Attrition, also known as employee turnover, is a common challenge many organisations face.
On the other hand, retention is a company’s ability to retain its employees over a while.
The two terms have quite different meanings, and in this blog, we will discuss the differences in attrition and retention, how they’re measured, and strategies that organizations can use to improve employee retention.
So whether you are an employer trying to retain your top talent or an employee considering leaving your current organization, this blog will provide valuable insights into the attrition vs retention debate.
Lets jump right in!
What is Employee Attrition?
Attrition refers to existing employees leaving a company over a certain period. Attrition is also referred to as employee turnover.
Attrition can occur voluntarily when an employee chooses to leave the organization or involuntarily when the organization terminates an employee’s employment.
Attrition can significantly impact a company’s productivity, profitability, and overall success. High attrition rates can result in increased recruitment and training costs, decreased morale among remaining employees, along with a loss of institutional knowledge and expertise.
Even though some level of attrition is standard across all companies and is even considered healthy, high rates of attrition can indicate underlying problems in the company’s functioning like poor leadership, toxic work culture, inadequate employee compensation and benefits or reduced employee engagement.
Companies can keep track of attrition rates and measure them to identify areas for improvement and develop suitable strategies to keep attrition in check and retain their top talent.
Why is it Important?
The employee attrition rate is a crucial subject for consideration for companies as it can significantly impact the company’s success.
High attrition rates can cause a significant increment in recruitment and training costs while also causing a dip in overall employee morale among remaining employees.
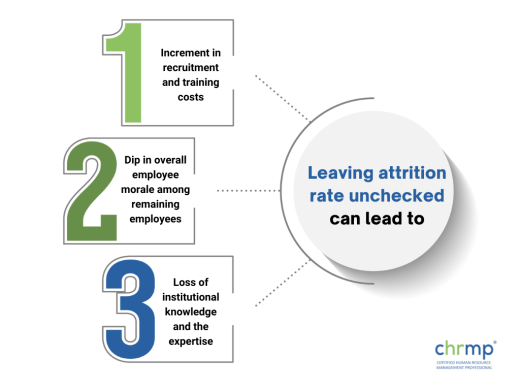
In addition, the loss of institutional knowledge and the expertise brought to the company by these employees can be significant, making it more difficult to maintain business continuity.
Besides, high employee attrition rates usually reflect serious underlying problems, such as poor leadership, inadequate compensation and benefits, or toxic work culture.
Hence it’s crucial for organizations to monitor and keep their attrition rates in check to retain their top talent and sustain business success.
What is Employee Retention?
Employee retention refers to a company’s ability to retain its employees over a while. It entails making efforts to create a positive work environment that promotes employee engagement and increases job satisfaction while fostering loyalty and trust.
Retention strategies usually address the underlying problems that give rise to high attrition rates and aim to maintain a stable workforce.
Effective retention strategies involve providing perks such as career development opportunities to employees, enforcing a fair compensation and benefits plan, ensuring work-life balance, recognition and rewards, and creating a supportive work culture.
These strategies can help create a sense of belonging and ownership among employees, increasing motivation, productivity, and commitment to the organization’s goals.
Employee retention is essential for organizations to maintain a stable workforce and reduce the costs associated with high turnover rates. It also helps maintain institutional knowledge and expertise, increasing efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, a high retention rate can contribute to a positive employer brand, making it easier to attract top talent and improve business success over the long term.
Why is it Important?
Employee retention is essential for organizations because it enables them to maintain a stable workforce and achieve business success.
When an organization invests in retaining its employees, it benefits from increased employee loyalty, commitment, and productivity.
This translates into better business outcomes, such as increased efficiency, better customer service, and improved employee morale.
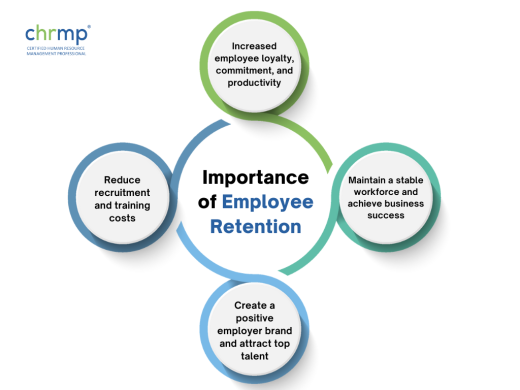
High retention rates can also reduce recruitment and training costs, often significant expenses for organizations. Additionally, employees who feel valued and supported are more likely to become brand ambassadors, contributing to a positive employer brand and attracting top talent to the organization.
Therefore, employee retention is crucial for organizations that want to create a positive work environment, build a solid corporate culture, and sustain business growth over the long term.
Attrition vs Retention: What’s the Difference?
Attrition and retention are two opposite concepts that describe the movement of employees in and out of an organization.
Attrition refers to the number of employees who leave an organization over a specified period, either voluntarily or involuntarily. It is a measure of the turnover or churn rate in an organization. It can be caused by various factors such as low employee morale, poor management, inadequate compensation and benefits, lack of career development opportunities, or toxic work culture.

Retention, on the other hand, refers to an organization’s ability to retain its employees over time. It is the opposite of attrition and describes the percentage of employees who choose to stay with the organization. Retention is influenced by various factors such as a positive work environment, supportive leadership, fair compensation and benefits, work-life balance, and opportunities for career development.
In summary, attrition and retention are two opposite concepts that describe the movement of employees in and out of an organization. Attrition measures the rate employees leave, while retention measures the percentage of employees who stay with the organization over time. Organizations need to monitor and manage both attrition and retention to maintain a stable workforce, reduce costs, and create a positive work environment.
How is Attrition Measured?
Attrition is typically measured as the employee turnover rate in an organization over a specified period, usually a year. The formula for calculating the attrition rate is as follows:
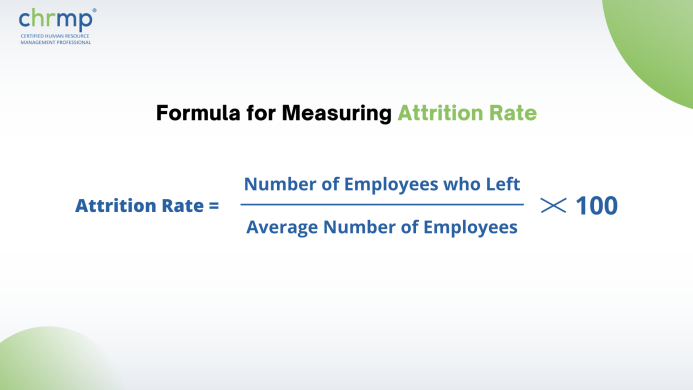
To calculate the average number of employees, you need to add the total number of employees at the beginning and end of the period and divide by two. For example, if an organization had 100 employees at the beginning of the year and 120 employees at the end of the year, the average number of employees would be (100+120)/2 = 110.
To calculate the attrition rate for the year, you need to divide the number of employees who left the organization during the year by the average number of employees and multiply by 100. For example, if 10 employees left the organization during the year, the attrition rate would be (10 ÷ 110) x 100 = 9.09%.
How is Retention Measured?
Retention is typically measured as the percentage of employees who remain with an organization over a specified period, usually a year. The formula for calculating the retention rate is as follows:

To calculate the retention rate for a year, you need to divide the number of employees who stayed with the organization by the total number of employees and multiply by 100. For example, if an organization had 100 employees at the beginning of the year and 120 employees at the end of the year, and ten employees left the organization during the year, the retention rate would be ((120-10) ÷ 120) x 100 = 91.67%.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What is the difference between attrition and retention?
Attrition and retention are two opposite concepts that describe the movement of employees in and out of an organization. Attrition refers to the number of employees who leave an organization over a specified period, either voluntarily or involuntarily. Retention, on the other hand, refers to an organization’s ability to retain its employees over time.
2. Why is it important to measure attrition and retention?
Measuring attrition and retention is important for organizations to monitor their ability to maintain a stable workforce and achieve business success. High attrition rates can be costly for organizations, leading to increased recruitment and training costs, reduced productivity, and a negative impact on employee morale. On the other hand, high retention rates can lead to better business outcomes, such as increased efficiency, better customer service, and improved employee morale.
3.What factors contribute to high attrition rates?
There are various factors that can contribute to high attrition rates, such as low employee morale, poor management, inadequate compensation and benefits, lack of career development opportunities, or toxic work culture. Employees are more likely to leave an organization when they feel undervalued, unsupported, and disengaged from their work.
4.How can organizations reduce attrition and improve retention rates?
Organizations can reduce attrition and improve retention rates by creating a positive work environment, providing fair compensation and benefits, offering opportunities for career development and growth, promoting work-life balance, and fostering a culture of support and recognition. By investing in employee engagement and development, organizations can create a workplace where employees feel valued, motivated, and committed to the organization’s success.
5. What are the long-term effects of high attrition rates on an organization’s success?
High attrition rates can have a negative impact on an organization’s success over the long term. It can lead to increased recruitment and training costs, reduced productivity, decreased employee morale, and a negative impact on the organization’s reputation. Additionally, high attrition rates can result in a loss of institutional knowledge, which can be challenging to replace and may hinder the organization’s ability to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. Therefore, it is important for organizations to monitor and manage attrition rates to maintain a stable workforce and sustain business growth over the long term.
Conclusion
In conclusion, employee attrition and retention are two critical factors that can have a significant impact on an organization’s success.
High attrition rates can be costly for organizations, resulting in reduced productivity, increased recruitment and training costs, and decreased employee morale. In contrast, high retention rates can lead to better business outcomes, such as increased efficiency, better customer service, and improved employee morale.
Managing attrition and retention is an ongoing process that requires consistent effort and attention.
CHRMP (Certified Human Resource Management Professional) is a leading HR institution that continuously strives to expand knowledge of the HR field—looking to transform your career and achieve new heights?
Enrol in one of our world-class HR certification courses today!