

In today’s ever-changing industrial landscape, data is important for making informed decisions instead of intuitive ones. In this blog, we shall explore the differences between HR metrics and HR analytics and why they’re both crucial for effective HR management and, in turn, a company’s success.
With the rise of HR metrics and HR analytics, HR professionals now have better access to data that can help them better understand the workforce and drive organizational success to new heights.
So sit back, relax, and let’s dive into the exciting world of HR data analysis!
HR analytics is a powerful analytical tool used by HR professionals. It is the practice of using data analysis techniques and tools to extract insights and knowledge from HR data to support data-driven decision-making that is not intuitive in the human resources function.
HR analytics involves collecting, organizing, and analyzing large sets of employee-related data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that can be used to form HR strategies, policies and tactics.
This can include data on employee performance, workforce demographics, turnover rates, engagement levels, absenteeism, sabbaticals and more. By leveraging HR analytics, organizations can make data-driven decisions that optimize the workforce, improve overall business outcomes, and enhance employee experience.
HR analytics is essential for companies to make informed, data-driven decisions regarding their human resources function rather than depending upon intuition alone.
HR analytics can provide valuable insights into the workforce, including trends, patterns, and correlations that can help identify improvement areas and optimisation opportunities.
By leveraging HR analytics, organizations can:
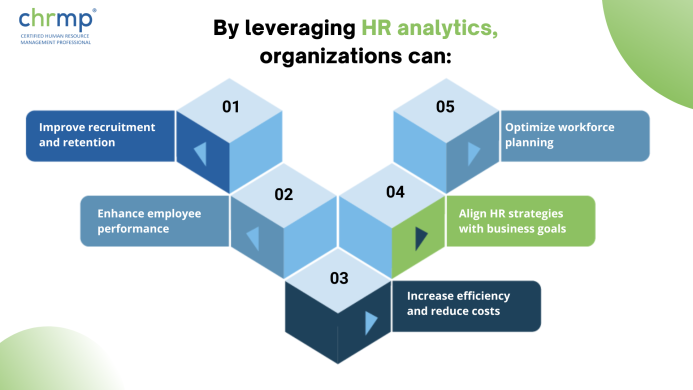
1.Improve recruitment and retention: HR analytics can help identify the sources of top talent and retention issues, enabling organizations to improve recruitment and retention strategies by curbing turnover rates.
2.Enhance employee performance: By analyzing employee performance data, organizations can identify areas where training and development programs are needed, improve welfare amenities, and offer competitive compensation specific to the industry, to enhance the overall employee experience.
3.Optimize workforce planning: HR analytics can provide insights into the workforce demographics and trends, patterns and correlations, helping organizations forecast future workforce needs and optimize workforce productivity.
4.Align HR strategies with business goals: By using HR analytics to identify the drivers of business success, organizations can align their HR goals, initiatives, drives and strategies with the overall goals of the organization.
5.Increase efficiency and reduce costs: HR analytics can help identify areas where HR processes can be streamlined or automated, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced costs to improve financial metrics like revenue and profits.
HR metrics are specific measurements used to track and evaluate various aspects of the human resources function. HR metrics are typically used to assess the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of HR processes and practices and to provide insights into workforce trends and patterns.
HR metrics include employee turnover rates, time-to-hire, training and development costs, absenteeism, skills gap and employee engagement levels.
By tracking and analyzing HR metrics, organizations can identify areas for improvement, make data-driven decisions, and ensure that HR initiatives, practices and drives are aligned with the business’s overall goals.
HR metrics are important for organizations to assess, measure and monitor specific aspects of their human resources function.
By measuring and tracking HR metrics, organizations can identify areas for improvement, make data-driven decisions, and ensure that their HR initiatives are aligned with their overall business goals.
Some key reasons why we need HR metrics are:
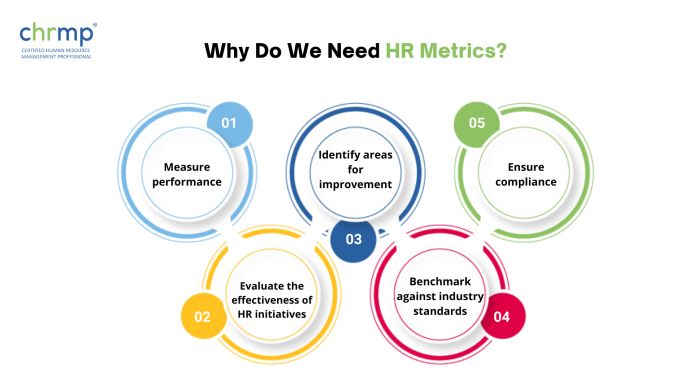
1.Measure performance: HR metrics provide a way to measure and assess the performance of specific HR processes and practices, such as recruitment, training, or employee engagement.
2.Identify areas for improvement: By tracking HR metrics, organizations can identify areas where they are underperforming and take action to improve their HR initiatives.
3.Ensure compliance: HR metrics can help organizations ensure that they are complying with relevant govt. and company laws, by-laws and regulations, such as those related to diversity and inclusion or equal pay.
4.Evaluate the effectiveness of HR initiatives: HR metrics provide a way to evaluate the effectiveness of HR initiatives and drives, such as training programs or performance management systems, and make data-driven decisions about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
5.Benchmark against industry standards: HR metrics enable organizations to benchmark their performance against industry standards and best practices, providing insight into how they compare with their peers and competitors.
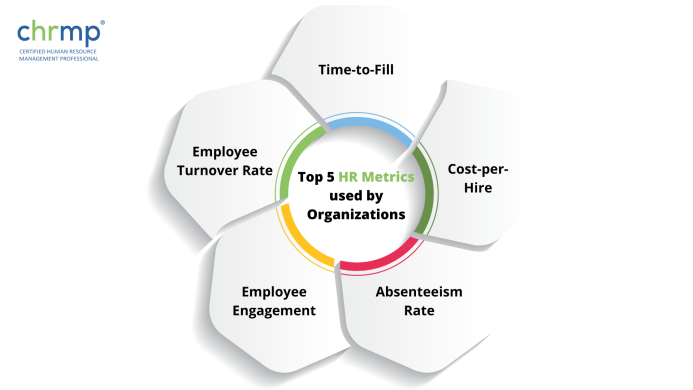
Here are 8 commonly used HR metrics that organizations use to measure the effectiveness of their HR practices:
The offer acceptance rate tracks the percentage of job offers extended to candidates that are accepted. This metric helps organizations evaluate the attractiveness of their compensation packages, workplace culture, and recruitment strategies. A low offer acceptance rate could indicate issues such as uncompetitive salary offers or misaligned job expectations. Improving this rate ensures that top talent joins the organization, contributing to its overall success.
Employee turnover rate measures how many employees leave an organization over a given period, typically expressed as a percentage of the total workforce. A high turnover rate can indicate problems with employee retention, job satisfaction, or other factors, while a low turnover rate may suggest a healthy and engaged workforce.
Time-to-fill is a metric that measures the length of time it takes to fill a vacant position, from the posting of the job opening to the offer of employment. This metric can help organizations evaluate their recruitment processes, identify improvement areas, and assess the impact of external factors such as the availability of qualified candidates.
Cost-per-hire is a metric that measures the total cost of recruiting and hiring a new employee, including advertising, recruitment fees, and other expenses. This metric can help organizations to evaluate the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their recruitment processes and identify areas where costs can be reduced.
The absenteeism rate is a measure of the percentage of employees who are absent from work on a given day or over a given period of time. High rates of absenteeism can indicate problems with employee morale, engagement, or workplace culture and can hurt productivity and organizational performance.
Employee engagement measures how committed and satisfied employees are with their work and the organization as a whole. This metric is typically measured through employee surveys or other feedback mechanisms and can provide valuable insights into areas where the organization can improve its HR practices and foster a more engaged and productive workforce.
Training effectiveness rate measures the impact of training programs on employee performance and productivity. This metric evaluates whether the learning objectives of a training program have been achieved and how well employees are able to apply new skills in their roles. It is typically measured through post-training assessments, employee feedback, and performance evaluations. A high training effectiveness rate indicates that the organization’s training initiatives are well-aligned with business goals, improving workforce capabilities.
Internal mobility rate measures the percentage of employees who move to new roles within the organization, whether through promotions, lateral moves, or cross-functional assignments. This metric reflects the organization’s commitment to employee development and career progression. A high internal mobility rate often indicates a strong culture of growth and retention, as well as effective talent management practices that keep top performers engaged.
HR metrics and HR analytics are both essential for effective HR management but are different in terms of their scope and focus, and application. Organizations have to use an integrated approach of HR metrics and analytics for effective workforce management using these parameters.
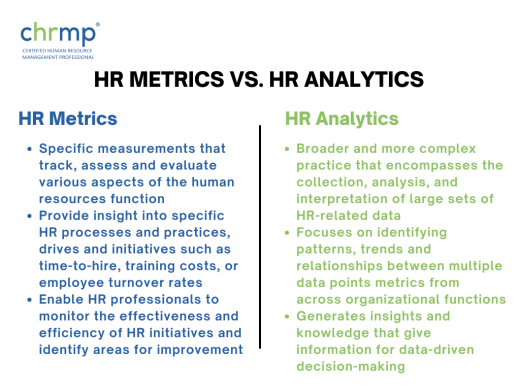
HR metrics are specific measurements that track, assess and evaluate various aspects of the human resources function. They provide insight into specific HR processes and practices, drives and initiatives such as time-to-hire, training costs, or employee turnover rates. HR metrics enable HR professionals to monitor the effectiveness and efficiency of HR initiatives and identify areas for improvement and implementation to drive the organization’s success to greater heights.
In contrast, HR analytics is a broader and more complex practice that encompasses the collection, analysis, and interpretation of large sets of HR-related data. HR analytics is not limited to specific metrics but instead focuses on identifying patterns, trends and relationships between multiple data points and multiple metrics from across the myriad functions of the organization.
The purpose of HR analytics is to generate insights and knowledge that give relevant information for strategic data-driven decision-making in the HR function. HR analytics can help organizations identify workforce trends, extrapolate and forecast future workforce needs, and develop data-driven HR strategies and practices doing away with intuitional decisions altogether.
In summary, HR metrics are specific measurements that track and evaluate the performance of individual HR processes. At the same time, HR analytics is a more comprehensive and integrated practice that encompasses data collection, data analysis and data interpretation to provide insights and provide relevant experience information for strategic decision-making in the HR function.
While HR metrics and HR Analytics are essential for effective HR management, HR analytics has a broader focus. It aims to provide a more holistic bird’s eye view of the organizational workforce.
HR metrics and HR analytics are closely intertwined and support each other in the field of Human Resources. Here’s how they are related:
HR metrics serve as the foundation for HR analytics. Metrics are specific measurements that help HR professionals track and assess various aspects of their workforce, such as employee turnover, recruitment effectiveness, training outcomes, performance evaluations, and more. These metrics provide valuable data points and benchmarks to evaluate the current state of HR practices within an organization.
HR analytics takes this data a step further by analyzing and interpreting the metrics to uncover meaningful insights. By applying statistical methods and data visualization techniques, HR analytics professionals can identify trends, patterns, and correlations within the metrics. This deeper analysis allows HR teams to gain valuable insights into the factors influencing HR outcomes and make data-driven decisions.
In essence, HR metrics provide the raw data, while HR analytics transforms that data into actionable insights. By leveraging HR analytics, organizations can better understand the drivers of their HR metrics, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions to optimize their human capital management practices.
HR metrics and analytics provide actionable insights to address diverse challenges across industries. Whether operational or strategic, they help organizations manage talent effectively, optimize processes, and bridge critical gaps. Below are practical examples showcasing how HR metrics and analytics are applied in real-world scenarios, demonstrating their value at various stages of the HR function.
A software company monitors the ratio of employees from underrepresented groups. This metric evaluates the effectiveness of diversity and inclusion initiatives and highlights areas for improvement in recruitment and retention.
A bank tracks the percentage of employees completing mandatory compliance training. This metric ensures readiness for audits and regulatory adherence while identifying gaps in employee participation.
A hotel chain evaluates the rate of internal promotions to measure career growth opportunities within the organization, reflecting on employee satisfaction and development programs.
A consulting firm tracks the percentage of job offers declined by candidates. High decline rates might indicate compensation mismatches or negative perceptions of the workplace culture.
A logistics company monitors the average overtime hours worked by drivers. High overtime can signal workforce shortages or inefficiencies in scheduling that need immediate attention.
An IT firm uses analytics to forecast employee turnover, identifying employees likely to leave based on trends like tenure, engagement scores, and performance data. This helps in designing retention strategies.
A construction company analyzes historical project data to forecast workforce needs for upcoming projects, optimizing labor allocation and reducing hiring delays.
A hospital analyzes the effect of upskilling programs on patient care quality and operational efficiency, linking training outcomes to improved performance metrics.
An online retailer evaluates the conversion rates at each stage of recruitment, identifying bottlenecks like low interview-to-offer ratios and addressing them to streamline hiring.
An automotive company analyzes employee compensation data against industry standards to ensure competitiveness, helping retain top talent and reduce poaching by competitors.
In conclusion, HR metrics and HR analytics are both valuable tools for managing and optimizing the human resources function of an organization.
HR metrics provide specific measurements to evaluate various aspects of the HR function, while HR analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of large sets of HR-related data to provide insights and inform strategic, data-driven decision-making so that it can be based on hard-core data and not intuition.
By using a more integrated approach of both HR metrics and HR analytics, organizations can improve recruitment and retention, enhance employee performance and engagement, optimize workforce planning, align HR strategies with business goals, and increase efficiency and reduce costs, turnover rates and absenteeism to push up financial metrics like revenue, sales and profits for the organization.
HR metrics and HR analytics have to be used in tandem to gain an in-depth insight into the organizational workforce and identify opportunities for improvement and implementation. With the right data and analysis, organizations can effectively manage their human resources and drive overall business success to greater heights.
1.What are the key differences between HR metrics and HR Analytics?
Answer: The key difference between HR metrics and HR Analytics is that HR metrics are specific measurements used to track and evaluate various aspects of the human resources function, while HR analytics is a more comprehensive practice that involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of large sets of HR-related data.
2.How are HR metrics and HR Analytics used differently in the human resources function?
Answer: HR metrics and HR Analytics are used quite differently in the human resources function. HR metrics are typically used to assess the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of HR processes and practices and to provide insights into workforce trends and patterns. In contrast, HR analytics generates insights and knowledge that can inform strategic decision-making in the HR function.
3.Can HR metrics be used as a part of HR analytics?
Answer: Yes, HR metrics and HR Analytics can be integrated. HR metrics provide specific data points that can be used in the broader practice of HR analytics to identify trends and correlations between multiple data points.
4.What is the scope of HR analytics compared to HR metrics?
Answer: The scope of HR analytics is broader than that of HR metrics. HR analytics involves the collection and analysis of large sets of HR-related data to provide insights and inform strategic decision-making, while HR metrics focus on specific measurements used to track and evaluate various aspects of the HR function.
5.Which one is more suitable for strategic decision-making, HR analytics or HR metrics?
Answer: HR analytics is more suitable for strategic decision-making than HR metrics. While HR metrics provide specific data points to assess performance and effectiveness, HR analytics can provide a more holistic view of the workforce, identifying trends and correlations that can inform strategic decision-making in the HR function.
© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited

Fill in the below details to get a CHRMP HR Analytics Program Plan.

One Response
Very useful information and and detailed explanation about HR metrics and HR analytics.