The Role of Business Acumen in Modern HR Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
How essential is business acumen in the realm of human resources? In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, HR professionals are increasingly expected to not only manage personnel but also to contribute strategically to the organization’s success. This requires a deep understanding of business dynamics, a skill set known as business acumen.
Business acumen, defined as the ability to understand and apply information to contribute to an organization’s strategic plan, involves a comprehensive grasp of an organization’s strategy, the key drivers of success, and the interrelationships among various functions within the organization. Essential skills associated with business acumen include financial acumen, strategic thinking, leadership, and effective communication.
For HR professionals, possessing business acumen means understanding the industry, the business environment, and the competitive landscape in which their organization operates. It entails making a compelling business case for HR initiatives by linking them to efficient and effective organizational performance. Furthermore, HR professionals must be adept at using organizational metrics to inform their decisions and articulate the value of their work in terms of the organization’s bottom line.
However, the extent to which HR executives possess business acumen is a topic of ongoing debate among scholars and practitioners. Some argue that they lack sufficient business acumen, which is crucial for leading and managing the HR function effectively. They emphasize the need to develop competencies in strategic acumen, financial knowledge, and economic awareness to excel in their roles.
Conversely, other researchers contend that many HR professionals already demonstrate a high level of business acumen. They point out that effective HR’s routinely exhibit strategic agility, systems thinking, and a thorough understanding of finance, accounting, technology, marketing, and business operations. These competencies enable them to measure the return on investment (ROI) of human capital, leverage HR for sustainable growth, audit HR functions, build organizational capabilities, and apply advanced analytics to HR management decisions.
So, what does all this mean for modern HR practices? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the critical role of business acumen in HR, the skills necessary to develop it, and practical steps for HR professionals to enhance their strategic contributions. By the end of this blog post, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to leverage business acumen to drive organizational success, making you not just an HR professional, but a strategic partner in your organization’s growth.
Section 1: Understanding Key Competency Models in HR
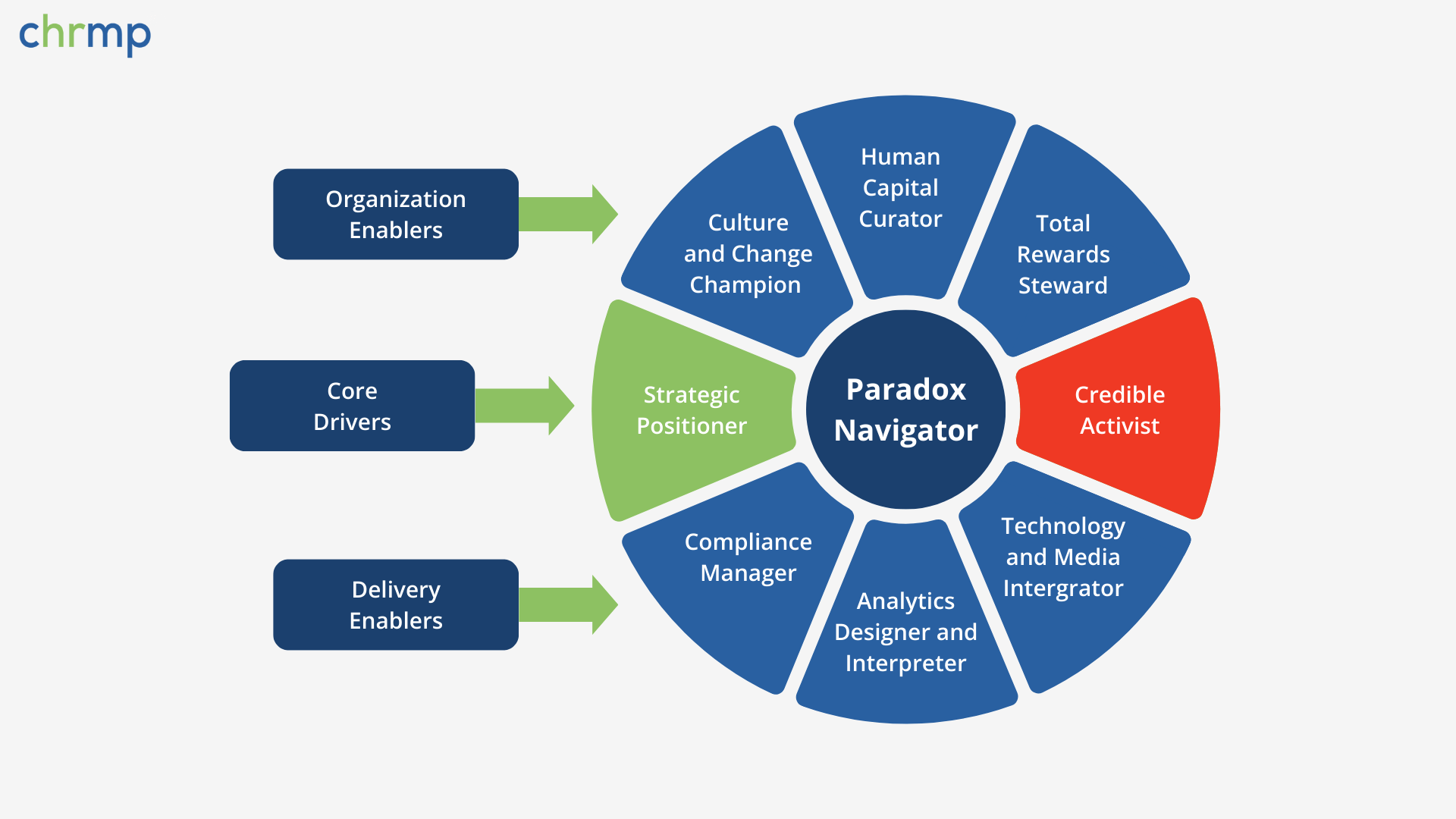
To truly appreciate the significance of business acumen in HR, it’s essential to explore the frameworks that define and develop this critical skill. Two prominent models stand out in this regard: the HR Competency Model developed by Dave Ulrich, David Kryscynski, Mike Ulrich, and Wayne Brockbank in 2017, and the ATD Competency Model, initially created in 2004 and last updated in 2013 by the Association for Talent Development. These models offer a comprehensive blueprint for HR professionals aiming to enhance their strategic and business capabilities.
The HR Competency Model (2017)
The HR Competency Model, established by Dave Ulrich and his colleagues, is a cornerstone in understanding the multifaceted role of HR professionals in modern organizations. This model highlights several key competencies necessary for HR professionals to succeed:
- Strategic Positioner: HR professionals must understand the business context and align HR strategies with business objectives. This involves knowing market trends, the competitive landscape, and economic forces that impact the organization.
- Credible Activist: Building trust and credibility within the organization is crucial. HR professionals need to demonstrate integrity, communicate effectively, and advocate for both the organization and its employees.
- Capability Builder: Developing organizational capabilities is a core responsibility. This includes fostering a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and adaptability.
- Change Champion: HR must lead and manage change initiatives, ensuring that the organization can navigate and thrive amidst transitions. This involves change management skills and the ability to influence and guide others through change.
- HR Innovator and Integrator: Innovating HR practices and integrating them into the broader organizational framework is essential. This competency focuses on developing and implementing HR strategies that drive performance and add value.
- Technology Proponent: Leveraging technology to improve HR processes and outcomes is increasingly important. HR professionals must be proficient in using HR tech tools and data analytics to make informed decisions.
The ATD Competency Model (2013)
The ATD Competency Model, developed by the Association for Talent Development, provides a framework for talent development professionals. This model emphasizes the skills and knowledge required to enhance employee performance and organizational effectiveness. Key components include:
- Performance Improvement: Identifying performance gaps and designing interventions to close them is fundamental. This involves assessing organizational needs, setting performance goals, and measuring outcomes.
- Instructional Design: Creating effective learning programs tailored to the needs of the workforce is crucial. This competency involves designing curricula that align with business objectives and enhance employee skills.
- Training Delivery: Delivering training in a way that engages and educates employees is essential. This includes facilitating workshops, seminars, and e-learning sessions.
- Learning Technologies: Utilizing technology to support learning and development is a key aspect. This includes integrating digital tools, platforms, and resources into the training process.
- Evaluating Learning Impact: Measuring the effectiveness of training programs and their impact on organizational performance is vital. This competency focuses on assessing the ROI of training initiatives and making data-driven improvements.
- Change Management: Like the HR Competency Model, the ATD model emphasizes the importance of managing change. Talent development professionals must be skilled in guiding organizations through transitions and fostering a culture of adaptability.
Both models underscore the necessity of business acumen in HR. They highlight how strategic thinking, change management, and technology integration are integral to modern HR practices. By understanding and applying these competencies, HR professionals can become invaluable strategic partners in their organizations.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into how these competency models can be practically applied to enhance business acumen and drive organizational success. Stay tuned to learn how to leverage these frameworks to elevate your HR practice and make a significant impact on your organization’s growth and performance.
Section 2: Practical Application of HR Competency Models to Enhance Business Acumen
In this section, we will delve deeper into how the HR Competency Model and the ATD Competency Model can be practically applied to enhance business acumen and drive organizational success. By leveraging these frameworks, HR professionals can elevate their practice and make a significant impact on their organization’s growth and performance. Below are actionable steps under each model.
The HR Competency Model: Action Steps
- Strategic Positioner: Aligning HR with Business Goals
- Conduct Market Analysis: Regularly review market trends, industry benchmarks, and economic indicators to understand the external environment.
- Develop Strategic Plans: Align HR initiatives with the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that HR activities support business goals.
- Collaborate with Leadership: Engage with senior leaders to understand their vision and how HR can contribute to achieving strategic targets.
- Credible Activist: Building Trust and Credibility
- Communicate Transparently: Maintain open lines of communication with employees at all levels to build trust and credibility.
- Demonstrate Integrity: Act ethically and consistently to establish yourself as a trusted advisor within the organization.
- Advocate for Employees: Balance the needs of the organization with those of its employees, advocating for fair and equitable treatment.
- Capability Builder: Fostering Organizational Development
- Identify Skill Gaps: Conduct regular assessments to identify skill gaps and areas for development within the organization.
- Develop Training Programs: Create targeted training and development programs to build necessary capabilities.
- Promote a Learning Culture: Encourage continuous learning and improvement by recognizing and rewarding employee development efforts.
- Change Champion: Leading Change Initiatives
- Plan Change Management Strategies: Develop and implement effective change management plans to guide the organization through transitions.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the change process to ensure buy-in and support.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the progress of change initiatives and make adjustments as needed to achieve desired outcomes.
- HR Innovator and Integrator: Innovating HR Practices
- Adopt Best Practices: Stay updated on HR best practices and incorporate them into your organization’s HR strategy.
- Integrate HR Systems: Ensure that HR practices are integrated into the broader organizational framework, aligning with overall business strategy.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage innovative thinking within the HR team to develop creative solutions to organizational challenges.
- Technology Proponent: Leveraging Technology in HR
- Utilize HR Tech Tools: Implement and use advanced HR technology tools to streamline HR processes and improve efficiency.
- Analyze HR Data: Use data analytics to make informed decisions and demonstrate the value of HR initiatives.
- Stay Tech-Savvy: Continuously update your knowledge of emerging HR technologies and trends.
The ATD Competency Model: Action Steps

- Performance Improvement: Enhancing Organizational Performance
- Conduct Needs Assessments: Regularly assess organizational performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Set Clear Goals: Establish specific, measurable goals for performance improvement initiatives.
- Implement Interventions: Design and implement interventions aimed at closing performance gaps.
- Instructional Design: Creating Effective Learning Programs
- Design Tailored Training: Develop training programs that are customized to meet the specific needs of your organization.
- Utilize Various Formats: Incorporate a mix of learning formats, including workshops, e-learning, and on-the-job training.
- Measure Effectiveness: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of training programs and make necessary adjustments.
- Training Delivery: Engaging and Educating Employees
- Engage Learners: Use interactive and engaging training methods to capture the attention of participants.
- Facilitate Workshops: Lead workshops and training sessions that are informative and practical.
- Provide Continuous Support: Offer ongoing support and resources to ensure employees can apply what they’ve learned.
- Learning Technologies: Integrating Digital Tools
- Adopt E-Learning Platforms: Implement e-learning platforms to provide flexible and accessible training options.
- Use Digital Resources: Incorporate digital resources such as webinars, online courses, and virtual simulations into training programs.
- Track Progress: Utilize technology to track employee progress and learning outcomes.
- Evaluating Learning Impact: Measuring Training Effectiveness
- Set Evaluation Metrics: Define clear metrics for evaluating the impact of training programs.
- Collect Data: Gather data on training outcomes and employee performance.
- Analyze Results: Analyze the results to determine the ROI of training initiatives and identify areas for improvement.
- Change Management: Navigating Organizational Change
- Develop Change Strategies: Create comprehensive change management strategies to guide the organization through transitions.
- Communicate Change: Clearly communicate the reasons for change and the benefits it will bring to the organization.
- Support Employees: Provide support and resources to help employees adapt to change.
By following these action steps, HR professionals can enhance their business acumen and strategically contribute to their organization’s success. In the next section, we will explore real-world examples of how these competency models have been applied to drive business outcomes. Stay tuned to learn how to translate these principles into actionable strategies that make a tangible impact on your organization.
Conclusion:
Business acumen is a critical competency for modern HR professionals, enabling them to align HR strategies with business objectives and drive organizational success. By leveraging the HR Competency Model and the ATD Competency Model, HR practitioners can develop the necessary skills to navigate the complexities of today’s business environment. These frameworks provide actionable steps for enhancing strategic positioning, building trust, fostering innovation, and leading change initiatives, all of which are essential for effective HR management.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into the importance of business acumen in HR and practical steps to enhance your capabilities. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. How have you applied business acumen in your HR role? What challenges have you faced, and what strategies have you found most effective? Join the conversation, and let’s learn from each other’s experiences.





