HR analytics, or people analytics, uses data analysis to help managers make informed HR decisions to improve workforce performance.
The key features of HR analytics are metrics to identify areas of improvement and tools like HRIS to make predictive analysis to automate processes and make accurate predictions about workforce trends.
HR analytics is an asset if appropriately managed. The goal is to help organisations gain an insight into their workforce to build a better workforce asset, create effective HR strategies, and improve the organisation’s bottom line.
In this blog, we shall look at the top 10 key features of HR Analytics along with other relevant topics.
So without further ado, let’s dive right in.
What is HR Analytics and Why is it Important?
HR analytics, also known as people analytics, uses data analysis and metrics to help management make informed HR decisions and improve workforce productivity.
It involves collecting, organising, analysing and making extrapolative predictions of data trends and patterns on various HR-related factors, such as employee engagement, retention, recruitment, performance, and diversity.
The importance of HR analytics lies in enabling organisations to make data-driven and informed decisions about their workforce, leading to improved employee productivity, reduced turnover, and optimised talent management.
By using HR analytics, organisations can gain valuable insights into their workforce, identify areas of improvement and create effective HR strategies that improve the organisation’s bottom line.
It also allows HR professionals to automate their processes, analyse data and make accurate extrapolative predictions about workforce trends and patterns, leading to better workforce planning and increased organisational agility and performance.
Top 10 Features of HR Analytics
Here are the top 10 features of HR analytics:

1.Metrics and KPIs for employee performance and engagement:
HR analytics uses various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure employee performance productivity, engagement, productivity, job satisfaction, and employee net promoter score (NPS).
2.Predictive analysis to extrapolative forecasting workforce trends and behaviors:
Predictive analysis uses historical data and statistical models to extrapolate and predict future trends and behaviour patterns, such as workforce attrition rates, workforce planning, and talent development.
3.HR information systems (HRIS) to automate HR processes:
HRIS is a software system that automates various HR processes such as payroll, employee benefits, overtime, attendance, and employee record keeping.
4.Data visualization tools to display HR metrics in a user-friendly format:
Data visualisation tools provide a user-friendly way to display HR metrics and KPIs using charts, graphs, diagrams and dashboards, which makes analysis of data easier, which in turn helps HR professionals quickly understand and communicate data insights.
5.Diversity and inclusion metrics to track representation and equality:
HR analytics provides metrics to track diversity and inclusion, such as the representation of different demographic groups, gender groups, pay gaps, and employee sentiment surveys.
6.Recruitment analytics to measure time-to-hire and cost-per-hire:
Recruitment analytics measures the effectiveness and efficiency of the recruitment process, such as the time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, source of hire and turnover rate, and the retention cost of the workforce in the organisation. All need to be carefully weighed and compared.
7.Turnover rate analytics to identify retention issues:
Turnover rate analytics measures the rate at which employees leave the organisation and helps to identify retention issues, such as poor management, lack of career growth, inadequate compensation or work-life balance.
8.Skills gap analysis to identify training needs and talent gaps:
Skills gap analysis identifies the gap between the skills required for a job and the skills possessed by employees for that particular job and helps identify training needs and talent gaps.
9.Succession planning to identify and develop future leaders:
Employees with exceptional leadership potential need to be identified and retained. Training and development opportunities need to be provided to them to fill critical positions when the need arises, thereby reducing the risk of organisational disruption and time-to-hire metric.
10.Benchmarking against industry standards and competitors:
Benchmarking compares an organisation’s HR metrics and KPIs with industry standards and that of competitors to help identify areas of improvement and best practices, initiatives and drives.
How Does HR Analytics Benefit the Company?
Implementing HR analytics in a company can provide many benefits, such as improving the effectiveness and efficiency of HR decision-making.
The management can make informed data-driven decisions instead of intuitive ones, thereby increasing employee engagement and productivity, reducing turnover and absenteeism, and optimising talent management and organisational performance.
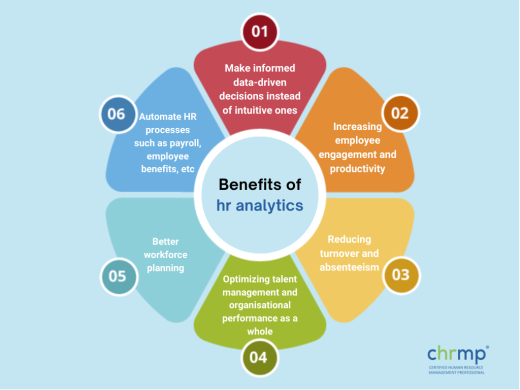
By using data analysis and HR metrics, organisations can gain valuable insights into their workforce, identify areas of improvement, and make informed decisions that lead to better workforce planning, optimised retention and increased organisational agility and performance.
For employee performance and engagement, the metrics and KPIs to be tracked through HR analytics are productivity, job satisfaction, employee net promoter score (NPS), and employee turnover rate.
HR analytics can also help automate HR processes such as payroll, employee benefits, overtime, attendance, and employee record keeping, which reduce manual tasks, and increase accuracy in predictions about workforce trends.
Ultimately, HR analytics can lead to better HR strategies, better business outcomes, and a competitive advantage in the market.
How to Implement HR Analytics in Your Company
Here are the general steps to implement HR analytics in your company:
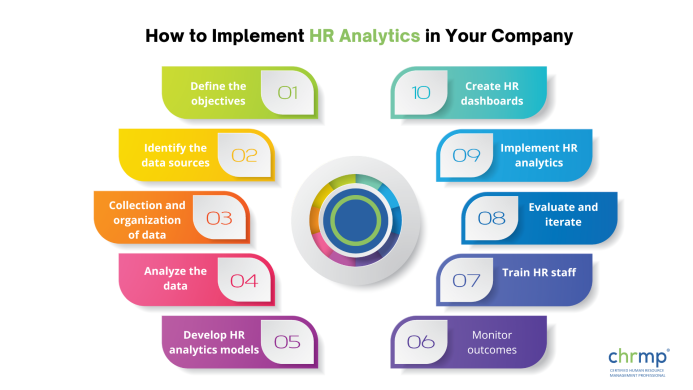
Step 1: Define the objectives
Identify the business objectives and specific HR issues that HR analytics will address, such as improving employee engagement and performance or reducing turnover and absenteeism.
Step 2: Identify the data sources
Determination of the data sources and systems that will be used to collect HR data, such as HRIS and employee surveys, is essential.
Step 3: Collection and organization of data
Collection and organisation of the collected HR data in a centralised location, such as a data warehouse, to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Step 4: Analyze the data
Use of statistical analysis and data visualisation techniques to analyse the HR data and extrapolate the data to predict trends, patterns, and insights.
Step 5: Develop HR analytics models
Development of HR analytics models and metrics that align with the identified business objectives, such as employee turnover rate, productivity or financial metrics.
Step 6: Create HR dashboards
Creation of HR dashboards that display the HR metrics and analytics models in a user-friendly format that enables straightforward interpretation, decision-making and prediction with reasonable precision.
Step 7: Implement HR analytics
Implementation of HR analytics into daily HR operations and data-driven decision-making processes, such as recruitment, employee training & development, and succession planning.
Step 8: Evaluate and iterate
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of HR analytics implementation and make necessary adjustments to improve the accuracy and relevance of the HR analytics models and metrics.
Step 9: Train HR staff
Training of HR staff on how to use HR analytics to interpret the HR metrics and analytics models to help the management make informed HR decisions.
Step 10: Monitor outcomes
Monitor the outcomes of HR analytics implementation, such as improvements in employee engagement, productivity and retention, and adjust the HR analytics models and metrics as necessary for best outcomes.
Challenges and Best Practices in HR Analytics
Challenges and best practices in HR analytics can vary depending on the organisation, the available data, and the level of expertise in using analytics in HR processes.
Here are some common challenges and best practices to consider:
Challenges in HR Analytics:
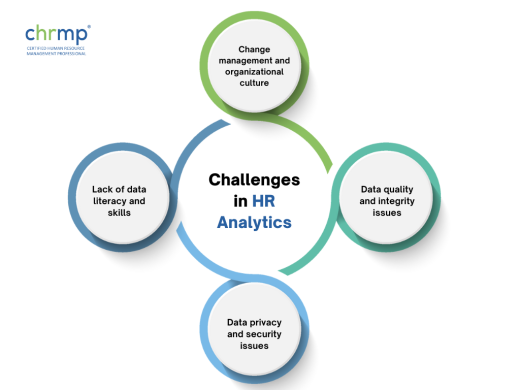
1. Data quality and integrity:
One of the major challenges in HR analytics is ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data. HR data can come from various sources, such as HRIS, employee surveys, and performance reviews, and may have issues like missing or inconsistent data, duplicate entries, or data entry errors. These data quality issues can affect the validity and reliability of HR analytics results, making it crucial to invest in data cleansing, validation, and integration efforts.
2. Lack of data literacy and skills:
Another challenge is the lack of data literacy and skills among HR professionals. HR teams may not have the necessary skills or expertise in data analysis, statistical techniques, and data visualisation to effectively analyse and interpret HR data. Bridging the gap in data literacy and skills through training and development initiatives can be key to ensuring that HR professionals can leverage HR analytics effectively.
3. Data privacy and security:
HR data often includes sensitive and confidential information, such as employee personal details, performance evaluations, and compensation data. Protecting the privacy and security of HR data is critical to comply with data protection regulations and maintain employee trust. HR analytics initiatives need to ensure that appropriate data privacy and security measures are in place, such as data encryption, access controls, and anonymisation techniques.
4. Change management and organizational culture:
Implementing HR analytics initiatives may require changes in HR processes, roles, and responsibilities, which can face resistance from HR teams and other stakeholders. Overcoming resistance to change and fostering a data-driven culture within the organisation can be a significant challenge. Change management strategies, including clear communication, stakeholder engagement, and training, can help mitigate these challenges.
Now that we have discussed the challenges in HR analytics, let’s look at some best practices to follow while implementing HR analytics in your organisation.
Best Practices in HR Analytics:
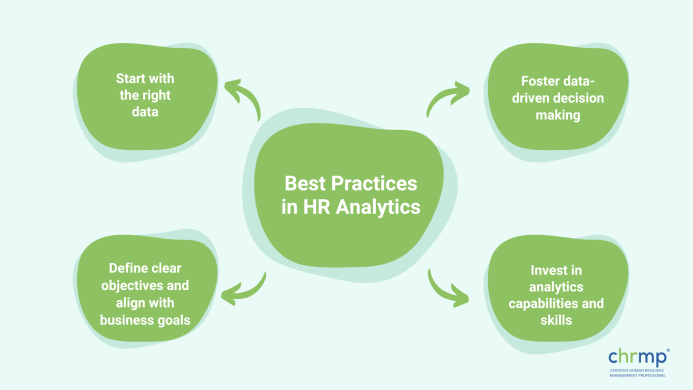
1. Define clear objectives and align with business goals:
Before embarking on HR analytics initiatives, it’s crucial to define clear objectives and align them with overall business goals. Understanding the specific HR challenges or opportunities that need to be addressed through analytics, setting measurable targets, and aligning HR analytics initiatives with broader business objectives can ensure that HR analytics efforts are focused and aligned with strategic priorities.
2. Start with the right data:
Having access to relevant and accurate data is crucial for effective HR analytics. Identifying the right data sources, ensuring data quality and integrity, and integrating data from multiple sources can provide a solid foundation for HR analytics. It’s essential to define data requirements, establish data governance practices, and invest in data management and integration tools to ensure the availability of clean and reliable data.
3. Foster data-driven decision making:
HR analytics should not be limited to just generating reports and insights but should also drive data-driven decision-making. Encouraging HR teams and decision-makers to use HR analytics insights in their decision-making processes can help create a culture of data-driven decision-making. This includes providing access to HR analytics findings, promoting data literacy, and embedding analytics into HR processes and workflows.
4. Invest in analytics capabilities and skills:
Building analytics capabilities and skills within the HR team is critical for successful HR analytics initiatives. Investing in training and development programs to enhance data literacy, statistical skills, and data visualisation skills can empower HR professionals to effectively analyse and interpret HR data. This can also involve hiring or partnering with data analysts or data scientists to support HR analytics efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What types of metrics and KPIs can HR analytics track for employee performance and engagement?
HR analytics can track various metrics and KPIs for employee performance and engagement, such as productivity, job satisfaction, employee net promoter score (NPS), and employee turnover rate.
2.How does predictive analytics help in workforce planning and talent development?
Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical models to predict future trends and behaviour patterns, such as workforce attrition rates and talent development needs. This helps organisations plan for workforce needs and develop employees accordingly.
3.How can HR information systems (HRIS) automate HR processes?
HRIS automates various HR processes, such as payroll, employee benefits, time and attendance, and employee record keeping, which reduces manual tasks and increases accuracy and efficiency.
4.What are the benefits of using data visualisation tools in HR analytics?
Data visualisation tools provide a user-friendly way to display HR metrics and KPIs using charts, graphs, and dashboards, which helps HR professionals quickly understand and communicate data insights.
5.How can benchmarking against industry standards and competitors help organisations improve their HR strategies?
Benchmarking against industry standards and competitors helps organisations identify areas of improvement and best practices, which can inform HR strategies and lead to better business outcomes and a competitive advantage in the market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HR analytics is a powerful tool that can provide organisations with valuable insights into their workforce and help management make informed and effective HR strategies which can be benchmarked against industry standards.
By using data analysis and metrics, organisations can improve decision-making, employee engagement, productivity, retention and talent management at the same time, reduce turnover.
The ten features of HR analytics – metrics and KPIs, predictive analytics, HR information systems, data visualisation tools, benchmarking, sentiment analysis, attrition analysis, diversity and inclusion metrics, employee engagement surveys, and real-time analytics – provide a comprehensive approach to utilising HR analytics to achieve these benefits.
Implementing HR analytics requires careful planning, effective data collection and analysis, and a commitment to using insights to help make informed decisions.
Ultimately, HR analytics can provide a competitive advantage in the market and drive enhanced customer experience and better business outcomes.







