management Training
- Workshops and Webinars: CHRMP.com organizes events with industry experts who share proven tactics to tackle PM challenges such as bias in evaluations.
- Customized Learning: From basic concepts like what is performance management to specialized modules on continuous feedback, the training is designed to meet professionals at their current level and help them advance.
Conclusion | What is Performance Management
Performance management has evolved far beyond the once-a-year review session. Nowadays, a robust performance management framework is dynamic, data-driven, and employee-centric. It begins with goal setting and weaves through continuous feedback, culminating in regular performance appraisals and structured development planning. By focusing on modern trends like real-time performance reviews and performance analytics, and addressing PM challenges such as bias in evaluations, organizations can significantly boost employee engagement and strengthen organizational success.
Call to Action
If you’re looking to enhance or reinvent your performance management approach, the time to act is now. CHRMP.com equips you with the CHRMP certifications, performance management training, and HR tools you need to implement a future-ready system. Why let outdated methods hold your organization back when you can create a high-performance culture?
Ready to transform your performance management strategy?
Visit CHRMP.com to explore our resources, enroll in our certifications, and discover the transformative power of effective performance management.
Empower your teams today—and watch your entire organization thrive.
What is Performance Management FAQs
1. What is performance management, and why is it important?
Performance management is a continuous process of aligning individual activities and goals with the broader organizational objectives. It involves goal setting, feedback, and evaluations to enhance employee performance. It’s important because it fosters transparency, drives engagement, and ultimately propels organizational success by ensuring everyone is working toward the same mission.
2. What are the key components of an effective performance management system?
An effective system typically includes clear goal setting, regular performance monitoring, open feedback channels, formal performance appraisals, and development planning. Each component supports a culture of constant learning and accountability.
3. How has performance management evolved in recent years?
Today’s trends emphasize continuous feedback and real-time performance reviews rather than annual evaluations. There’s also a growing reliance on performance analytics for data-driven insights into workplace trends and employee engagement levels.
4. What tools can improve performance management processes?
Numerous HR tools and platforms offer features like goal-tracking dashboards, 360-degree feedback mechanisms, and analytics capabilities. By automating repetitive tasks and providing real-time data, these tools help managers make more informed decisions and offer timely support.
5. How can HR professionals implement effective performance management strategies?
Start by defining clear goals aligned with the company mission. Next, ensure managers are trained in delivering constructive, unbiased feedback. Integrate technology for real-time insights and automate routine tasks. Finally, encourage professional growth through personalized development plans and performance management training.
6. What challenges are associated with performance management?
Common PM challenges include a lack of clear objectives, inconsistent feedback, and bias in evaluations. Organizations can mitigate these by establishing structured guidelines, promoting transparency, and training managers to recognize and combat various forms of bias.
7. How does CHRMP.com support performance management?
CHRMP.com offers CHRMP certifications, specialized performance management training, and state-of-the-art HR tools. These resources help HR professionals stay updated on best practices, implement modern feedback systems, and address pitfalls like PM challenges effectively.
8. What is the difference between performance management and performance appraisal?
A performance appraisal is typically a formal, periodic evaluation of an individual’s work. Performance management, however, is an ongoing system that includes setting goals, tracking progress, and fostering development. While appraisals are part of performance management, the latter is a more holistic, continuous cycle.