

Compensation issues are common challenges for organizations, including pay disparities, insufficient compensation packages, opaque compensation practices, and challenges with performance-based remuneration.
Effective compensation policies and procedures can address these issues by creating precise pay guidelines, performing routine compensation audits, and training managers and HR specialists on pay equality practices.
By developing a fair and competitive compensation plan that considers the business’s and its employees’ specific requirements and objectives, organizations can recruit and retain top talent, prevent pay inequalities, and better align employee behavior with their goals.
Compensation in HRM refers to the overall package of rewards and benefits that employees receive in exchange for their work and contributions to an organization. It encompasses both monetary and non-monetary elements provided to employees as a means of recognizing and remunerating their efforts.
Monetary compensation includes the base salary or wages paid to employees for their regular work hours. It also includes additional financial incentives such as bonuses, commissions, profit-sharing, and stock options.
Non-monetary compensation comprises various benefits and perks offered to employees. This can include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other forms of support that contribute to employee well-being and work-life balance.
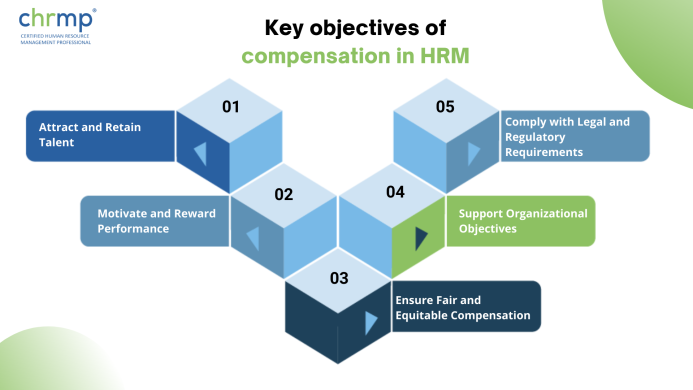
The key objectives of compensation in HRM are:
Compensation policies greatly impact the many compensation difficulties that firms encounter.
These regulations encourage staff members and assist them in connecting their conduct with the company’s objectives to recruit and keep top personnel.
Employees frequently base their decision to accept a job offer on the fair and competitive remuneration package, underscoring the significance of pay policies in resolving compensation issues.
Compensation rules also support pay equity, ensuring that all workers, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity, are paid equally for equivalent labor.
This approach can help prevent discrimination and create a more diverse and inclusive workplace, addressing compensation issues related to bias and inequality.
These rules aid in reducing compensation issues, including disputes and complaints, by offering a uniform and open framework for managing compensation.
When employees are aware of the factors that determine their pay, the organization’s compensation policies can be trusted and believed to be fair if the process is transparent.
In summary, compensation policies are essential for addressing compensation issues in businesses.
With the promotion of justice, equity, and transparency in compensation processes, these policies guarantee that the company has a pay structure that is competitive, efficient, effective, and consistent with its values and aims.
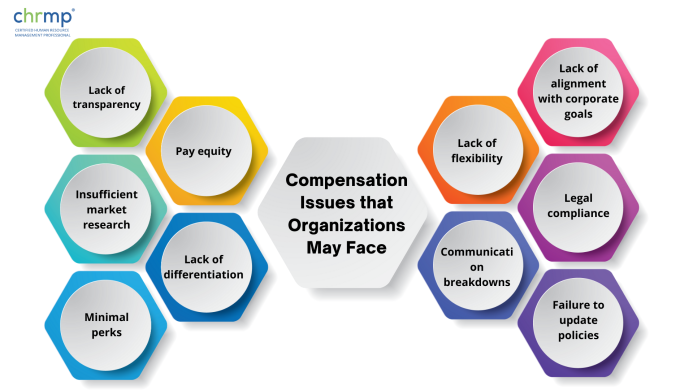
1. Pay equity: When workers believe their salaries are unjust or unequal to those of their coworkers at the company, it can cause low morale, discontent, and attrition.
2. Lack of transparency: Employees may not understand how their pay is set when firms don’t explain their compensation practices, which can breed mistrust and unhappiness.
The social media toolkit provider for small businesses, Buffer, perhaps takes the most unconventional approach by posting its employees’ salaries publicly for all to see.
3. Insufficient market research: Businesses that do not perform proper market research to identify competitive pay rates may give remuneration that is not competitive, which can make it challenging to recruit and keep talent.
4. Lack of differentiation: High-performing employees may feel undervalued and depart for greater possibilities elsewhere when firms must distinguish compensation based on performance, abilities, and experience.
5. Minimal perks: Companies that provide limited benefits may cause low morale and problems keeping talent since employees may believe that their overall pay needs to be increased.
6. Lack of flexibility: Employees may believe that a company only appreciates their preferences and requirements if it offers flexible remuneration packages, such as the option to work remotely or select a benefits package that suits their demands.
7. Lack of alignment with corporate goals: Employees may not be motivated to work towards those goals when remuneration practices are out of line with those objectives, making them more difficult to attain.
8. Legal compliance: Businesses that violate rules about remuneration, such as anti-discrimination or minimum wage legislation, risk legal repercussions as well as reputational harm.
9. Communication breakdowns: Businesses need to inform employees properly of modifications to pay rules or other changes to avoid confusion and discontent among them.
10. Failure to update policies: When businesses frequently evaluate and update their compensation plans to account for shifting market dynamics or employee demands, they refrain from providing outdated or uncompetitive pay packages that make recruiting and keeping top people difficult.
Following are some actions businesses can take to identify and address compensation issues:
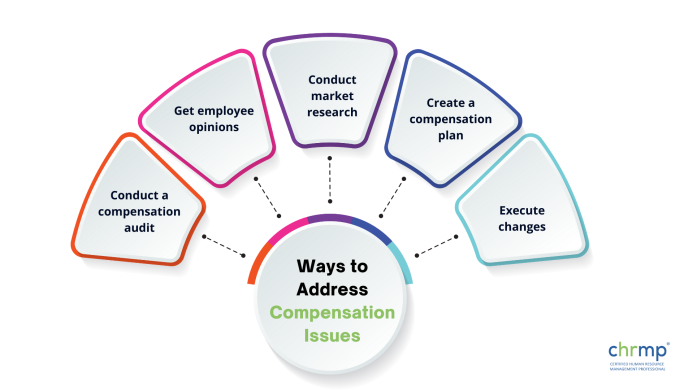
Step 1: Conduct a compensation audit: Review your present compensation rules and practices before conducting a compensation audit.
Determine any problems, such as salary disparities, a lack of distinctiveness, or poor benefits.
Step 2: Get employee opinions: Involve workers and ask them for input on pay practices and policies. You can conduct surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one interviews.
Use this feedback to pinpoint areas that need work and learn more about your staff’s requirements and expectations.
Step 3: Conduct market research: Do rigorous market research to identify competitive pay rates for your sector and area. Use this data to assess your present pay rules and procedures and pinpoint improvement areas.
Step 4: Create a compensation plan: Create a thorough compensation strategy that aligns with your firm’s objectives and core values based on the results of the compensation audit, employee input, and market research.
Clear standards for deciding on salary, benefits, and other compensation-related choices should be part of this plan.
Step 5: Execute changes: Put into practice the adjustments noted in your compensation strategy.
This can entail changing pay scales, enhancing benefits packages, or creating pay structures depending on performance. Be careful to inform staff members of these changes understandably and openly.
In order to suit the changing demands of both individuals and companies, compensation policies are continually changing.
Here are some new developments in pay practices and how they could affect businesses:
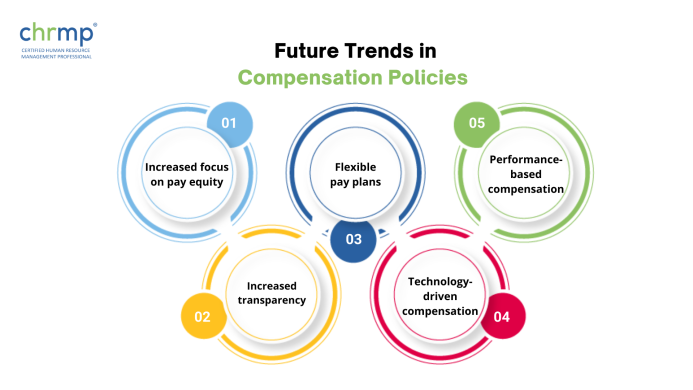
1. Increased focus on pay equity: Pay fairness is becoming more of a priority, and several groups are taking action to find and address wage inequalities.
As workers express their opinions about their pay more openly and as more countries pass pay equity legislation, this trend is likely to persist.
Companies that promote pay parity are more likely to draw in and keep top talent, as well as gain from increased employee satisfaction and productivity.
2. Flexible pay plans: As employees place higher importance on flexibility, more companies are providing personalized compensation plans that let workers select the perks and benefits that best suit their requirements.
Organizations may benefit from this trend by attracting and keeping top talent, enhancing employee engagement and happiness, and boosting productivity.
3. Performance-based compensation: Companies are placing increasing focus on performance-based compensation, connecting pay to individual and organizational goals.
This pattern can improve employee motivation and productivity by coordinating their actions with company goals.
4. Increased transparency: The demand for firms to be more transparent about their remuneration policies and practices is a result of the popularity of social media and online evaluations.
For both consumers and workers, this tendency may help foster trustworthiness and recruit top talent.
5. Technology-driven compensation: With tools like automated payroll systems, online benefit portals, and real-time performance monitoring, technology is increasingly being utilized to support compensation policies and practices.
Organizations may benefit from this trend by streamlining their compensation procedures, lowering mistakes, and providing more precise and up-to-date compensation data.
Overall, these new developments in pay practise will probably have a big influence on businesses in the years to come.
Organizations can attract and keep top talent, boost employee happiness and engagement, and accomplish their company goals by embracing these trends and implementing creative compensation policies and practices.
In conclusion, pay policies are a crucial part of human resource management and have a big impact on employee retention, productivity, and satisfaction. It is crucial to keep current with new trends in pay practices as firms continue to change and adapt to shifting employee demands and expectations.
Consider taking a CHRMP certification course if you’re interested in learning more about compensation and benefits planning. This course can give you helpful tips and resources for creating and putting into practice compensation schemes that are in line with the objectives and core values of your company.
So why not take the first step towards becoming a compensation and benefits expert? Your organization and your employees will thank you for it.
1. Why is compensation important? What is it?
To recruit and keep top talent, motivate staff to give their all, and connect their behavior with organizational goals, businesses must handle compensation issues.
A key component of an organization’s entire compensation plan, compensation includes both monetary and non-monetary advantages, including salaries, incentives, perks, and bonuses.
2. What distinguishes remuneration from benefits?
Compensation issues deal with the financial and intangible benefits, including compensation, incentives, and perks, that an employee receives in exchange for their labor.
Contrarily, perks like health insurance, retirement programs, and paid time off to provide value above and beyond salaries.
Both compensation issues and benefits are vital for maintaining employee satisfaction and retention, but they provide distinct forms of value.
3. How can businesses guarantee pay equity?
To achieve pay parity among their employees, organizations must address compensation issues.
To achieve this, it is necessary to create precise pay standards, carry out frequent compensation audits to identify and close pay discrepancies, and train managers and HR employees on pay equality principles and procedures.
Technology-driven compensation can assist firms in ensuring pay equity and minimizing the possibility of bias.
Businesses may promote a just and inclusive workplace where employees feel appreciated and inspired to perform at their best by addressing pay concerns.
© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited

Fill in the below details to get a C&B Program Plan.
