What is Organizational Development?
Organizational Development (OD) is a strategic and systematic approach aimed at improving an organization’s effectiveness, adaptability, and overall health. It focuses on enhancing business processes, employee engagement, and workplace culture to drive sustainable organizational growth.
At its core, OD is a continuous, data-driven effort that aligns an organization’s goals with workforce capabilities. It goes beyond traditional HR practices by incorporating behavioral science, change management, and leadership development to create high-performing teams and agile structures.
Objectives of Organizational Development
- Enhancing Employee Potential – A key focus of OD is to implement HR development strategies that nurture talent, upskill employees, and create a thriving work environment.
- Driving Business Growth – By refining structures, workflows, and leadership approaches, OD ensures long-term organizational growth that keeps businesses competitive.
- Strengthening Organizational Culture – A well-executed OD strategy fosters a culture of trust, innovation, and collaboration, making the organization resilient to change.
- Improving Change Management – Organizations that embrace OD can adapt more effectively to industry disruptions, technological advancements, and market shifts.
How OD Aligns Organizational Goals with Workforce Capabilities
For an organization to succeed, its strategic objectives must align seamlessly with the skills, mindset, and capabilities of its workforce. Organizational Development (OD) serves as the bridge between business goals and employee potential, ensuring that both move forward in tandem. This alignment is achieved through a combination of structured interventions, leadership development, and continuous learning.
1. Identifying Organizational Goals and Workforce Needs
Before alignment can take place, organizations must assess their current and future objectives alongside their workforce’s existing skill sets. This involves:
- Conducting workforce capability assessments to evaluate employees’ strengths and gaps.
- Analyzing market trends to understand the skills required for future growth.
- Setting clear performance expectations that reflect the company’s mission and long-term vision.
For example, if an organization is expanding its digital operations, OD strategies may focus on reskilling employees in data analytics, artificial intelligence, or digital marketing to ensure they can support the company’s growth trajectory.
2. Implementing HR Development Strategies for Skill Enhancement
Once gaps are identified, Organizational Development leverages HR development strategies to equip employees with the necessary competencies. These may include:
- Training & Development Programs – Continuous learning ensures employees stay updated with industry best practices and emerging technologies.
- Leadership & Succession Planning – Identifying and nurturing future leaders strengthens organizational stability and ensures smooth transitions.
- Competency-Based Hiring & Internal Mobility – Recruiting based on skills required for future business objectives, while also creating opportunities for internal career growth.
By proactively developing talent, organizations future-proof their workforce and create a more agile and adaptive business environment.
3. Strengthening Employee Engagement & Organizational Culture
A key aspect of OD is ensuring that employees feel connected to the organization’s mission and values. This is done through:
- Clear Communication of Organizational Goals – Employees perform better when they understand how their contributions impact overall business success.
- Employee Involvement in Decision-Making – Encouraging feedback, innovation, and collaboration fosters a sense of ownership.
- Workplace Culture Transformation – OD interventions, such as diversity and inclusion programs, leadership coaching, and team-building initiatives, create a work environment that drives motivation and high performance.
When employees feel valued and empowered, they naturally become more committed to achieving organizational objectives.
4. Aligning Performance Management with Business Objectives
Traditional performance reviews are evolving into continuous feedback mechanisms that align individual performance with company goals. OD enhances this process by:
- Implementing goal-setting frameworks like OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) or SMART goals.
- Establishing real-time feedback and coaching to keep employees aligned with evolving business needs.
- Recognizing and rewarding employees who contribute significantly to the organization’s success.
When employees see a direct link between their efforts and company growth, productivity, engagement, and retention increase significantly.
5. Enhancing Change Management & Agility
In today’s dynamic business landscape, organizations must be agile to remain competitive. OD facilitates this by:
- Creating a culture of adaptability, where employees embrace rather than resist change.
- Providing change management training to help leaders and employees navigate transitions smoothly.
- Encouraging a mindset of continuous improvement and innovation.
For instance, when a company undergoes a digital transformation, OD ensures that employees receive proper training, support, and motivation to adopt new technologies without resistance.
The Importance of Organizational Development
An organization’s success is not solely determined by its vision or strategy—it depends on how effectively its workforce capabilities align with business objectives. This is where Organizational Development (OD) becomes essential. When OD is embedded in a company’s culture, it ensures that employees are skilled, engaged, and empowered, driving both individual and organizational success.
OD is not just about improving processes; it is a transformational force that enhances competitiveness, efficiency, and innovation. Companies that prioritize OD are better equipped to navigate change, sustain growth, and create a workplace where employees thrive.
Why Organizational Development is Essential for Sustaining Competitive Advantage
In an era of rapid technological advancements and market disruptions, organizations must continuously evolve to stay ahead. OD plays a critical role in ensuring companies do not just react to change but proactively drive it. Here’s how:
- Facilitating Organizational Transformation
- OD helps companies adapt to change seamlessly, whether it’s digital transformation, business expansion, or restructuring.
- By equipping employees with the right skills and mindset, organizations can implement change with minimal resistance, ensuring smooth transitions.
- Enhancing Workforce Development for Future Readiness
- A future-ready workforce is an organization’s biggest asset. OD ensures employees continuously develop new skills that align with evolving business needs.
- Training programs, leadership development, and reskilling initiatives are integral to keeping employees relevant and competitive.
- Driving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
- Process optimization and data-driven decision-making are core elements of OD that eliminate inefficiencies.
- When OD interventions refine workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and improve collaboration, employees can focus on high-impact work, increasing overall productivity.
- Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Organizations that embrace OD foster an environment where innovation is encouraged, and improvement is ongoing.
- Employees feel empowered to experiment, contribute ideas, and take ownership of their roles, leading to breakthrough solutions and sustained business growth.
How OD Enhances Employee Engagement, Efficiency, and Innovation
Employees perform at their best when they feel valued, supported, and aligned with their company’s mission. OD ensures that workforce development is not just a one-time initiative but an ongoing process that fuels engagement, efficiency, and innovation.
- Boosting Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
- Engaged employees drive better business outcomes. OD helps organizations build inclusive, high-trust work environments where employees are motivated, recognized, and invested in their roles.
- Employee-centric initiatives such as mentorship programs, flexible work policies, and career progression frameworks significantly enhance job satisfaction and retention.
- Improving Efficiency Through Strategic Workforce Development
- OD strategies align employee skill sets with organizational needs, ensuring teams are equipped to perform at their highest potential.
- Performance management systems that provide real-time feedback and development opportunities help employees stay focused, agile, and productive.
- Encouraging Innovation as a Business Imperative
- OD fosters a mindset where employees are not just task executors but problem solvers and innovators.
- Through collaborative learning, cross-functional projects, and leadership development, OD enables organizations to harness creativity and drive continuous growth.
Core Principles of Organizational Development
For Organizational Development (OD) to be truly effective, it must be guided by key principles that drive long-term success, adaptability, and employee engagement. These principles serve as the foundation for business growth strategies, ensuring that organizations evolve in a structured and sustainable manner.
Having explored how OD aligns workforce capabilities with organizational goals and its significance in maintaining a competitive edge, it is crucial to now understand the core principles that make OD successful. These principles ensure that organizations not only implement change but sustain it, fostering continuous organizational improvement.
Focus on Continuous Improvement
What It Is
Continuous improvement is at the heart of OD, emphasizing ongoing refinement of processes, systems, and employee performance. Organizations that adopt this principle recognize that success is not a one-time achievement but a continuous journey.
How It Aligns with OD
OD is fundamentally about evolution and growth, and continuous improvement ensures that organizations do not stagnate. This principle encourages businesses to regularly:
- Assess current processes for efficiency and effectiveness.
- Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Implement incremental changes that lead to sustained business growth.
What It Involves
- Implementing methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to streamline operations.
- Encouraging employee-driven innovation to improve workflows.
- Creating feedback loops to assess and refine OD interventions continuously.
By focusing on continuous improvement, organizations remain resilient, agile, and ready to adapt to market demands.
Employee Involvement in Change Processes
What It Is
OD is not just about top-down decision-making—it thrives on employee participation. This principle ensures that employees are not just recipients of change but active contributors to the transformation process.
How It Aligns with OD
Organizational change often faces resistance, but when employees are involved in the process, they:
- Feel a greater sense of ownership and accountability.
- Develop a deeper understanding of why change is necessary.
- Contribute valuable insights that may enhance the effectiveness of OD initiatives.
What It Involves
- Encouraging open communication and transparency during change implementation.
- Providing platforms for employees to share their ideas and concerns.
- Using collaborative problem-solving approaches to drive innovation and improvement.
By ensuring that employees play a role in OD, organizations create a culture of engagement, trust, and proactive change adoption.
Data-Driven Decision-Making in OD
What It Is
In modern OD, decisions must be based on quantifiable insights rather than intuition. Data-driven OD ensures that every intervention is backed by measurable outcomes, analytics, and trends.
How It Aligns with OD
Effective OD strategies rely on:
- Workforce analytics to track employee performance, productivity, and satisfaction.
- Business intelligence tools to evaluate operational efficiency.
- Change impact assessments to measure the effectiveness of OD initiatives.
What It Involves
- Utilizing HR metrics such as employee engagement scores, turnover rates, and skill gaps.
- Implementing AI and predictive analytics to foresee workforce and industry trends.
- Using performance dashboards to track OD intervention success.
With data-driven decision-making, OD strategies become more targeted, efficient, and results-oriented, ensuring businesses make informed choices that support sustainable growth.
Emphasis on Leadership Development
What It Is
Leadership is the driving force behind organizational transformation. OD prioritizes the development of strong, adaptable, and visionary leaders who can guide teams through change, foster innovation, and drive business success.
How It Aligns with OD
Effective leadership ensures that OD principles are:
- Embedded in the company culture.
- Translated into actionable strategies.
- Sustained over time through mentorship and succession planning.
What It Involves
- Leadership training programs to develop essential skills like emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and change management.
- Coaching and mentoring initiatives to nurture future leaders.
- Succession planning to ensure leadership continuity and prevent disruptions in business operations.
A strong leadership pipeline is crucial for ensuring OD efforts do not lose momentum, making this principle a cornerstone of long-term organizational success.
Building a Culture of Adaptability
What It Is
The business world is in constant flux, and organizations must be flexible enough to evolve. A culture of adaptability ensures that employees and leadership can embrace change rather than resist it.
How It Aligns with OD
Adaptability is a fundamental organizational improvement strategy that:
- Helps businesses stay competitive in dynamic industries.
- Encourages creative problem-solving and experimentation.
- Reduces employee resistance to new initiatives.
What It Involves
- Encouraging growth mindsets where employees see change as an opportunity rather than a threat.
- Implementing agile methodologies in business processes to enable quick pivots.
- Providing reskilling and upskilling programs to keep the workforce future-ready.
By embedding adaptability into company culture, OD ensures that businesses remain resilient and forward-thinking.
Strengthening Organizational Communication
What It Is
Effective communication is a pillar of OD. Without it, even the best strategies fail due to misunderstandings, lack of clarity, and disengagement.
How It Aligns with OD
Transparent communication fosters:
- Stronger collaboration across departments.
- Higher employee trust and morale.
- Smoother implementation of OD initiatives.
What It Involves
- Creating open channels for feedback and dialogue at all organizational levels.
- Using technology (e.g., intranet platforms, digital collaboration tools) to enhance knowledge sharing.
- Training leaders to effectively communicate vision, expectations, and changes.
A well-communicated OD strategy ensures that everyone is aligned and moving towards the same goals.
Promoting Employee Well-Being and Inclusion
What It Is
A successful OD strategy does not only focus on business outcomes—it also prioritizes employee well-being, mental health, and workplace inclusivity.
How It Aligns with OD
A well-supported workforce is a productive, engaged, and innovative workforce. OD interventions that emphasize well-being lead to:
- Higher job satisfaction and retention.
- Lower burnout and absenteeism.
- A more inclusive, diverse, and collaborative work environment.
What It Involves
- Work-life balance initiatives such as flexible work schedules and mental health programs.
- Diversity and inclusion efforts to create equitable opportunities for all employees.
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs) that provide support for personal and professional challenges.
By integrating well-being into OD, organizations create an empowered workforce that is motivated to contribute to business success.
The Organizational Development Process
After understanding the core principles of Organizational Development (OD), the next logical step is to explore how OD is practically implemented within an organization. OD is not a one-time initiative but a structured, step-by-step process designed to drive long-term success, ensure smooth change implementation, and promote organizational growth.
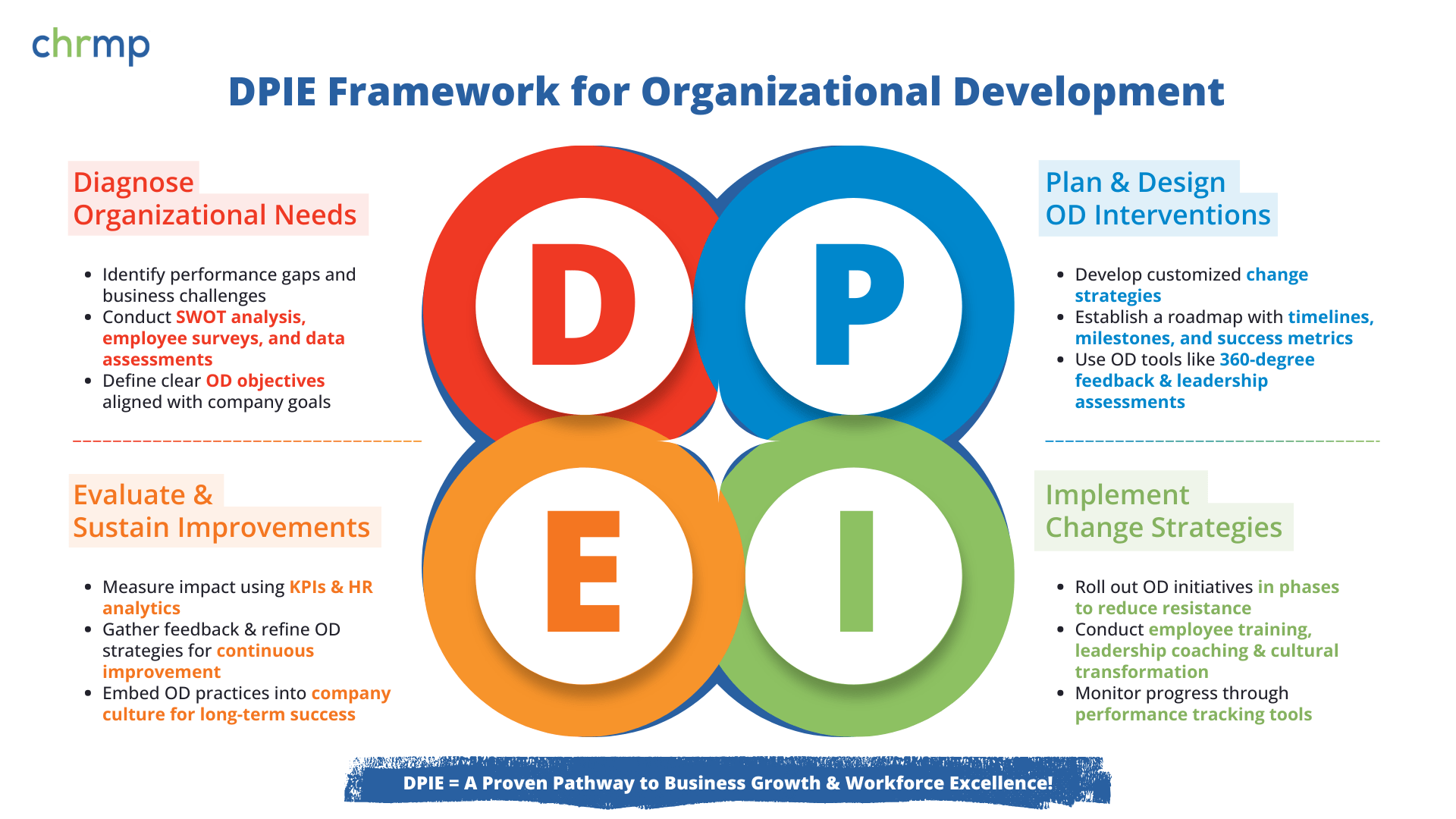
To simplify the OD process, we use the acronym D-P-I-E, which stands for:
- D – Diagnosing Organizational Needs
- P – Planning and Designing OD Interventions
- I – Implementing Change Strategies
- E – Evaluating Outcomes and Sustaining Improvements
Each stage of the DPIE framework plays a vital role in transforming an organization, ensuring that OD interventions are data-driven, effective, and sustainable.
1. Diagnosing Organizational Needs
What It Is
The first step in the OD process is identifying areas that require improvement. This involves understanding the current state of the organization, recognizing performance gaps, and determining the root causes of challenges.
3 Key Sub-Steps
A. Conducting Organizational Assessments
- Utilize employee surveys, focus groups, and feedback mechanisms to gauge workplace morale, engagement, and productivity.
- Assess company culture, leadership effectiveness, and operational efficiency to identify weaknesses.
- Analyze business performance metrics such as revenue trends, turnover rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
B. Identifying Performance Gaps and Challenges
- Compare desired organizational outcomes with current performance levels.
- Determine whether issues stem from structural inefficiencies, leadership gaps, cultural barriers, or employee skill deficits.
C. Defining OD Objectives
- Set clear, measurable goals that address identified problems.
- Align OD objectives with business growth strategies to ensure sustainable improvements.
A thorough diagnosis ensures that OD efforts target the right areas, increasing the likelihood of successful change implementation.
2. P – Planning and Designing OD Interventions
What It Is
Once the problem areas are diagnosed, the next step is to create a customized OD plan that outlines strategies, timelines, and success metrics.
Key Sub-Steps
A. Developing OD Strategies Based on Diagnosis
- Determine whether interventions should focus on leadership development, process improvement, culture change, or workforce training.
- Involve key stakeholders (leaders, managers, employees) in the planning process to ensure alignment and buy-in.
B. Creating a Roadmap for Change Implementation
- Establish short-term and long-term milestones to track progress.
- Assign clear roles and responsibilities for execution.
- Develop communication plans to ensure transparency throughout the process.
C. Selecting the Right OD Tools and Techniques
- Use frameworks such as Lean Six Sigma, Change Management Models (e.g., Kotter’s 8-Step Process), and Employee Engagement Programs.
- Implement digital tools such as HR analytics, leadership assessment software, and performance tracking systems.
Proper planning ensures that OD interventions are well-structured, goal-oriented, and scalable.
3. I – Implementing Change Strategies
What It Is
This is where actual change implementation begins. Effective execution requires strong leadership, clear communication, and ongoing employee engagement.
Key Sub-Steps
A. Rolling Out OD Interventions in Phases
- Pilot testing initiatives on a small scale before full implementation.
- Launching interventions in stages to manage risks and improve adaptability.
B. Managing Resistance to Change
- Addressing concerns by educating employees on the benefits of OD initiatives.
- Encouraging employee involvement in decision-making to foster ownership.
- Using change champions (key influencers within the organization) to drive adoption.
C. Training and Development Programs
- Conducting workshops, coaching sessions, and mentorship programs to equip employees with the necessary skills.
- Implementing cross-functional collaboration to improve teamwork and innovation.
A well-executed implementation phase transforms strategic plans into actionable results, ensuring that change is effective and embraced.
4. E – Evaluating Outcomes and Sustaining Improvements
What It Is
Sustained OD success depends on measuring the impact of interventions and continuously refining strategies for long-term growth.
Key Sub-Steps
A. Measuring Organizational Development Effectiveness
- Use key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Employee engagement scores
- Productivity and efficiency metrics
- Revenue growth and cost reduction
- Leadership effectiveness ratings
- Gather employee and stakeholder feedback to assess satisfaction levels.
B. Making Data-Driven Adjustments
- Identify what worked, what didn’t, and why.
- Refine OD interventions based on real-time insights and performance analytics.
- Implement continuous feedback loops for ongoing improvements.
C. Embedding OD into Organizational Culture
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptability.
- Regularly review and revise OD strategies to align with market trends and business goals.
- Encourage ongoing leadership development and workforce training to maintain momentum.
By evaluating results and making necessary adjustments, organizations ensure that OD initiatives lead to lasting, meaningful transformation.
Tools and Techniques in Organizational Development
A well-structured Organizational Development (OD) process requires the right tools and frameworks to ensure effectiveness, precision, and sustainability. Having established the step-by-step OD process, it is crucial to explore the practical methodologies that enable organizations to diagnose issues, implement change, and drive continuous improvement.
This section will cover key OD tools used for assessment and analysis, as well as change management models that guide successful organizational transformation.
Essential Organizational Development Tools for Organizational Assessment and Development
OD tools help organizations identify challenges, assess employee feedback, and measure progress. Below are some widely used OD tools that aid in decision-making and strategic planning:
1.1 SWOT Analysis
What It Is:
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate an organization’s internal and external environment.
How It Helps in OD:
- Strengths – Identifies core competencies and areas where the organization excels.
- Weaknesses – Highlights internal inefficiencies and gaps that need improvement.
- Opportunities – Recognizes external factors that can be leveraged for growth.
- Threats – Identifies external risks such as market competition or regulatory changes.
Implementation:
- Conducted during the diagnosis phase of the OD process to understand the organization’s position.
- Used in leadership strategy sessions and workforce development planning.
1.2 360-Degree Feedback
What It Is:
360-degree feedback is an employee assessment tool that gathers feedback from multiple sources, including peers, subordinates, managers, and self-evaluations.
How It Helps in OD:
- Provides a holistic view of an employee’s strengths and improvement areas.
- Identifies leadership gaps and training needs.
- Improves employee self-awareness and encourages personal development.
Implementation:
- Used in performance management and leadership development programs.
- Helps in designing customized training and coaching interventions.
1.3 Employee Engagement and Satisfaction Surveys
What It Is:
Surveys are used to gather insights on employee morale, job satisfaction, and workplace culture.
How It Helps in OD:
- Identifies pain points affecting employee engagement.
- Provides data for culture improvement initiatives.
- Helps measure the impact of OD interventions over time.
Implementation:
- Conducted annually or quarterly as part of continuous OD efforts.
- Used to guide HR policies and employee well-being programs.
1.4 Organizational Network Analysis (ONA)
What It Is:
ONA is an advanced OD tool that maps interactions and relationships within an organization to identify key influencers, collaboration patterns, and communication bottlenecks.
How It Helps in OD:
- Enhances cross-functional collaboration by identifying communication gaps.
- Aids in leadership succession planning by pinpointing key informal leaders.
- Improves knowledge sharing across departments.
Implementation:
- Used in change management and restructuring initiatives.
- Applied to optimize team dynamics and improve decision-making structures.
2. Change Management Models in Organizational Development
While OD tools help in assessment and planning, change management models provide structured approaches for implementing transformation successfully.
2.1 Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
What It Is:
Developed by John Kotter, this model provides an eight-step framework for managing organizational change effectively.
How It Helps in OD:
Kotter’s model ensures that change is gradual, structured, and employee-driven, preventing resistance and ensuring long-term success.
The 8 Steps:
- Create a Sense of Urgency – Communicate why change is necessary.
- Build a Guiding Coalition – Form a team of influential leaders to drive change.
- Develop a Vision and Strategy – Define a clear roadmap for change.
- Communicate the Change Vision – Ensure transparency and clarity across all levels.
- Empower Employees for Action – Remove obstacles and provide necessary resources.
- Generate Short-Term Wins – Celebrate early successes to build momentum.
- Consolidate Gains and Drive More Change – Embed change deeper into processes.
- Anchor Change in Corporate Culture – Make change a permanent part of the organization.
Implementation:
- Best suited for large-scale organizational transformations.
- Applied in culture change initiatives, restructuring efforts, and mergers/acquisitions.
2.2 Lewin’s Change Management Model
What It Is:
Developed by Kurt Lewin, this model describes organizational change in three simple phases: Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze.
How It Helps in OD:
Lewin’s model emphasizes behavioral change and ensuring that transitions are well-accepted and sustained.
The 3 Phases:
- Unfreeze – Prepare employees for change by addressing fears and breaking old habits.
- Change – Implement new processes, behaviors, or structures with support and guidance.
- Refreeze – Reinforce the change by embedding it in company culture.
Implementation:
- Suitable for process improvement, technology adoption, and leadership transitions.
- Helps in overcoming employee resistance to change.
2.3 ADKAR Model for Individual Change Management
What It Is:
The ADKAR model, developed by Prosci, focuses on individual change as a foundation for organizational success.
How It Helps in OD:
The model ensures that employees move through five key stages before fully adopting change:
- Awareness – Understand why change is necessary.
- Desire – Develop willingness to support and participate in the change.
- Knowledge – Gain the skills and training needed for the change.
- Ability – Apply the change in daily work.
- Reinforcement – Sustain the change through continued support.
Implementation:
- Ideal for HR-driven change initiatives such as employee training, policy changes, and leadership development programs.
- Helps in ensuring high employee adoption rates.
3. Additional Techniques for Organizational Development
3.1 Appreciative Inquiry (AI)
A strengths-based OD approach that focuses on what works well rather than problems. Used to build positive workplace cultures.
3.2 Six Sigma and Lean Methodologies
Process improvement techniques that focus on eliminating inefficiencies and optimizing productivity.
3.3 Emotional Intelligence (EQ) Assessments
Used to measure and improve leadership effectiveness, teamwork, and workplace relationships.
Challenges in Organizational Development
While Organizational Development (OD) is a powerful driver of business growth, it is not without its challenges. Implementing organizational change often disrupts established workflows, requires leadership commitment, and demands cultural shifts—factors that can lead to resistance and setbacks.
To ensure successful OD initiatives, organizations must identify potential hurdles early and adopt strategies to overcome them. This section explores the most common OD challenges and provides practical solutions to address them effectively.
1. Resistance to Change
The Challenge
One of the biggest hurdles in OD is employee resistance to change. Employees often feel uncomfortable with change due to:
- Fear of job loss (automation, restructuring).
- Uncertainty about new roles and responsibilities.
- Lack of trust in leadership decisions.
- Comfort with existing processes and reluctance to step out of their comfort zones.
How to Overcome It
✅ Create a Clear Change Vision: Explain why change is necessary, how it benefits employees, and what the end goal looks like.
✅ Engage Employees Early: Involve employees in decision-making and feedback loops to give them a sense of ownership.
✅ Provide Training & Support: Offer skill-building programs to prepare employees for transitions.
✅ Use Change Agents: Identify key influencers within teams who can advocate for the change.
2. Misaligned Leadership and Lack of Executive Buy-In
The Challenge
Leadership plays a crucial role in OD, but challenges arise when:
- Executives and managers are not aligned on OD goals.
- Leaders fail to communicate change effectively to employees.
- Middle management does not fully support OD interventions, leading to inconsistent implementation.
How to Overcome It
✅ Ensure Leadership Alignment: Conduct leadership strategy sessions to align OD goals with business objectives.
✅ Train Leaders on Change Management: Provide coaching programs for managers on how to lead through change.
✅ Demonstrate Business Impact: Use data-driven insights to show how OD enhances business performance.
✅ Encourage Two-Way Communication: Leaders must actively listen to employee concerns and adjust strategies accordingly.
3. Cultural Resistance and Ingrained Organizational Norms
The Challenge
Organizational culture is deeply rooted, and shifting long-standing traditions, mindsets, and work ethics can be difficult. Employees may perceive OD as a threat to their workplace identity rather than an opportunity for growth.
How to Overcome It
✅ Assess and Understand the Existing Culture: Use employee surveys and focus groups to identify cultural barriers.
✅ Redefine Core Values Gradually: Introduce incremental cultural shifts rather than abrupt changes.
✅ Lead by Example: Senior leaders must demonstrate new cultural behaviors before expecting employees to adopt them.
✅ Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize and reward teams that embrace cultural transformation to reinforce positive behavior.
4. Lack of Resources and Budget Constraints
The Challenge
OD initiatives require financial investment, time, and dedicated personnel, which some organizations may lack. Limited budgets often lead to:
- Incomplete implementation due to insufficient funding.
- Minimal employee training, leading to ineffective OD execution.
- Lack of OD expertise, as organizations struggle to hire skilled professionals.
How to Overcome It
✅ Prioritize OD Initiatives Strategically: Focus on high-impact interventions with measurable ROI.
✅ Leverage Technology for Cost-Effective Solutions: Use digital learning platforms, virtual workshops, and AI-driven analytics.
✅ Secure Executive Sponsorship: Show data-backed evidence of OD benefits to secure funding.
✅ Utilize Internal Talent: Develop internal OD champions rather than relying solely on external consultants.
5. Poor Communication and Lack of Transparency
The Challenge
Without clear, transparent communication, employees may feel left in the dark, leading to misunderstandings, rumors, and disengagement. Common communication issues include:
- Lack of clarity on OD objectives and expected outcomes.
- One-way communication where leadership dictates changes without gathering feedback.
- Delayed or inconsistent messaging about OD progress.
How to Overcome It
✅ Develop a Comprehensive Communication Plan: Use town halls, newsletters, and intranet updates to keep employees informed.
✅ Encourage Open Dialogue: Create safe spaces for employees to ask questions and voice concerns.
✅ Use Multiple Communication Channels: Leverage email updates, video messages, and internal social platforms to reach diverse teams.
✅ Assign OD Ambassadors: Designate team members to relay information and gather feedback from their peers.
6. Measuring Organizational Development Success and Sustaining Change
The Challenge
Even when OD initiatives are implemented, organizations often struggle with:
- Tracking progress effectively and proving ROI.
- Sustaining changes over time rather than reverting to old habits.
- Ensuring continuous improvement rather than treating OD as a one-time project.
How to Overcome It
✅ Set Clear KPIs and Success Metrics: Define measurable indicators such as employee engagement scores, productivity improvements, and retention rates.
✅ Use Data-Driven Insights: Leverage HR analytics and performance dashboards to monitor OD impact.
✅ Reinforce Change Through Training and Development: Conduct regular refresher sessions to ensure OD principles remain active.
✅ Build OD into Organizational Culture: Encourage leaders to embed OD practices into daily operations rather than viewing them as temporary initiatives.
The Role of HR in Organizational Development
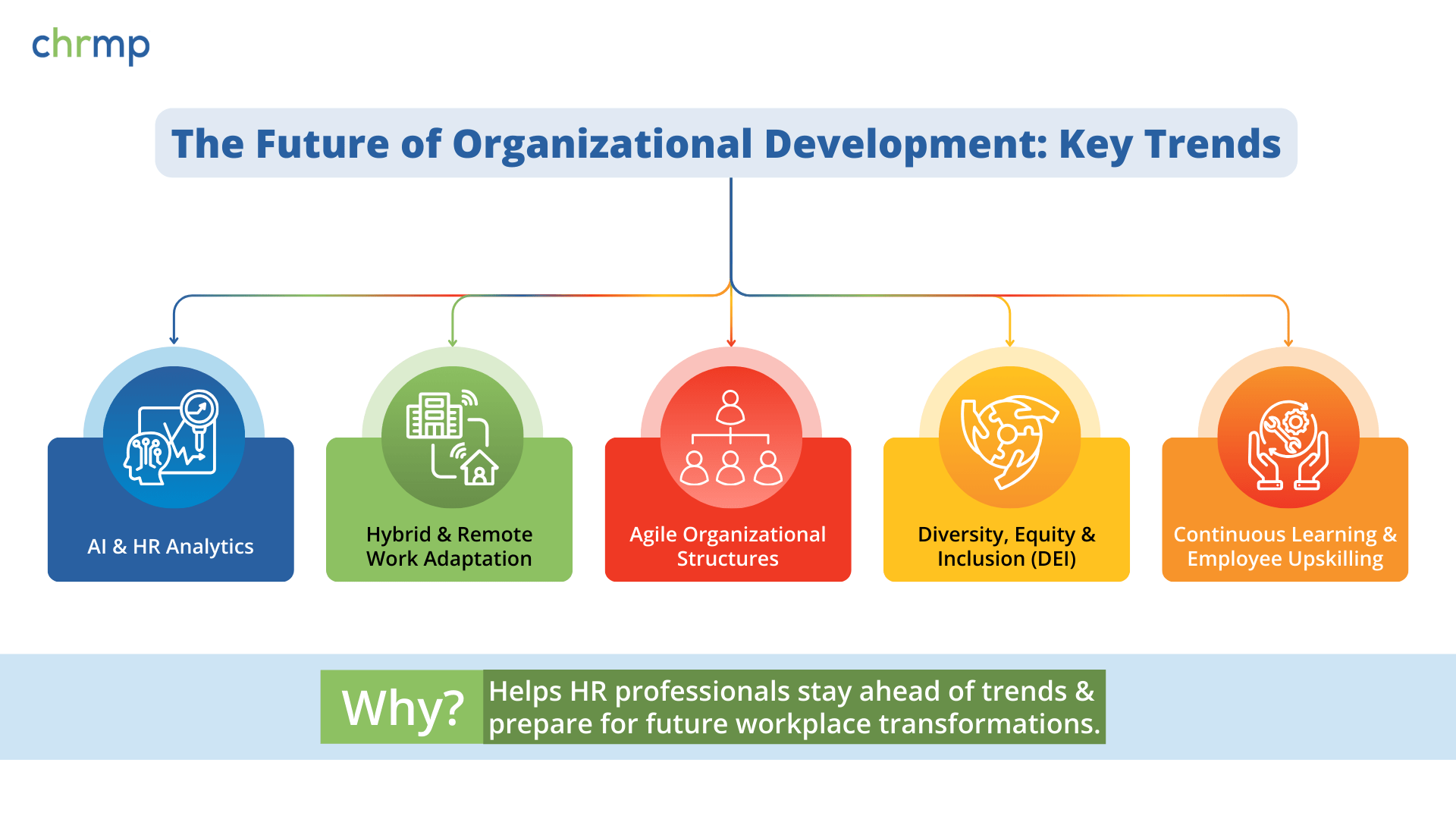
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizational development (OD) is no longer limited to traditional change management and talent interventions. The future of OD focuses on workplace innovation—encompassing data-driven decision-making, flexible structures, inclusive cultures, and continuous learning. Below are some key trends shaping the OD landscape:
1. AI & HR Analytics
The growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics in HR is a major force reshaping OD. From predictive modeling for employee retention to sentiment analysis of workforce culture, organizations are leveraging data to gain real-time insights and make strategic decisions.
- Data-Driven Decisions: HR analytics platforms help leaders identify competency gaps, forecast future hiring needs, and measure the impact of development programs.
- Automation & Efficiency: Routine tasks—like screening applications or scheduling interviews—can be automated, freeing HR professionals to focus on more strategic OD initiatives such as leadership development and organizational culture.
- Personalization: AI-driven insights allow organizations to personalize learning pathways and career development plans, boosting engagement and job satisfaction.
2. Hybrid & Remote Work Adaptation
As remote and hybrid work models become mainstream, organizations are rethinking their structures, processes, and cultural practices to accommodate flexible work arrangements.
- Digital Transformation: Virtual collaboration tools, cloud-based systems, and asynchronous communication platforms are no longer optional; they’re central to how teams operate and stay productive.
- Inclusive Workplace Culture: A hybrid model demands new norms to ensure all employees—onsite and remote—feel supported, connected, and engaged.
- Policy Redesign: From flexible scheduling to remote onboarding, OD professionals are recalibrating policies to manage performance and maintain team cohesion across geographically dispersed teams.
3. Agile Organizational Structures
Agility is more than a buzzword; it’s a fundamental principle guiding OD in complex and rapidly changing markets.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Breaking down silos allows for faster decision-making, continuous improvement, and better alignment with organizational goals.
- Rapid Iteration & Feedback: Agile organizations embrace pilot programs, quick feedback loops, and iterative changes rather than large-scale transformations that take years to implement.
- Empowered Employees: Flattened hierarchies give teams more autonomy, fostering innovation and a sense of ownership in outcomes.
4. Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI)
A strong DEI focus is crucial for both organizational health and sustainability. In the future of OD, DEI efforts go beyond box-checking initiatives—they become ingrained in everyday practices.
- Talent Attraction & Retention: Diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces attract top talent and reduce turnover by creating supportive environments where all employees can thrive.
- Innovation & Problem-Solving: Teams that reflect diverse perspectives are more creative and better equipped to tackle challenges in a global market.
- Accountability & Transparency: OD professionals are developing clear metrics and accountability measures to track DEI progress and ensure leadership buy-in.
5. Continuous Learning & Employee Upskilling
The rapid pace of technological and social change requires organizations to invest heavily in ongoing employee development.
- Learning Ecosystems: Microlearning, online courses, and peer-to-peer knowledge sharing enable quick and efficient skill-building.
- Career Mobility: Employees are seeking clear pathways for growth—whether through lateral moves, stretch assignments, or leadership tracks.
- Future-Proofing Talent: Upskilling and reskilling initiatives ensure the workforce remains adaptable and ready for emerging roles driven by new tech and shifting market demands.
Why Do These Trends Matter?
These evolving OD trends help HR professionals stay ahead of the curve, adapt to future workplace transformations, and create environments where employees can flourish. By focusing on data and technology, flexible structures, inclusion, and continuous learning, organizations can fuel sustainable growth, retain top talent, and foster a culture of innovation.
Embracing these trends means going beyond the status quo—actively designing an adaptable, people-centric organization that thrives in uncertainty and remains resilient in the face of ongoing disruption. This is the future of organizational development—a future that calls on leaders, teams, and HR professionals to be agile, inclusive, and forward-thinking.
As organizations strive for growth, transformation, and sustainability, HR plays a pivotal role in driving Organizational Development (OD). HR professionals are not just administrative support—they act as strategic partners, change enablers, and workforce developers who ensure that OD initiatives align with business objectives and employee needs.
A successful OD strategy requires strong leadership, cultural transformation, and continuous workforce development—all of which fall under HR’s domain. This section explores how HR functions as a catalyst for OD and contributes to leadership development, culture building, and employee training.
1. HR as a Catalyst for Organizational Transformation
HR professionals are at the forefront of organizational change, ensuring that business transformation efforts are smooth, effective, and people-centric. Their role in OD includes:
A. Driving Change Management Initiatives
- HR ensures that change is introduced gradually and strategically, reducing employee resistance.
- Implements structured change management frameworks (e.g., Kotter’s Change Model, ADKAR) to guide transitions.
- Supports leadership in communicating change effectively to employees.
B. Aligning Business Goals with Workforce Development
- HR ensures that OD strategies are people-focused and align with business objectives.
- Conducts workforce planning to prepare employees for future business needs.
- Uses HR analytics and data to track OD effectiveness and suggest improvements.
C. Acting as Employee Advocates During Organizational Development Transitions
- HR listens to employee concerns and addresses issues that arise during organizational change.
- Creates feedback loops through engagement surveys and town halls.
- Ensures that OD initiatives are fair, inclusive, and support employee well-being.
Through these efforts, HR professionals minimize disruption, improve employee buy-in, and ensure OD initiatives lead to lasting transformation.
2. HR’s Contribution to Leadership Development
OD success depends on strong leadership, and HR plays a crucial role in identifying, developing, and nurturing leaders within the organization.
A. Leadership Training and Development Programs
- HR designs and implements leadership training workshops to develop essential skills.
- Introduces mentorship and coaching programs to groom emerging leaders.
- Uses 360-degree feedback to assess leadership effectiveness and provide improvement plans.
B. Succession Planning for Long-Term Growth
- HR ensures that businesses have a pipeline of future leaders ready to step into key roles.
- Identifies high-potential employees and creates tailored development plans for them.
- Prevents leadership gaps that could disrupt Organizational Development efforts and organizational continuity.
C. Building Leadership Accountability in Organizational Development
- HR holds leaders accountable for supporting OD initiatives and driving cultural change.
- Provides ongoing leadership assessments to measure their impact on OD strategies.
- Encourages leaders to model desired behaviors that reflect OD goals.
By ensuring effective leadership development, HR strengthens the foundation for long-term organizational success and agility.
3. HR’s Role in Culture Building
Culture is the backbone of an organization, and OD efforts often fail if they do not align with cultural values. HR ensures that organizational culture supports OD principles and drives positive change.
A. Defining and Reinforcing Organizational Values
- HR ensures that OD initiatives reflect company values, ethics, and long-term vision.
- Introduces culture-building programs that align employees with OD objectives.
- Reinforces cultural transformation through policies, rewards, and recognition programs.
B. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) in Organizational Development
- Integrates DEI principles into OD strategies to create a more inclusive workforce.
- Promotes a culture of belonging and collaboration that enhances productivity.
- Implements bias training and inclusive leadership development.
C. Encouraging Employee Engagement and Well-Being
- HR fosters a work environment that encourages participation, innovation, and feedback.
- Introduces well-being programs (mental health support, flexible work policies) to ensure employees thrive during OD transitions.
- Creates initiatives that boost morale, motivation, and commitment to OD goals.
A strong, adaptable culture ensures that OD interventions are embraced, sustained, and deeply embedded in daily operations.
4. HR’s Role in Employee Training and Development
One of the most critical aspects of OD is ensuring that employees have the right skills, knowledge, and tools to adapt and succeed. HR is responsible for developing comprehensive workforce training programs that align with Organizational Development objectives.
A. Skill Development and Reskilling Programs
- HR identifies skills gaps and implements targeted learning programs.
- Facilitates reskilling and upskilling initiatives to prepare employees for evolving roles.
- Uses e-learning platforms, workshops, and on-the-job training for continuous development.
B. Performance Management and Continuous Learning
- HR establishes clear performance metrics that align with OD goals.
- Introduces personalized career development plans for employees.
- Ensures that OD efforts are reinforced through coaching, peer learning, and knowledge-sharing programs.
C. Leveraging Technology for Workforce Development
- Uses HR analytics tools to measure the effectiveness of training programs.
- Implements AI-driven learning management systems (LMS) for personalized learning experiences.
- Integrates virtual reality (VR) and gamification techniques to enhance employee engagement in training.
A well-trained workforce is more adaptable, productive, and aligned with organizational transformation goals, making HR a driving force in OD implementation.
Conclusion: Organizational Development
Organizational Development (OD) is not just a corporate initiative—it is a strategic necessity for businesses aiming for long-term success, agility, and growth. Throughout this discussion, we have explored the fundamental principles, processes, challenges, and HR’s crucial role in shaping a thriving organization through OD.
The Power of OD for Long-Term Success
From aligning workforce capabilities with business goals to fostering continuous improvement and innovation, OD ensures that organizations stay competitive in an ever-changing landscape. By adopting structured OD frameworks, leveraging data-driven insights, and developing strong leadership, businesses can drive transformation that is both effective and sustainable.
Key Takeaways from the OD Journey
- OD Principles Drive Sustainable Growth – A culture of continuous improvement, data-driven decision-making, and employee involvement ensures that businesses evolve efficiently.
- The OD Process Provides a Structured Path to Change – The DPIE model (Diagnose, Plan, Implement, Evaluate) serves as a practical approach to executing OD strategies.
- HR is the Driving Force Behind OD – From leadership development to workforce training, HR professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring OD strategies are embraced, executed, and sustained.
- Challenges in OD Can Be Overcome with the Right Approach – Resistance to change, leadership misalignment, and cultural barriers can be mitigated through clear communication, strategic planning, and continuous employee engagement.
- Effective OD Tools and Frameworks Ensure Success – Utilizing SWOT analysis, 360-degree feedback, Kotter’s Change Model, and Lewin’s Change Management Model provides organizations with the structure and clarity needed for transformation.
Call-to-Action:
Discover how CHRMP.com can equip you with the tools and certifications needed to master organizational development and lead impactful change in your organization.
Organizational Development FAQs
1. What is organizational development (OD)?
Organizational Development (OD) is a systematic, strategic process aimed at improving an organization’s efficiency, adaptability, and overall performance. It involves workforce development, leadership enhancement, cultural transformation, and process optimization to drive sustainable business growth.
2. Why is OD important for organizational success?
OD is essential for business agility and long-term success. It helps organizations:
- Adapt to market changes and technological advancements.
- Improve employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction.
- Strengthen leadership and decision-making capabilities.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
3. What are the key steps in the OD process?
The OD process follows the DPIE framework:
- Diagnose – Identify organizational challenges and growth opportunities.
- Plan – Design tailored OD interventions based on findings.
- Implement – Execute change strategies with leadership support.
- Evaluate – Measure success and ensure long-term sustainability.
4. What tools and techniques are commonly used in OD?
Some widely used OD tools include:
- SWOT Analysis – Evaluates an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- 360-Degree Feedback – Collects multi-source feedback for leadership and employee development.
- Employee Engagement Surveys – Measures morale and workplace satisfaction.
- Change Management Models – Frameworks like Kotter’s 8-Step Model and Lewin’s Change Model guide successful transformations.
5. How does HR contribute to organizational development?
HR plays a crucial role in OD by:
- Driving leadership development and succession planning.
- Shaping organizational culture and ensuring employee engagement.
- Facilitating change management and workforce training.
- Aligning talent strategies with business goals.
6. What are common challenges in implementing OD initiatives?
Some key OD challenges include:
- Resistance to change from employees and leaders.
- Misalignment between leadership and workforce expectations.
- Cultural barriers that slow down transformation efforts.
- Lack of resources, time, or expertise to implement OD effectively.
7. How can OD improve workplace culture and employee engagement?
OD enhances workplace culture by:
- Creating a collaborative and inclusive environment.
- Encouraging employee involvement in decision-making.
- Fostering continuous learning and professional growth.
- Implementing recognition and well-being programs that boost morale.
8. What trends are shaping the future of organizational development?
Emerging OD trends include:
- AI and HR analytics for data-driven decision-making.
- Hybrid and remote work models influencing workplace culture.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives gaining prominence.
- Agile and adaptive organizational structures replacing traditional hierarchies.
9. How can CHRMP.com support professionals in mastering organizational development?
CHRMP.com offers specialized OD certifications, expert-led training, and practical resources to help HR professionals:
- Develop strategic OD skills for real-world application.
- Stay updated with the latest OD trends and best practices.
- Gain globally recognized credentials for career advancement.





