Defining the Human Resource Executive Role
An Human Resource Executive serves as a pivotal figure within an organization’s human resources department, orchestrating various functions that drive both employee satisfaction and organizational success. Their multifaceted role encompasses:
- Recruitment and Staffing: Recruitment and Staffing is a cornerstone of the HR executive’s role, and it involves a comprehensive process of identifying, attracting, and selecting top talent to meet organizational goals. This process begins by:
- Identifying Staffing Needs: Human Resource Executive assess the current workforce and organizational goals to pinpoint gaps in skills or staffing levels. This could involve working closely with department heads to understand project requirements, upcoming changes in the company, or areas requiring specialization. A clear understanding of workforce planning helps ensure that the right people are in the right positions at the right time.
- Crafting Job Descriptions: Once staffing needs are identified, Human Resource Executive collaborate with hiring managers to create clear, detailed job descriptions. These descriptions specify the key responsibilities, required qualifications, competencies, and skills for the role. A well-crafted job description ensures that the hiring process is aligned with the company’s expectations and attracts suitable candidates.
- Leading the Hiring Process: HR executives oversee the entire recruitment process, from creating recruitment campaigns to selecting and interviewing candidates. This includes using job boards, social media platforms, and recruitment agencies to attract a diverse pool of candidates. They also ensure that the hiring process is efficient, fair, and complies with labor laws and organizational policies. By managing this process effectively, Human Resource Executive not only attract the right talent but also help shape the future of the organization.
2. Performance Management: Performance management is a continuous process that enables organizations to measure and improve employee performance, ensuring that employees contribute meaningfully to the company’s goals.
- Implementing Appraisal Systems: One of the primary responsibilities of Human Resource Executive is to implement effective performance appraisal systems. These systems allow managers to evaluate employees’ job performance over a specific period, typically annually or semi-annually. The HR executive ensures that the system is structured to be objective, transparent, and aligned with company goals. They may choose between different appraisal methods, such as 360-degree feedback or self-assessments, depending on the organization’s culture and needs.
- Setting Performance Standards: HR executives collaborate with managers to define clear, measurable performance standards for each role. These standards often include both quantitative metrics (e.g., sales targets, productivity levels) and qualitative factors (e.g., teamwork, communication skills). These standards serve as benchmarks against which employee performance is evaluated. Ensuring that standards are both challenging and achievable is crucial to motivating employees and ensuring that their goals are in alignment with organizational objectives.
- Providing Feedback to Nurture Employee Development: Performance feedback is a crucial part of performance management. HR executives guide managers to provide constructive feedback to employees on a regular basis, not just during formal performance reviews. By doing so, employees can continuously improve and develop the necessary skills for their current role and future growth within the company. HR executives may also oversee coaching and mentoring programs to help employees address performance gaps and achieve professional development goals.
3. Training and Development: Training and development are key responsibilities that help employees enhance their skills, increase job satisfaction, and improve overall organizational performance.
- Assessing Training Requirements: HR Executives work closely with department heads and managers to evaluate the training needs of employees. This involves conducting skill gap analyses, reviewing performance data, and gathering feedback from employees and managers. Human Resource Executive must determine whether the organization’s training needs are technical (e.g., software proficiency), managerial (e.g., leadership training), or interpersonal (e.g., communication skills).
- Organizing Programs to Enhance Employee Skills and Competencies: Once the training requirements are identified, HR executives design or source appropriate training programs that align with the organization’s objectives. This could include in-house workshops, online learning, seminars, or external certification courses. These programs are strategically planned to build employees’ competencies and ensure that they are equipped to meet future challenges.
- Evaluating Training Effectiveness: Human Resource Executive must also assess whether the training programs are effective. This involves collecting feedback from participants, reviewing changes in performance post-training, and analyzing if the skills learned are being applied in day-to-day work. This evaluation process allows Human Resource Executive to refine training initiatives and ensure that the investment in employee development results in a measurable performance improvement.
4. Compliance Management: Compliance management is critical in maintaining a lawful and ethical working environment. Human Resource Executive are responsible for ensuring that the organization adheres to all applicable labor laws and regulations to avoid legal issues and penalties.
- Adherence to Labor Laws: HR Executives monitor and implement policies that ensure the organization is in compliance with local, regional, and international labor laws. This includes ensuring that workplace safety regulations, wage laws, anti-discrimination policies, and other legal obligations are met. HR executives must stay updated on changes in labor laws and promptly adjust policies to ensure compliance.
- Safeguarding the Organization from Legal Repercussions: By ensuring compliance, Human Resource Executive help protect the organization from potential legal disputes and financial losses related to wrongful termination, discrimination claims, or violations of wage and hour laws. This may involve conducting regular audits, working with legal teams, and providing training to managers and employees on legal requirements.
5. Employee Relations: Employee relations focuses on maintaining healthy relationships between employees and management, creating a positive, productive work environment.
- Addressing Grievances: Human Resource Executive play a vital role in addressing and resolving employee grievances. Whether the issues relate to job dissatisfaction, interpersonal conflicts, or perceived unfair treatment, HR executives act as mediators, listening to employees’ concerns and ensuring that they are resolved promptly and fairly. This role is crucial in maintaining employee trust and ensuring that issues do not escalate into larger problems.
- Mediating Conflicts: Conflict resolution is a key skill for HR executives. In cases of interpersonal conflict, Human Resource Executive facilitate discussions between employees or between employees and management to find a mutually agreeable solution. HR executives need to maintain neutrality and fairness to ensure that resolutions are balanced and in the best interest of both the individuals involved and the organization.
- Promoting Employee Engagement: Employee engagement is essential to maintaining a motivated and productive workforce. HR executives develop and implement initiatives to foster employee engagement, such as recognition programs, team-building activities, wellness programs, and regular surveys to gauge employee satisfaction. Engaged employees are more likely to be productive, loyal, and committed to the organization’s mission.
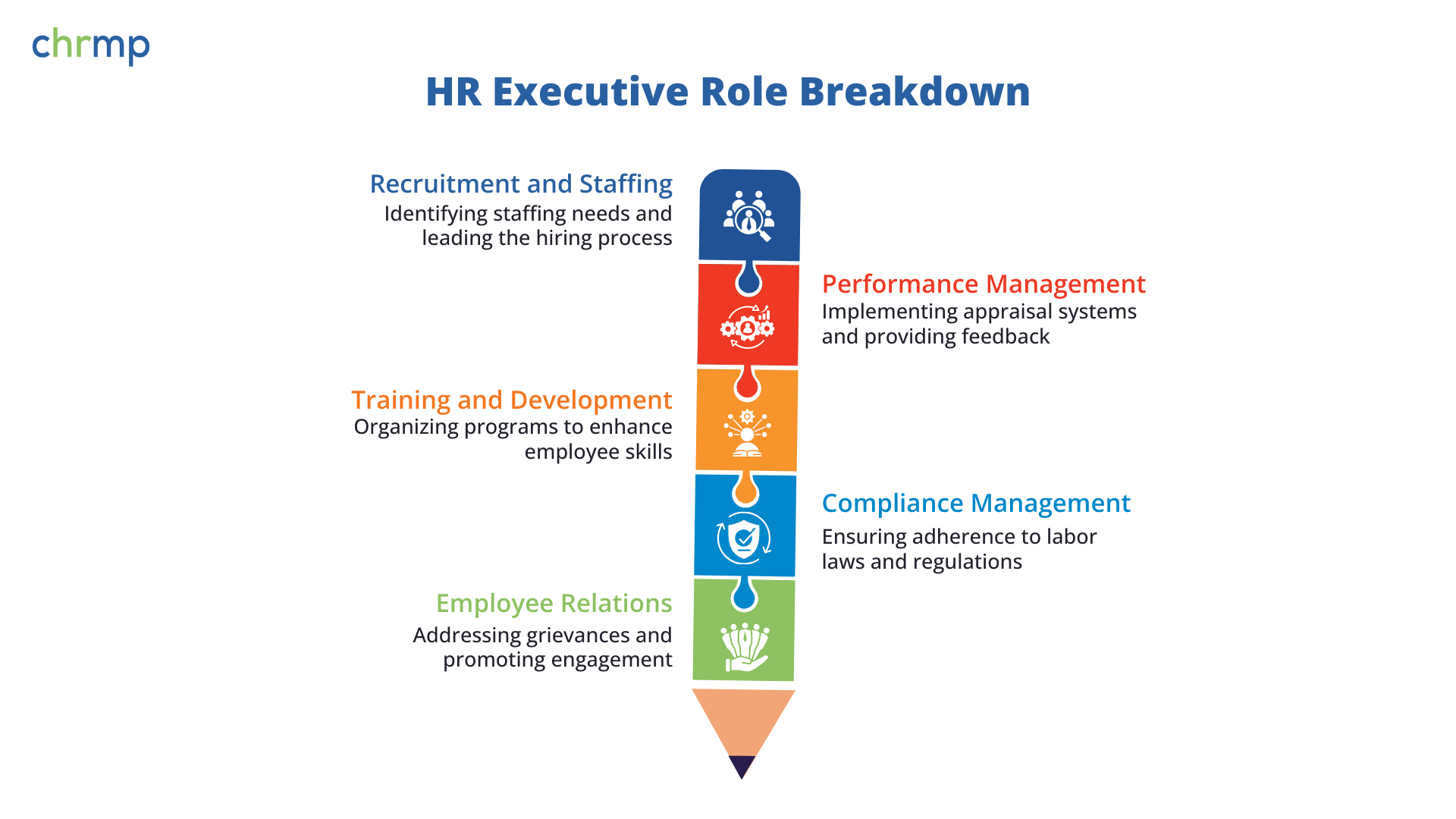
By adeptly managing these key responsibilities, HR Executives act as the linchpin connecting management and employees, ensuring that human resource strategies align seamlessly with organizational goals.
Also Read: Human Resources Assistant: Roles, Responsibilities, and Career Insights
Importance of Human Resource Executive in Organizational Structures
In the intricate tapestry of organizational structures, Human Resource Executive hold a strategic position that influences various facets of the business:
- Strategic Partner: Collaborating with senior leadership to develop and implement HR strategies that support business objectives.
- Change Agent: Leading organizational change initiatives, such as mergers or cultural transformations, to ensure smooth transitions.
- Employee Advocate: Championing employee needs and concerns, thereby enhancing job satisfaction and retention rates.
- Risk Manager: Identifying and mitigating risks related to employee relations and compliance issues.
For instance, during a company-wide restructuring, an HR Executive would play a crucial role in communicating changes, managing talent redeployment, and maintaining morale. Their involvement is instrumental in aligning the workforce with the new organizational vision, thereby ensuring continuity and productivity.
Differentiating HR Executives from Other HR Positions
Understanding the distinctions between various HR roles is essential for delineating responsibilities and optimizing departmental efficiency:
- HR Generalist: Engages in a broad spectrum of HR activities, including recruitment, benefits administration, and employee relations, often focusing on day-to-day operations.
- HR Manager: Oversees the HR department, develops policies, and aligns HR strategies with organizational goals, often with a focus on strategic planning.
- HR Specialist: Concentrates on a specific HR function, such as compensation and benefits, training, or recruitment, providing in-depth expertise in that area.
In contrast, an Human Resource Executive often operates at a higher strategic level, integrating various HR functions to ensure cohesive implementation of policies and initiatives. They may also have a more pronounced role in decision-making processes and in shaping organizational culture.
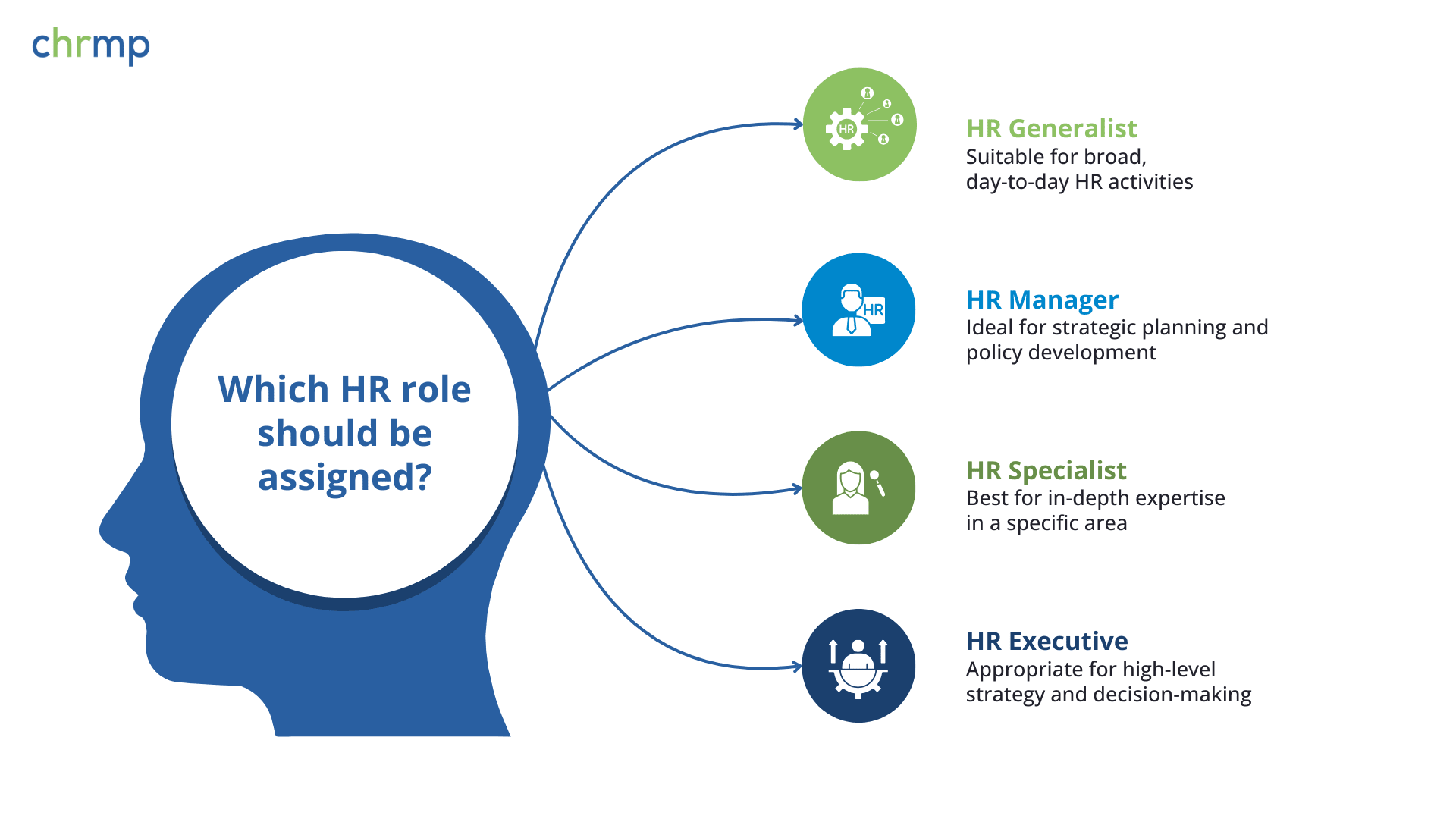
By comprehending these nuances, organizations can allocate resources effectively, ensuring that each HR role contributes optimally to the company’s success.
In summary, the HR Executive overview encapsulates a role that is both dynamic and integral to organizational prosperity. Through adept management of their key responsibilities, HR Executives not only enhance employee well-being but also drive strategic initiatives that underpin the organization’s competitive advantage.
Key Responsibilities of an Human Resource Executive
The role of an HR executive is multi-dimensional, and their HR executive responsibilities span across various critical functions that ensure the organization attracts, develops, and retains top talent while maintaining a smooth and efficient workplace. Below, we explore these responsibilities in greater detail, demonstrating how each aspect contributes to the organization’s success, along with relevant examples.
2.1. Talent Acquisition and Recruitment
One of the most essential Human Resource Executive responsibilities is overseeing the talent acquisition and recruitment process, which is fundamental to ensuring the organization has the right skills and competencies to achieve its goals.
- Strategic Workforce Planning: HR executives work closely with business leaders and department heads to understand the current and future needs of the organization. They analyze staffing levels, skill gaps, and growth forecasts, ensuring that recruitment efforts align with the company’s long-term vision.
- Sourcing and Attracting Candidates: HR executives are responsible for creating and executing sourcing strategies to attract top talent. This can include posting job advertisements, using recruitment platforms like LinkedIn, attending job fairs, and developing relationships with recruitment agencies. By leveraging digital platforms and social media, HR executives ensure that the organization reaches a broad pool of candidates from diverse backgrounds.
- Screening and Interviewing Candidates: Once candidates are sourced, HR executives are deeply involved in screening resumes, conducting initial interviews, and coordinating interview panels. They assess not only the qualifications and experience of candidates but also their cultural fit within the company. For example, an HR executive at a tech startup might place emphasis on hiring innovative, adaptable candidates who can thrive in a fast-paced, dynamic environment.
Selecting and Onboarding Candidates: Once the best candidates are identified, HR executives coordinate the selection process, extend offers, and facilitate the onboarding of new hires. Their role is crucial in ensuring that the hiring process is fair, efficient, and compliant with relevant hiring laws and company policies.
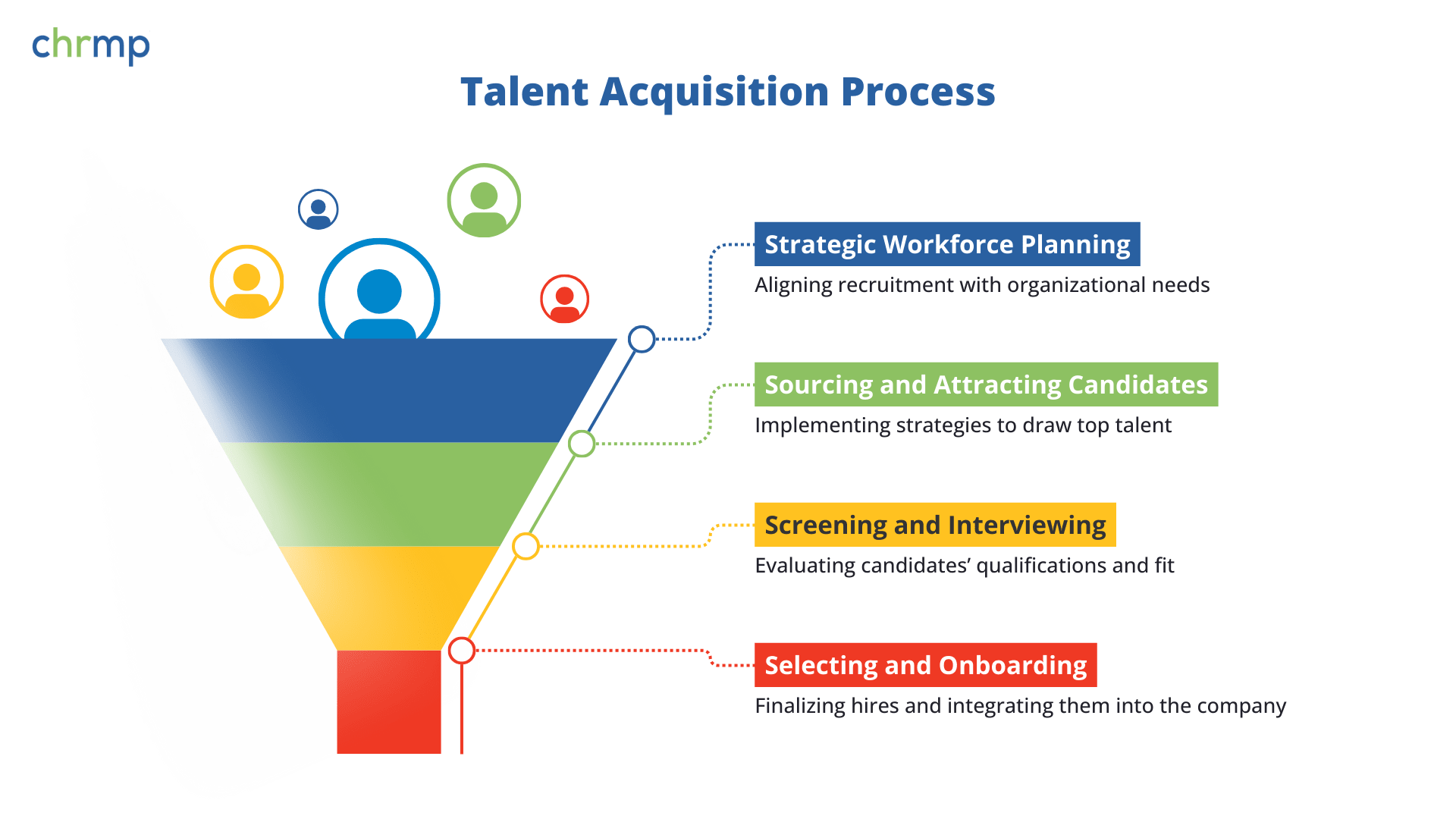
By managing HR functions in the recruitment process effectively, HR executives ensure that the organization attracts and selects the most qualified candidates, which directly contributes to overall business performance and growth.
2.2. Onboarding and Training of New Employees
Once a candidate has been hired, the next critical responsibility is to ensure that the new hire is successfully integrated into the organization. Onboarding and training of new employees are central to employee management, as they lay the foundation for a successful, long-term employee relationship.
- Onboarding Process: HR executives ensure that the onboarding process is smooth, welcoming, and structured. They prepare orientation programs to introduce new hires to the organization’s mission, values, culture, and policies. A thorough onboarding program can significantly improve employee retention, as new hires feel more engaged and aligned with the company’s vision from the start. For example, an HR executive at a large retail chain may introduce a comprehensive onboarding experience, including online training modules, in-person introductions, and mentorship programs to help new employees feel integrated into the team.
- Training Programs: HR executives assess the training needs of new hires based on their role and experience level. They collaborate with department managers to design tailored training programs that ensure employees are equipped with the necessary skills to succeed in their role. These training programs may include technical skills development, product knowledge, soft skills (e.g., communication, leadership), and compliance training (e.g., sexual harassment prevention, workplace safety). A well-executed training program not only improves productivity but also enhances job satisfaction and loyalty.
Continuous Development: In addition to initial training, HR executives are responsible for facilitating continuous learning and development opportunities for employees. This may involve organizing workshops, providing access to e-learning platforms, or encouraging employees to attend industry conferences. For example, HR executives in a financial services firm might offer specialized certifications or professional development courses to ensure employees remain competitive in the industry.
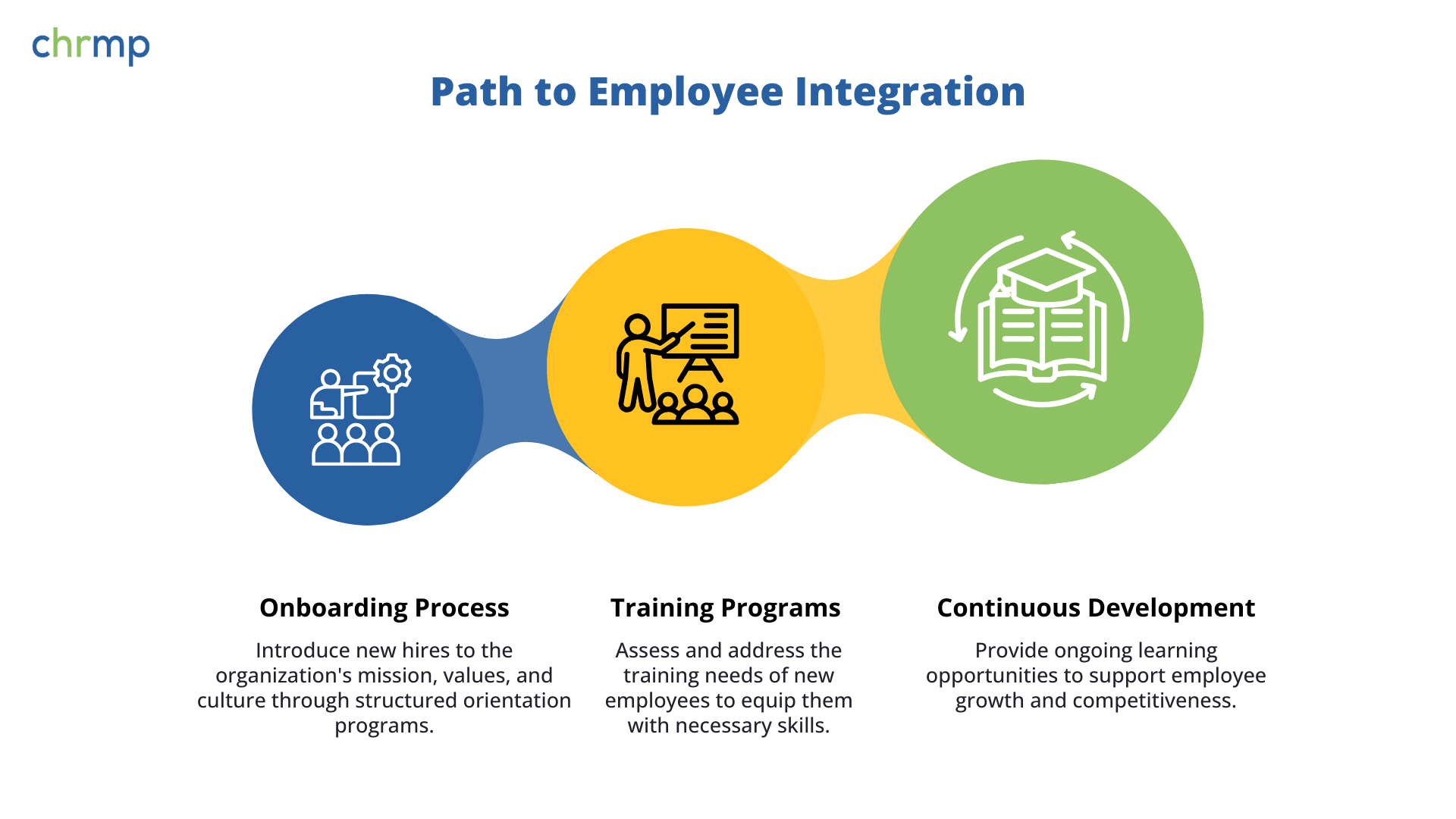
By executing these HR executive responsibilities, HR executives ensure that new hires are effectively onboarded and adequately trained, ultimately boosting productivity, reducing turnover, and fostering employee growth.
2.3. Managing Employee Relations and Conflict Resolution
Employee relations is an essential area of focus for HR executives, as maintaining a positive work environment is key to fostering high levels of employee engagement and productivity.
- Promoting Positive Employee Relations: Human Resource Executive are responsible for building and nurturing a positive relationship between employees and the organization. This includes implementing initiatives to promote a culture of respect, trust, and collaboration. HR executives regularly assess employee satisfaction through surveys, one-on-one meetings, and focus groups to identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Conflict Resolution: When conflicts arise between employees or between employees and management, HR executives play a pivotal role in resolving disputes. Whether it’s interpersonal conflicts, disagreements over job responsibilities, or issues related to performance, HR executives act as mediators to help parties find mutually agreeable solutions. For instance, an HR executive in a corporate setting might facilitate a conflict resolution workshop to teach employees effective communication and negotiation skills, which can help prevent conflicts from escalating.
Disciplinary Actions: In cases where conflicts cannot be resolved amicably, Human Resource Executive are responsible for administering disciplinary actions in accordance with company policies. This may involve issuing warnings, conducting investigations, or even initiating termination proceedings if necessary. For example, if an employee consistently violates company policies despite repeated warnings, the HR executive would follow the established procedure for addressing misconduct and taking corrective actions.

By effectively managing employee relations and resolving conflicts, Human Resource Executive create a harmonious work environment that enhances employee morale and retention, ultimately supporting the company’s long-term success.
2.4. Overseeing Payroll and Benefits Administration
Payroll and benefits administration is one of the most critical functions of Human Resource Executive, as it directly impacts employee satisfaction and retention.
- Payroll Management: HR executives ensure that employees are paid accurately and on time. This involves overseeing the payroll system, ensuring that salary structures are in line with industry standards, and managing deductions such as taxes, benefits contributions, and retirement plans. They must also handle overtime, bonuses, and commission calculations, ensuring full compliance with compensation policies and labor laws.
- Benefits Administration: In addition to managing compensation, HR executives are responsible for overseeing employee benefits programs, which may include health insurance, retirement plans, stock options, and wellness programs. HR executives collaborate with benefits providers to ensure that the company offers competitive and comprehensive benefits packages. For instance, an HR executive in a tech company might offer unique benefits such as flexible work hours or remote work options to attract top talent.
Compliance with Tax and Legal Requirements: HR executives ensure that the payroll process adheres to all legal requirements, including tax filings, benefits reporting, and compliance with labor laws such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Regular audits and checks are performed to avoid discrepancies or legal issues.
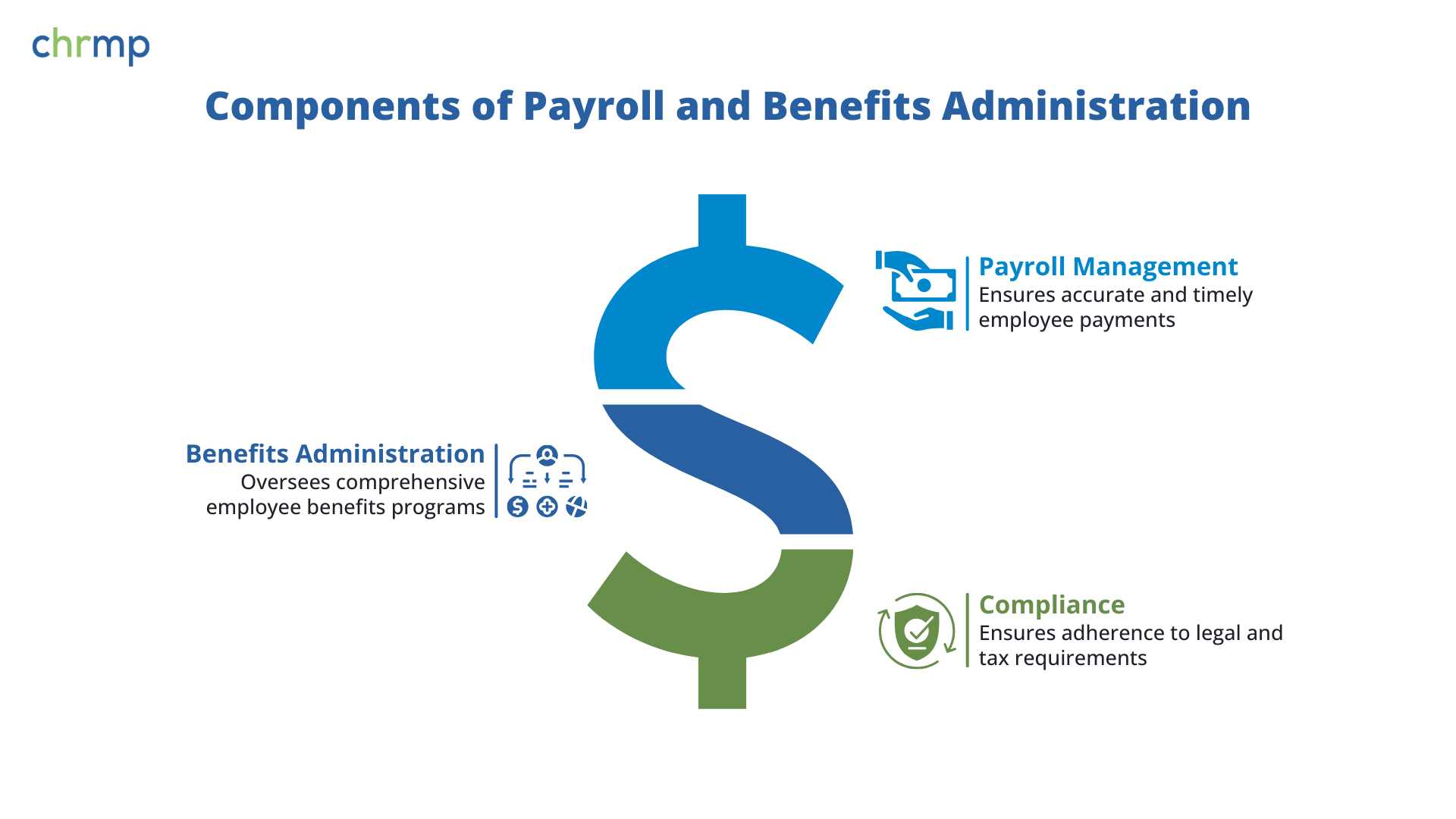
By managing payroll and benefits efficiently, HR executives contribute to employee satisfaction and retention, as employees are more likely to feel valued when they receive timely, accurate compensation and enjoy attractive benefits packages.
2.5. Ensuring Compliance with Labor Laws and Regulations
Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations is one of the most significant Human Resource Executive responsibilities, as non-compliance can lead to costly legal consequences, penalties, and reputational damage.
- Staying Updated on Legal Changes: HR executives must stay current with changes in local, state, and federal labor laws. They continuously monitor updates regarding wage laws, discrimination laws, safety regulations, and other employment-related matters. By doing so, HR executives ensure that the organization remains compliant and avoids legal risks.
- Developing and Implementing Policies: Based on the regulatory landscape, HR executives develop and implement policies and procedures that align with labor laws. This includes drafting anti-discrimination policies, creating employee leave policies, and ensuring that health and safety protocols meet legal standards. For example, HR executives in a manufacturing company must ensure that workplace safety regulations are strictly followed to prevent accidents and comply with OSHA standards.
- Training and Auditing: To further ensure compliance, HR executives conduct regular training for employees and managers on legal requirements and company policies. They also perform audits and internal checks to confirm that the organization’s practices are compliant with laws and regulations.

By maintaining robust compliance practices, HR executives protect the organization from legal and financial risks while promoting a fair, safe, and ethical work environment.
In conclusion, the HR executive responsibilities span a broad range of essential functions that directly impact the success of the organization. From talent acquisition to payroll administration and compliance management, HR executives play a central role in shaping the company’s workforce, fostering a positive work environment, and ensuring that the organization remains legally compliant and competitive in the market.
Also Read: The Role of Human Resource Management (HRM) in Organizations
Skills and Qualifications for an HR Executive
An HR executive’s role requires a broad range of qualifications, including educational credentials, technical expertise, and essential interpersonal skills. To ensure they can successfully navigate the complexities of HR functions, executives must possess specific HR executive skills and meet certain HR qualifications. Below are the critical skills and qualifications necessary for an HR executive to thrive.
3.1. Educational Requirements: Degrees and Certifications
An HR executive’s educational background lays the foundation for a successful career in HR management. While a variety of academic paths can lead to this career, the right degrees and certifications help boost credibility and demonstrate expertise in HR competency requirements.
- Degrees:
- A Bachelor’s degree in Human Resources, Business Administration, Psychology, or a related field is the starting point for most HR professionals. This degree equips HR executives with a solid understanding of business operations, management principles, and organizational dynamics.
- A Master’s degree in Human Resource Management (HRM), Organizational Development, or an MBA with an HR concentration is highly recommended for those aspiring to senior HR positions. These advanced degrees allow HR professionals to delve deeper into strategic planning, leadership development, and advanced HR functions, preparing them to lead complex projects and teams.
- Certifications:
- CHRMP Certifications: One of the most recognized certifications in the HR field is the Certified Human Resource Management Professional (CHRMP) certification, which offers an advanced understanding of HR best practices, laws, and leadership skills. The CHRMP program provides HR executives with specialized knowledge in core HR areas, such as recruitment, compensation management, performance management, and employee relations.
- Other CHRMP certifications include:
- CHRMP Executive: For experienced professionals who want to take their HR strategy, leadership, and governance skills to the next level.
- CHRMP Specialist Certifications: Focused certifications in areas such as HR Analytics, Talent Acquisition, and Learning & Development, helping HR executives specialize in specific HR functions and deepen their expertise.
- These certifications, along with any other relevant HR or leadership training, demonstrate a commitment to continued learning and mastery of essential HR functions, positioning executives as trusted experts within their organizations.
3.2. Core Skills: Communication, Organization, and Problem-Solving
To successfully execute HR executive responsibilities, a set of core skills is essential. Human Resource Executive need to interact with a wide range of individuals, from employees to top management, and navigate complex situations where problem-solving and clear communication are key.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is paramount for an Human Resource Executive, as they are constantly required to relay information, mediate discussions, and provide guidance. Whether speaking with an employee about performance issues, negotiating a labor contract, or presenting company policies, HR executives need to convey information clearly and persuasively. Strong written communication skills are also important when drafting policies, emails, or reports for management.
Example: An HR executive might communicate a company-wide policy change regarding remote work options, ensuring all employees understand the new guidelines and are equipped with the necessary resources to comply.
- Organizational Skills: HR executives manage a wide array of tasks, from recruitment and onboarding to compliance checks and employee development initiatives. Being highly organized is crucial to managing competing priorities effectively. Human Resource Executives often oversee complex schedules, multiple projects, and large volumes of information—hence, the ability to keep everything on track and well-documented is a key success factor.
Example: In a growing organization, an Human Resource Executive would be responsible for ensuring that recruitment efforts for multiple departments are running concurrently, managing onboarding schedules, and conducting performance reviews on time.
- Problem-Solving Skills: HR executives are frequently called upon to address and resolve employee issues, disputes, and challenges. The ability to think critically and come up with effective solutions is essential, particularly when faced with conflict or when policies need to be adapted to address unique situations. Whether dealing with a complicated performance management issue or resolving an employee grievance, the HR executive’s ability to analyze problems and implement solutions efficiently can significantly impact the organization’s success.
Example: In the case of an employee dispute over workplace harassment, an HR executive would investigate the situation, provide mediation, and ensure that a fair resolution is reached, aligning with company policies and legal guidelines.
3.3. Technical Skills: HR Software, Data Analytics, and Compliance Tools
In today’s data-driven world, Human Resource Executive must be proficient in a variety of technical tools and systems to manage HR functions efficiently. These skills allow HR executives to streamline operations, make data-informed decisions, and stay compliant with regulations.
- HR Software: HR executives are expected to manage and leverage various HR software systems (e.g., HRIS, applicant tracking systems, payroll software) to streamline recruitment, track performance, manage employee data, and oversee payroll. Familiarity with systems like Workday, ADP Workforce Now, or BambooHR is often essential in managing daily operations. A strong command of HR software helps HR executives save time and ensure smooth operations across all HR activities.
- Data Analytics: HR executives use data analytics to make informed decisions about employee performance, recruitment trends, and compensation strategies. By leveraging data, they can identify patterns, forecast workforce needs, and evaluate the effectiveness of HR programs. For example, an HR executive might use analytics to determine which recruitment channels yield the highest-quality candidates or analyze employee turnover data to identify and address retention challenges.
- Compliance Tools: Compliance with labor laws and regulations is a fundamental part of an HR executive’s role. Human Resource Executive must stay informed about evolving laws and regulations while ensuring that the organization’s policies are compliant. Utilizing tools that help manage legal compliance—such as compliance management software—ensures that the organization avoids legal risks and maintains a healthy workplace.
3.4. Key Attributes: Empathy, Confidentiality, and Leadership
Beyond technical skills, HR executives need to embody certain personal attributes that help them excel in their role. These attributes are essential for building trust, fostering a positive organizational culture, and effectively managing people.
- Empathy: Empathy is one of the most critical qualities for an Human Resource Executive, as they regularly deal with employees’ personal and professional concerns. Being able to understand and respond to the emotions and needs of others builds trust and rapport, making it easier to resolve conflicts and address employee issues. Empathetic HR executives can foster an environment where employees feel supported and valued.
Example: An HR executive who listens to an employee’s concerns about work-life balance and takes proactive steps to offer flexible working arrangements demonstrates empathy in action.
- Confidentiality: HR executives handle sensitive information on a daily basis, including employee personal data, performance reviews, and confidential business strategies. Maintaining strict confidentiality is paramount to protect both the individual and the organization. Breaches in confidentiality can result in legal consequences and damage employee trust.
Example: When conducting a sensitive investigation regarding workplace misconduct, an Human Resource Executive must ensure that all parties involved feel safe knowing their personal details are protected throughout the process.
Leadership: Human Resource Executive are leaders who guide their teams, manage complex situations, and make strategic decisions that impact the entire organization. Leadership skills enable HR executives to inspire their teams, make tough decisions, and drive HR initiatives that align with business objectives. Strong leadership fosters a positive organizational culture and ensures the effective implementation of HR strategies.
Example: In times of organizational change, an HR executive must lead the way by communicating the changes, motivating employees, and ensuring smooth transitions.
In conclusion, the HR executive skills and HR qualifications required to excel in this role are vast and varied. From possessing the right educational background and certifications to demonstrating core competencies such as communication and leadership, Human Resource Executive play an integral role in the success of an organization. With their ability to manage HR functions effectively, foster positive employee relations, and lead strategic initiatives, HR executives are key drivers of organizational growth and success.
Challenges Faced by HR Executives
As strategic leaders within an organization, HR executives face numerous HR challenges in managing both the workforce and organizational growth. These challenges require a combination of innovative thinking, adaptability, and robust problem-solving skills to ensure that HR functions remain aligned with company goals while addressing evolving employee needs. Below, we explore the key workplace dynamics and challenges that Human Resource Executive commonly face, along with how they navigate these challenges.
4.1. Balancing Employee Needs with Organizational Goals
One of the most critical HR challenges is balancing the needs and expectations of employees with the overarching goals of the organization. Employees want competitive salaries, professional development, work-life balance, and job satisfaction, while organizations are focused on profitability, productivity, and long-term sustainability.
- Employee Needs: HR executives must ensure that employees are motivated, engaged, and feel supported in their roles. This involves offering benefits like healthcare, wellness programs, and professional development opportunities. Additionally, HR must ensure that employees have clear career paths and the resources they need to perform at their best.
- Organizational Goals: On the other hand, Human Resource Executive must ensure that these employee needs are balanced with organizational objectives. This might include ensuring that employees align with the company’s vision, maintaining operational efficiency, and driving performance in line with strategic goals.
- Problem-Solving: Navigating this balance often requires creative problem-solving. For instance, if an organization needs to cut costs but still wants to retain top talent, an HR executive might explore non-monetary incentives like flexible work hours or additional vacation days to keep morale high. Striking a balance between employee satisfaction and organizational performance is a constant challenge, but when done right, it leads to a productive and harmonious work environment.
4.2. Adapting to Changing Workplace Trends
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, HR executives must remain agile in adapting to new workplace dynamics and trends. The nature of work is continuously changing, from technological advancements to new employee expectations and societal shifts.
- Technological Advancements: HR executives must stay updated on new tools, platforms, and systems that can improve HR functions, from talent management to payroll and compliance. Automation and AI tools are becoming more prevalent in recruitment, employee management, and data analytics. This means Human Resource Executive need to integrate these technologies while ensuring a smooth transition and buy-in from employees.
- Employee Expectations: Today’s employees, especially younger generations, place more emphasis on work-life balance, purpose-driven work, and opportunities for continuous learning. HR executives need to anticipate and address these shifting priorities. For example, offering flexible work arrangements or remote work options has become crucial for attracting and retaining top talent.
- HR Problem-Solving: In this ever-changing environment, HR executives need to be strategic, continuously seeking ways to foster innovation and implement progressive policies. For example, HR may invest in new HR software to manage employee performance, track data more effectively, and ensure a seamless experience for remote teams.
Adapting to these workplace dynamics and evolving trends requires HR executives to be forward-thinking, flexible, and proactive in implementing changes that align with both current and future organizational needs.
4.3. Managing Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Challenges
As diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) continue to be at the forefront of organizational priorities, HR executives must lead the charge in ensuring that their organizations not only attract a diverse workforce but also foster an inclusive environment that promotes equity for all employees.
- Diversity in Hiring: Ensuring diversity in recruitment is one of the primary HR challenges. Human Resource Executive must actively promote diversity by ensuring that hiring practices are unbiased, implementing diverse recruitment strategies, and working with external agencies to attract underrepresented talent. For instance, an HR executive might work with universities or community organizations to attract candidates from diverse backgrounds, ensuring that the company has a robust talent pipeline.
- Equity in Advancement: Beyond hiring, HR executives need to ensure that all employees have equal opportunities for growth and advancement. This requires monitoring promotions, pay equity, and professional development opportunities to ensure fairness. HR executives may need to implement programs that specifically focus on mentorship for underrepresented groups, ensuring that everyone has the tools they need to succeed in their careers.
- Creating an Inclusive Culture: Inclusion is about ensuring that all employees feel valued and respected. Human Resource Executive must address potential bias in the workplace, implement inclusion training programs, and foster a company culture that encourages openness and acceptance. This might involve creating employee resource groups (ERGs) for various identities and hosting company-wide DEI events.
- Problem-Solving in DEI: HR executives often face the challenge of creating meaningful change in this area. For example, if an organization struggles with gender diversity in leadership roles, an Human Resource Executive might develop mentorship and sponsorship programs specifically targeted at supporting women’s professional growth.
Managing DEI effectively is crucial not just for compliance but for creating a positive workplace culture that attracts diverse talent and ensures every employee has an equal opportunity to thrive.
4.4. Navigating Remote Work and Hybrid Models
The rise of remote and hybrid work models, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has presented HR executives with both unique challenges and opportunities. Managing a workforce that may be spread across various locations requires new strategies, tools, and HR practices.
- Managing Remote Teams: HR executives must adapt traditional management strategies to effectively manage remote teams. This includes ensuring that communication remains strong, performance is tracked, and employees feel connected despite working from home. Human Resource Executive often need to implement new tools for communication, collaboration, and project management to ensure that teams remain productive and engaged.
- Hybrid Work Models: Many companies are transitioning to hybrid models, where employees split time between working from the office and remotely. HR executives must navigate this shift by ensuring that hybrid work policies are clear, employees have the necessary resources to work effectively in both environments, and that team dynamics are not disrupted by the blend of in-person and remote work.
- HR Problem-Solving: HR executives face the challenge of maintaining a unified company culture and high employee morale when workers are not physically present in the office. They may need to create virtual team-building activities, establish clear expectations for remote work, and provide technology support to ensure that employees can work efficiently from home.
- Work-Life Balance in Remote Work: Another major challenge is managing work-life balance in a remote or hybrid environment. Without clear boundaries between work and home, employees may struggle with burnout. HR executives must provide resources to help employees manage their time effectively and ensure that the company culture remains supportive, no matter where employees work.
Navigating remote work and hybrid models involves rethinking old HR practices and developing new ones that are suited for flexible work environments. It requires HR executives to continually assess how these models impact employee engagement, collaboration, and productivity.
In conclusion, HR executives are at the forefront of addressing HR challenges that arise from constantly evolving workplace dynamics. From managing shifting employee expectations and maintaining a diverse, inclusive environment to adapting to new work models and navigating the complexities of DEI, HR executives are critical problem-solvers who drive positive change. By addressing these challenges head-on, HR executives help their organizations stay competitive, resilient, and aligned with both their workforce’s needs and broader business goals.
Tools and Resources for HR Executives
In the ever-evolving landscape of human resource management, HR tools and HR resources are critical for HR executives to streamline processes, manage workforce data, and support decision-making. With the advent of new technology and advancements in HR practices, HR executives need to be well-versed in using various tools and platforms to optimize HR functions. This section delves into the essential tools, resources, and platforms that empower HR executives to perform their roles more effectively.
5.1. Popular HR Tools for Streamlining Processes (HRIS, ATS)
To keep HR functions running efficiently, HR executives rely on HR tools that help automate and streamline a variety of tasks, from recruiting to performance management. Two of the most important HR tools are HRIS systems and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), both of which can significantly enhance HR operations.
- HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems): HRIS systems are essential for managing employee data, tracking performance, and handling payroll. These systems enable HR executives to maintain a centralized database where they can store important information like employee records, benefits details, attendance, and performance metrics. Well-known HRIS systems like Workday, ADP Workforce Now, and BambooHR offer easy-to-use platforms that simplify administrative tasks, ensuring HR executives can focus on strategic initiatives.
- Benefits of HRIS:
- Centralized database for all employee data.
- Streamlined payroll processing and compliance tracking.
- Real-time reporting and analytics for data-driven decision-making.
- Improved employee self-service for personal information updates.
- ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems): An ATS is crucial for HR executives in recruitment management. It allows for the efficient tracking of applicants through the hiring process, from initial application to the final offer. Tools like Greenhouse, Lever, and iCIMS help HR executives manage job postings, screen resumes, schedule interviews, and communicate with candidates more effectively.
- Benefits of ATS:
- Faster recruitment process with automated resume screening.
- Improved collaboration among hiring managers.
- Reduced time-to-hire and better candidate experience.
- Enhanced reporting on recruitment metrics, such as sourcing channels and candidate pipeline stages.
Both HRIS and ATS help HR executives save time, reduce errors, and improve efficiency in managing critical HR functions.
5.2. Recommended HR Certifications for Executives
HR executives must stay at the forefront of HR trends, best practices, and legal requirements to maintain their credibility and improve organizational performance. One way to ensure this is through professional certifications that deepen their expertise and expand their knowledge base.
- CHRMP (Certified Human Resource Management Professional): The CHRMP certification is one of the most recognized qualifications for HR professionals and HR executives. It offers comprehensive training on key HR concepts, including recruitment, performance management, employee relations, and compliance. The CHRMP Foundation certification is specifically designed for Human Resource Executive who wish to deepen their strategic HR leadership capabilities. This certification equips HR leaders with the skills required to align HR strategies with business goals and drive organizational success.
- HRCI Certifications (PHR, SPHR): The PHR (Professional in Human Resources) and SPHR (Senior Professional in Human Resources) certifications from the Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI) are also widely respected. The PHR is suitable for HR professionals looking to develop their foundational HR knowledge, while the SPHR is targeted at senior HR executives who manage organizational strategy and leadership.
- Specialized Certifications: For HR executives looking to specialize further, certifications in areas such as HR Analytics, Labor Relations, and Compensation & Benefits can be valuable. Specializations help HR leaders provide more in-depth knowledge and strategies in specific areas of HR, which can be crucial for organizations looking for expertise in these fields.
By earning these HR certifications, HR executives demonstrate their ongoing commitment to professional growth and leadership excellence, thereby enhancing their ability to drive success within the organization.
5.3. HR Learning Platforms and Communities for Continuous Growth
Continuous learning is crucial for HR executives to stay relevant and effective in their roles. Thankfully, a wealth of HR resources and HR learning platforms are available to help HR professionals enhance their skills, share insights, and stay updated on emerging trends.
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like LinkedIn Learning, Coursera, and Udemy offer HR executives a vast library of courses covering HR topics such as leadership, talent acquisition, diversity and inclusion, and HR technology. These platforms provide flexibility in learning, allowing HR professionals to upskill at their own pace while gaining new knowledge from industry experts.
- HR Webinars and Virtual Conferences: Participating in webinars and virtual conferences is another excellent way for HR executives to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices. HR conferences such as HR Tech Conference and CIPD Annual Conference offer networking opportunities with industry leaders and hands-on workshops that address key HR challenges and innovations.
- HR Communities and Networks: Joining HR communities such as HR.com, Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), or HR Exchange Network can provide HR executives with valuable insights, discussion forums, and networking opportunities. These communities allow HR professionals to exchange ideas, share solutions to common HR challenges, and learn from one another’s experiences.
- Specialized HR Blogs and Journals: Reading HR blogs, research journals, and articles from reputable sources like Harvard Business Review, HR Magazine, and TLNT offers HR executives the latest thought leadership on leadership, talent management, organizational culture, and emerging HR technologies.
By regularly engaging with HR learning platforms and communities, HR executives can ensure that they are not only keeping their skills up-to-date but also embracing new trends, methodologies, and tools to remain effective and influential in their roles.
In conclusion, the HR tools, HR resources, and HRIS systems available today provide HR executives with powerful platforms to optimize processes, enhance decision-making, and stay ahead of industry trends. From utilizing technology like HRIS and ATS to pursuing continuous professional development through certifications and learning platforms, HR executives are equipped with the necessary resources to drive organizational success and foster a high-performing, compliant workforce.
Conclusion | Human Resource Executive
In conclusion, the role of an Human Resource Executive is indispensable in shaping organizational success. With their strategic involvement in advancing HR roles, HR executives not only manage day-to-day operations but also drive long-term organizational growth. Their Human Resource Executive impact extends across recruitment, performance management, employee relations, and compliance, aligning workforce strategies with business goals. By managing people effectively, fostering positive work environments, and ensuring legal compliance, HR executives help organizations thrive in an increasingly competitive and complex business landscape.
For aspiring HR professionals, the path to becoming an Human Resource Executive offers an exciting and dynamic career. As organizations continue to recognize the value of strategic HR, the demand for skilled HR leaders grows. Those who embrace the challenge of advancing HR practices and navigating organizational change can look forward to a fulfilling career that not only impacts business outcomes but also enhances employee experiences. For anyone passionate about making a tangible difference in the workplace, pursuing a career as an HR executive is a rewarding and impactful choice.
Human Resource Executive FAQs
1. What is the role of an HR executive?
An HR executive plays a crucial leadership role in managing an organization’s human resources. They oversee all aspects of human resource management, including recruitment, performance management, employee relations, compliance, and training. They ensure that HR strategies align with organizational goals, fostering a positive work culture while ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. HR executives also contribute to shaping long-term workforce strategies, enhancing employee engagement, and driving talent development within the organization.
2. What are the key responsibilities of an HR executive?
The key responsibilities of an HR executive include:
- Recruitment and Staffing: Identifying hiring needs and overseeing the recruitment process to attract top talent.
- Performance Management: Implementing performance appraisal systems and ensuring employees meet organizational goals.
- Employee Relations: Addressing employee concerns, mediating conflicts, and ensuring workplace harmony.
- Training and Development: Identifying training needs and providing opportunities for employee skill enhancement.
- Compliance: Ensuring adherence to labor laws and organizational policies.
- Compensation and Benefits: Managing payroll, bonuses, and other benefits for employees.
3. What qualifications are needed to become an Human Resource Executive?
To become an HR executive, individuals typically need a Bachelor’s degree in human resources, business administration, or a related field. A Master’s degree in Human Resource Management (HRM), Business Administration (MBA), or Organizational Development is often preferred. Additionally, professional certifications such as CHRMP (Certified Human Resource Management Professional), HRCI’s PHR (Professional in Human Resources), or SPHR (Senior Professional in Human Resources) can enhance an HR executive’s qualifications and credibility in the field.
4. How does an HR executive contribute to organizational growth?
An HR executive directly influences organizational growth by ensuring that the company attracts and retains top talent, drives employee productivity, and maintains a positive work culture. By managing recruitment, training, and development, HR executives help build a skilled workforce that can drive innovation and performance. They also create strategies that support employee engagement and align HR practices with business objectives, contributing to the company’s long-term success.
5. What skills are essential for Human Resource Executive to succeed?
Essential skills for HR executives include:
- Communication: Strong verbal and written communication to effectively interact with employees, management, and external stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: The ability to resolve conflicts and address workplace issues.
- Leadership: The capability to inspire and lead teams, fostering collaboration and guiding HR strategy.
- Organization: Managing multiple tasks, deadlines, and HR projects simultaneously.
- Analytical Skills: Leveraging data and analytics for decision-making, particularly in areas like employee performance and recruitment.
6. What challenges do HR executives typically face in their role?
HR executives face several challenges, including:
- Balancing employee needs with organizational goals: Aligning employee satisfaction with the company’s long-term objectives.
- Adapting to changing workplace trends: Keeping up with remote work, hybrid models, and evolving employee expectations.
- Managing diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI): Ensuring fair and inclusive hiring practices while fostering an equitable work environment.
- Navigating legal and compliance issues: Staying updated with ever-changing labor laws and ensuring the organization’s policies comply with regulations.
7. How can HR executives advance in their careers?
HR executives can advance their careers by gaining additional experience in strategic HR functions, such as talent management, organizational development, and leadership. Pursuing advanced certifications (e.g., CHRMP Executive) and Master’s degrees in HRM or Business Administration will help them further develop leadership skills. Additionally, networking with other HR professionals and engaging in industry-specific training can help executives stay updated with trends and gain new opportunities for growth.
8. What tools and software do Human Resource Executive commonly use?
HR executives commonly use several tools and software to manage HR processes, including:
- HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems) like Workday, BambooHR, and ADP Workforce Now for managing employee data, payroll, and benefits.
- ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems) like Greenhouse and Lever to streamline recruitment and track applicants.
- Performance management software like Lattice or 15Five to evaluate and track employee performance.
- Compliance and analytics tools like Zenefits to ensure legal compliance and gain insights from HR data.
9. How does an HR executive handle compliance and legal issues?
HR executives handle compliance and legal issues by staying informed about labor laws, regulations, and workplace safety standards. They ensure the company adheres to federal and state employment laws related to wage and hour laws, anti-discrimination policies, and workplace safety. HR executives also develop and enforce policies that protect both the company and employees. Regular audits, employee training on legal issues, and working closely with legal counsel are also key actions to maintain compliance.
10. Are there certifications that can help Human Resource Executive grow professionally?
Yes, there are several certifications that can help HR executives grow professionally, including:
- CHRMP (Certified Human Resource Management Professional) for comprehensive HR training and certification.
- HRCI Certifications (PHR, SPHR): These certifications provide in-depth knowledge of HR policies and practices, enhancing an executive’s ability to manage HR functions.
- Specialized certifications in HR Analytics, Diversity & Inclusion, or Labor Relations can help HR executives gain expertise in niche areas, improving their strategic value to the organization.










