In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, human resource management (HRM) must constantly adapt to new challenges and opportunities. One powerful tool that has emerged to help HR professionals navigate these changes is competency mapping. This strategic approach not only enhances the effectiveness of HRM practices but also drives organizational success by aligning employee capabilities with business goals. In this Competency Mapping in HRM guide, we will delve into the benefits of competency mapping in HRM, explore various methods and techniques, and provide a step-by-step guide on implementing this practice in your organization.
Competency Mapping in HRM?
Competency mapping in HRM is the process of identifying, assessing, and developing the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for employees to perform their roles effectively. By creating a detailed competency map, organizations can ensure that their workforce possesses the necessary attributes to meet current and future business needs. This strategic alignment helps in optimizing talent management processes, enhancing employee performance, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Competency-Based HRM vs. Traditional HRM
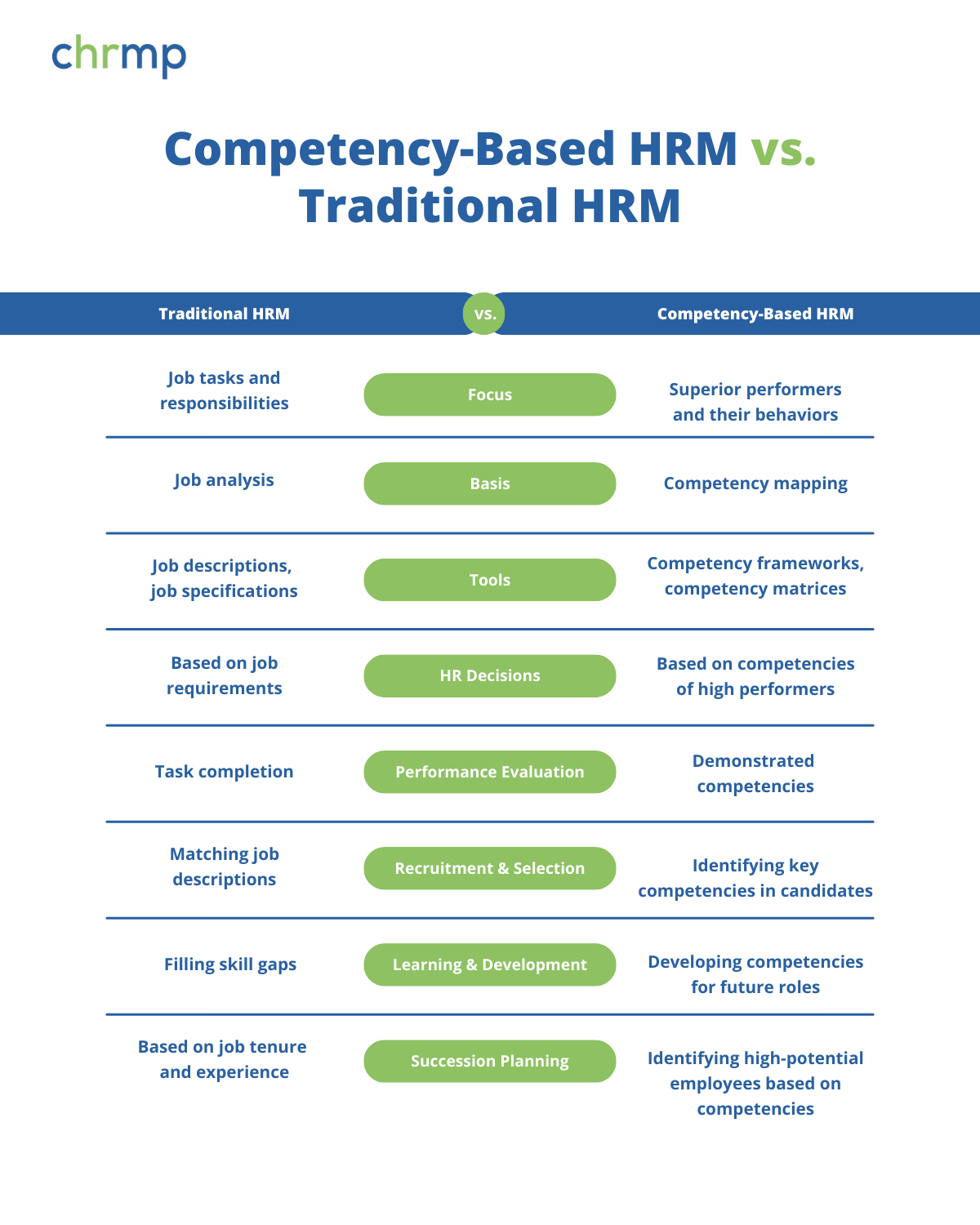
Competency-based HRM is a significant departure from the traditional way of managing the Human Resource function, which has been practiced by organizations worldwide for decades. The traditional approach uses job analysis as the basis for conducting human resource activities. In comparison, the modern and more progressive way utilizes competency mapping as the focal point for all HR activities.
In the traditional approach, job descriptions and job specifications are employed, whereas competency-based HRM uses competency frameworks and competency matrices. Traditional approaches study the job and aspects like tasks, duties, responsibilities, skills, experience, and qualifications required for the job. All HR decisions, such as hiring, training, and appraising, are based on the job.
On the contrary, the competency-based approach does not study the job but the superior performers who do a job well. All HR decisions are based on the competencies displayed by these exceptional performers, which the organization aims to replicate in all its employees.
Benefits of Competency Mapping in HRM
- Enhanced Recruitment and Selection:
Competency mapping allows HR professionals to create precise job descriptions and specifications, ensuring that the recruitment process targets candidates with the right skills and attributes. This leads to more effective hiring decisions and reduces the risk of turnover. - Improved Performance Management:
By clearly defining the competencies required for each role, organizations can set specific performance expectations and provide targeted feedback. This helps employees understand their strengths and areas for development, leading to improved performance and job satisfaction. - Targeted Learning and Development:
Competency mapping identifies skill gaps within the workforce, enabling HR to design tailored training programs that address these gaps. This targeted approach to learning and development enhances employee capabilities and supports career progression. - Succession Planning:
With a comprehensive competency map, HR can identify high-potential employees and prepare them for future leadership roles. This proactive approach to succession planning ensures business continuity and minimizes disruptions caused by key personnel changes. - Strategic Workforce Planning:
Competency mapping provides insights into the current and future competency needs of the organization. This information is crucial for strategic workforce planning, helping HR to anticipate and address talent shortages or surpluses.
Characteristics of Competency
A competency is an underlying characteristic of a person which results in effective and/or superior performance of the job. Competencies can be a combination of various elements like knowledge, skills, and attitudes that translate into observable behavior, leading to successful outcomes. Competencies provide evidence-based criteria for successful outcomes. Therefore, competency-based HRM allows the organization to base decisions on the observable behavior of high performers.
Skill vs. Competency
- Skill: Developed abilities or capabilities acquired through practice. These are specific to a particular task and can be acquired in a short period. For example, financial skills such as budgeting or verbal skills such as making a presentation.
- Competency: Underlying characteristics of a person which result in effective performance of a job role. These are exhibited as actual behaviors demonstrated by people leading to successful outcomes. Competencies encompass skills, knowledge, and personal attributes that are observable and lead to effective performance.
Components of Competency
There are four major components of competency:
- Skill: Capabilities acquired through practice, such as budgeting or making a presentation.
- Knowledge: Understanding acquired through learning relevant to job performance, such as knowledge of policies and procedures.
- Personal Attributes: Inherent characteristics brought to the job, forming the foundation upon which knowledge and skills can be developed.
- Behavior: The observable demonstration of competencies, skills, knowledge, and personal attributes, defining competency through measurable activities.
Types of Competencies
- Core Competencies:
These are aligned with organizational goals and provide a competitive advantage. Derived from the vision and mission of the organization, they help it perform better and remain distinct. - Cross-Functional Competencies:
Required when an individual works across teams and functions, these competencies facilitate collaboration and integration. - Functional Competencies:
Also known as technical competencies, these are necessary for performing specific roles regularly. Identified from high performers, these competencies ensure effective job performance.
Methods of Data Collection for Competency Mapping
Effective data collection is crucial for accurate competency mapping. Here are some commonly used methods:
- Interviews:
Conduct interviews with employees and managers to gather qualitative data on the competencies required for different roles. This method provides in-depth insights and helps in understanding the context behind each competency. - Observations:
Observe employees in their work environment to identify the behaviors and skills that contribute to successful job performance. This method is particularly useful for roles that involve hands-on tasks or interactions with customers. - Document Analysis:
Review job descriptions, performance appraisals, training records, and other relevant documents to identify the competencies required for various roles. This method provides a historical perspective and helps in understanding the evolution of competency requirements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Competency Mapping in HRM
Step 1: Define Objectives
Clearly define the objectives of your competency mapping initiative. Determine what you aim to achieve, such as improving recruitment processes, enhancing performance management, or supporting succession planning.
Step 2: Identify Key Roles and Competencies
Identify the critical roles within your organization and the competencies required for each role. Consider both technical skills and behavioral attributes that contribute to successful job performance.
Step 3: Select Appropriate Methods
Choose the methods of competency mapping that best suit your organization’s needs and resources. Consider using a combination of techniques to obtain a comprehensive view of employees’ competencies.
Step 4: Collect and Analyze Data
Gather data using the selected methods and analyze the results to identify competency gaps and strengths. Use this information to create detailed competency profiles for each role.
Step 5: Develop and Implement Action Plans
Based on the competency profiles, develop targeted action plans for recruitment, training, performance management, and succession planning. Ensure that these plans are aligned with your organization’s strategic goals.
Step 6: Monitor and Review
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your competency mapping initiative and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review the competency profiles and update them to reflect changes in business needs or job requirements.
How is Competency Mapping Conducted?
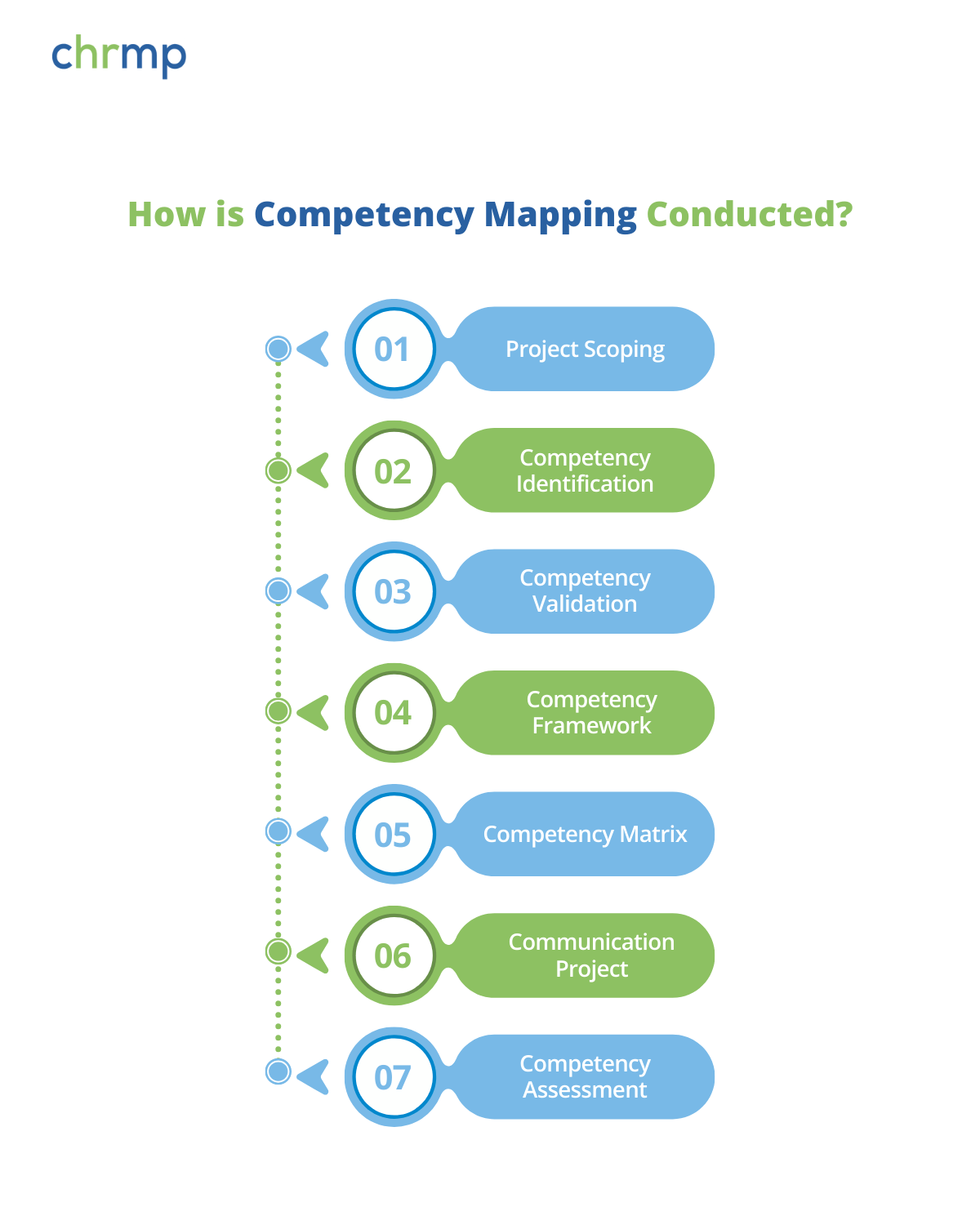
Competency mapping is the process of identifying and validating competencies required to produce successful outcomes for various roles within the organization. Here’s a detailed look at how it is conducted:
- Project Scoping:
Define the scope of the project, including the size, approach, alignment with organizational goals, and timeline. - Competency Identification:
Identify high performers and use methods like observation, in-depth interviews, and focus groups to document observable behaviors. - Competency Validation:
Analyze and clean the data on observable behaviors through methods like jury validation, ensuring the data is relevant and accurate. - Competency Framework:
Organize validated competencies into clusters and levels, describing each level’s indicators. - Competency Matrix:
Cross-reference job roles with competency areas and levels to create a competency matrix. - Communication Project:
Share the competency matrix with the organization, helping employees understand the competencies needed for their current and future roles. - Competency Assessment:
Assess employees against the competency framework to determine where they stand and identify development needs. This assessment can be done periodically to ensure continuous improvement.
Real-World Success Stories of Applying Competencies at the Workplace
Example 1: Enhancing Recruitment at ABC Corp
ABC Corp, a leading technology company, implemented competency mapping to improve its recruitment process. By defining the specific technical and behavioral competencies required for each role, the company was able to create more accurate job descriptions and selection criteria. As a result, ABC Corp saw a 30% reduction in time-to-hire and a 25% increase in new hire retention rates.
Example 2: Improving Performance Management at XYZ Ltd
XYZ Ltd, a global manufacturing firm, used competency mapping to revamp its performance management system. By aligning performance appraisals with clearly defined competencies, the company provided more targeted feedback and development opportunities to its employees. This led to a 15% increase in overall employee performance and a significant boost in employee engagement.
The Evolution of HR: From Task-Based to Competency-Based Approaches
The evolution of HR from being task-based to skill-based to competency-based reflects a broader shift in understanding what drives performance and success in organizations. This transition underscores the changing nature of work, the importance of human capital, and the strategic role of HR in fostering organizational growth and adaptability. Here’s an overview of this evolution:
Task-Based Approach
- Era: Predominantly before the 1980s.
- Focus: Jobs were defined by a specific set of tasks. The primary concern was ensuring that each employee knew their tasks and performed them efficiently.
- HR Role: In a task-based system, HR’s role was largely administrative, focusing on defining job descriptions, managing work allocation, and ensuring tasks were completed. Recruitment and performance evaluations were based on the ability to perform specific tasks.
Skill-Based Approach
- Era: Began to emerge in the 1980s and 1990s.
- Focus: The focus shifted to the skills and abilities that employees brought to their jobs. Organizations started to recognize the importance of hiring and developing employees based on a broader set of skills that could be applied across various tasks.
- HR Role: HR began to play a more developmental role, focusing on identifying skill gaps, providing training and development opportunities, and recruiting individuals with key skills that matched the organization’s needs. Performance management started to include skill assessments, and career paths were developed to enhance skill acquisition.
Competency-Based Approach
- Era: Gained prominence in the late 1990s and continues to evolve.
- Focus: This approach extends beyond skills to include behaviors, knowledge, and abilities that contribute to an individual’s and the organization’s success. Competencies are often aligned with strategic goals and are considered in a broader context, including how individuals fit within teams and contribute to organizational culture and values.
- HR Role: HR’s role becomes strategic and integrated into all aspects of talent management, including recruitment, development, performance management, and succession planning. HR develops competency frameworks that align with the organization’s strategic objectives, and these frameworks guide hiring practices, development programs, and performance evaluation processes. The competency-based approach supports a more holistic understanding of employee contributions, focusing on both what is achieved and how it is achieved.
The Strategic Shift in HRM
In the last couple of decades, HR has transformed from a merely administrative support function to a strategic partner in business. This transformation is driven by several factors:
- Competency-Based HRM: By focusing on competencies, HR can ensure that the workforce aligns with the strategic goals of the organization. This shift supports a more dynamic and adaptable workforce capable of meeting the challenges of today’s business environment.
- HR Analytics: The increasing use of HR analytics allows HR professionals to make data-driven decisions. By analyzing data on employee performance, engagement, and turnover, HR can develop strategies that improve overall organizational effectiveness.
- HR Business Partner (HRBP) Model: The HRBP model embeds HR professionals within business units, allowing them to work closely with line managers to develop and implement HR strategies that support business objectives. This model ensures that HR is not just a support function but an integral part of the strategic planning process.
Flexibility and Adaptability of Competency-Based HRM
While competencies provide a structured approach to HRM, they are not meant to be rigid or inflexible. Competencies can be adapted and updated as organizational needs, job roles, and industry trends evolve. The flexibility of a competency-based approach lies in its ability to be tailored to the unique context of each organization and to accommodate changes over time.
Competencies are applicable and beneficial across all levels of an organization, not just for high-level or managerial positions. They provide a clear framework that can help employees at every level understand what is expected of them, how their roles contribute to the organization’s goals, and how they can grow and develop professionally.
Conclusion
Competency mapping in HRM is a powerful tool that can transform your organization’s talent management practices. By identifying and developing the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success, you can enhance recruitment, performance management, learning and development, and succession planning. Implementing competency mapping involves selecting appropriate methods, collecting and analyzing data, and developing targeted action plans. Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of this strategic approach, making it a valuable asset for any HR professional.
The evolution from task-based to competency-based HRM reflects a deeper understanding of what drives performance and success in organizations. This transition supports a more dynamic and adaptable workforce, capable of meeting the challenges of today’s business environment. By leveraging the benefits of competency mapping, HR professionals can drive organizational success, foster a culture of continuous improvement, and ensure that their workforce is equipped to meet the challenges of today and tomorrow.