Recruiting metrics are essential tools for HR professionals and hiring managers, offering valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of recruitment processes. These metrics help organizations optimize their hiring strategies, enhance candidate experiences, and improve overall business performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what recruiting metrics are, why they are important for HR and recruitment, and provide detailed explanations of the top 22 metrics, including how to measure them, the data required, their impact on the organization, and best practices.
What Are Recruiting Metrics and Their Importance?
Recruiting metrics are quantitative measurements used to evaluate various aspects of the hiring process. They provide data-driven insights into the efficiency, effectiveness, and quality of recruitment activities. Metrics can cover a range of areas, including time to hire, cost per hire, candidate experience, and the quality of new hires. For HR professionals, these metrics are invaluable for making informed decisions, identifying areas for improvement, and demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of recruitment efforts.
In the field of recruitment, metrics play a crucial role in helping organizations understand and optimize their talent acquisition processes. By tracking and analyzing these metrics, companies can ensure that their recruitment strategies align with business objectives, improve candidate experiences, and ultimately attract and retain top talent. Metrics also provide a basis for benchmarking against industry standards and competitors, enabling continuous improvement and strategic planning.
Top 22 Recruiting Metrics: Definitions, Measurements, and Best Practice:
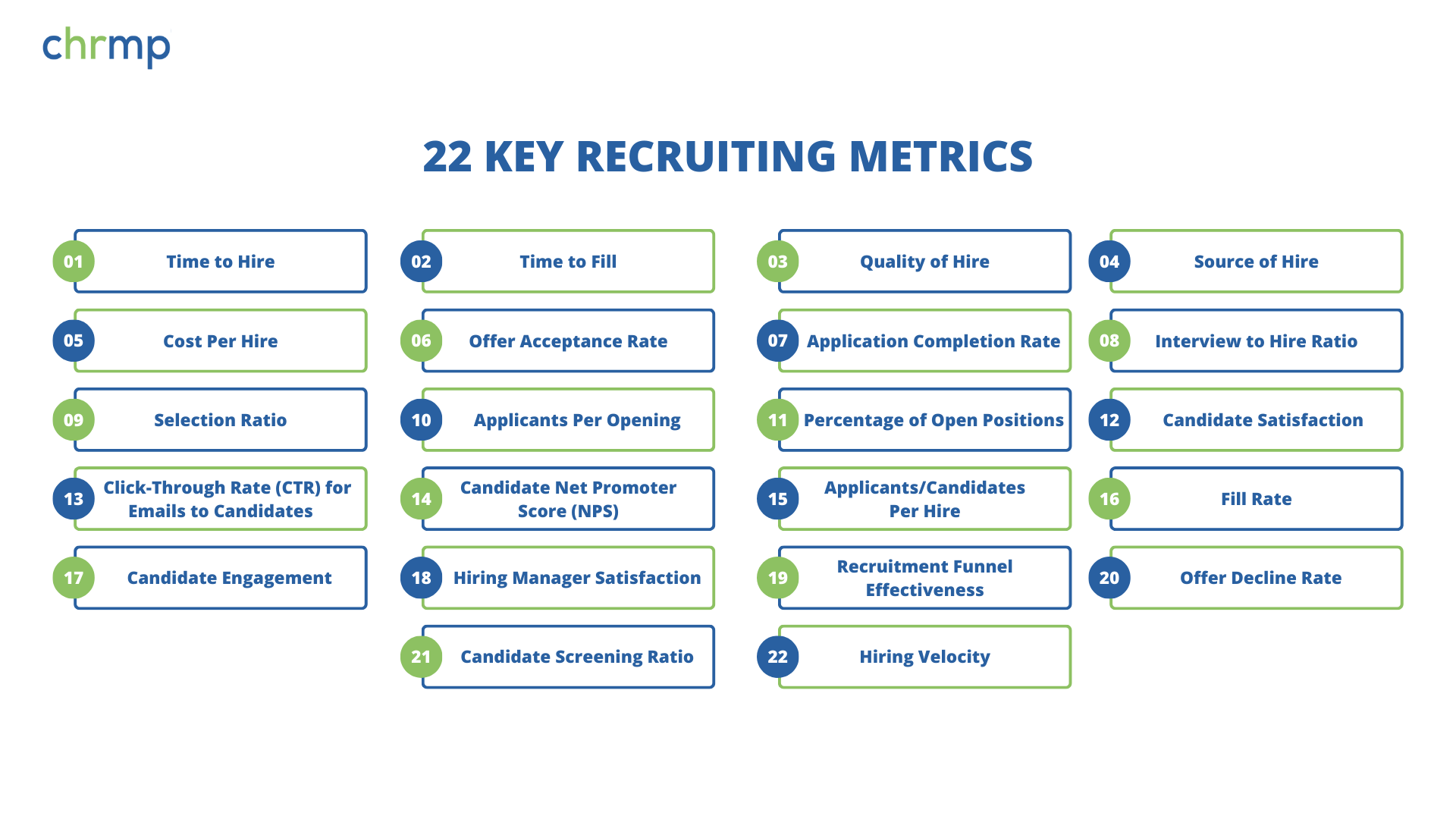
1. Time to Hire
- Definition: Time to hire measures the number of days from when a candidate enters the recruitment pipeline until they accept the job offer. This metric focuses on the efficiency of the recruitment process after the candidate has been engaged.
- Formula for Calculating: Time to Hire= Date of Offer Acceptance−Date Candidate Entered Pipeline Data Required:
- Date when the candidate was first engaged (e.g., application date, date sourced)
- Date when the candidate accepted the job offer
- Impact on Organization: Time to hire affects the speed and efficiency of the recruitment process. A shorter time to hire means the company can fill positions quickly, minimizing disruptions and maintaining productivity. Conversely, a longer time to hire can lead to lost productivity and increased recruitment costs, as well as potentially losing top candidates to competitors.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Track each stage of the hiring process to identify bottlenecks and streamline procedures.
- Do maintain clear communication with candidates to keep them engaged.
- Don’t compromise on the quality of the hire by rushing the process.
- Don’t ignore delays; address them to improve future hiring cycles.
2. Time to Fill
- Definition: Time to fill measures the total time taken to fill a job vacancy, from the moment the job requisition is opened to the date a candidate accepts the offer. It provides a comprehensive view of the recruitment cycle.
- Formula for Calculating: Time to Fill=Date of Offer Acceptance−Date Job Requisition Opened
- Data Required:
- Date when the job requisition was opened
- Date when the candidate accepted the job offer
- Impact on Organization: Time to fill is crucial for planning and operational efficiency. A shorter time to fill ensures that the organization can meet its staffing needs promptly, reducing the impact on productivity. A prolonged time to fill can lead to overburdened employees, delayed projects, and lost opportunities.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do evaluate the recruitment process regularly to identify inefficiencies.
- Do use recruitment technology to streamline the process.
- Don’t neglect to engage with hiring managers to understand their requirements and timelines.
- Don’t underestimate the importance of a well-organized recruitment team.
3. Quality of Hire
- Definition: Quality of hire measures the value that new employees bring to the organization. This metric assesses new hires’ performance, cultural fit, and overall contribution to organizational goals.
- Formula for Calculating: Quality of Hire=3(Performance Score + Cultural Fit + Retention Rate)
- Data Required:
- Performance evaluation scores
- Retention rates
- Hiring manager satisfaction surveys
- Cultural fit assessments
- Impact on Organization: Quality of hire directly correlates with the organization’s success, as high-quality hires are more productive, have better retention rates, and positively impact the company’s culture and performance.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do set clear performance expectations and metrics.
- Do use a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures.
- Don’t rely solely on short-term metrics; consider long-term potential.
- Don’t overlook the importance of cultural fit in assessing quality.
4. Source of Hire
- Definition: Source of hire identifies the channels through which successful candidates are sourced, such as job boards, social media, referrals, or recruitment agencies.
- Formula for Calculating: Source of Hire=Total Number of HiresNumber of Hires from Source×100
- Data Required:
- Data on the initial source of each hire (e.g., job board, referral, social media)
- Impact on Organization: Understanding the most effective sources of hire helps optimize recruitment spending and strategies, improving the quality of applicants and overall recruitment efficiency.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do track and analyze the effectiveness of all recruitment sources.
- Do invest more in high-performing sources.
- Don’t disregard underperforming sources without understanding the cause.
- Don’t focus solely on volume; consider the quality of hires from each source.
5. Cost Per Hire
- Definition: Cost per hire calculates the total expenses incurred in hiring a new employee, including both internal and external costs.
- Formula for Calculating: Cost Per Hire=Total Number of HiresTotal Internal + External Recruiting CostsData Required:
- Internal recruiting costs (e.g., salaries, training)
- External recruiting costs (e.g., advertising, agency fees)
- Number of hires
- Impact on Organization: This metric is vital for budgeting and financial planning, helping organizations manage recruitment expenses and make cost-effective decisions.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do include all relevant costs in your calculations.
- Do analyze cost variations across different roles and levels.
- Don’t focus solely on reducing costs; ensure quality is maintained.
- Don’t overlook the long-term impact of cost-cutting measures on recruitment outcomes.
6. Offer Acceptance Rate
- Definition: The offer acceptance rate measures the percentage of job offers accepted by candidates, reflecting the offer’s attractiveness and the organization’s reputation.
- Formula for Calculating: Offer Acceptance Rate= Total Number of Offers MadeNumber of Accepted Offers×100
- Data Required:
- Number of offers made
- Number of offers accepted
- Impact on Organization: A high acceptance rate indicates that the company’s offers are competitive and appealing. A low acceptance rate may highlight issues with compensation, job role clarity, or company reputation.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Gather feedback from candidates who decline offers.
- Do ensure your offers are competitive with market standards.
- Don’t assume that compensation is the only factor affecting acceptance.
- Don’t ignore the importance of a positive candidate experience.
7. Application Completion Rate
- Definition: Application completion rate measures the percentage of candidates who start and complete the job application process.
- Formula for Calculating:Application Completion Rate=Number of Started ApplicationsNumber of Completed Applications×100
- Data Required:
- Number of applications started
- Number of applications completed
- Impact on Organization: This metric indicates the user-friendliness of the application process and can impact the quality and quantity of applicants. A low completion rate may suggest that the application process is too cumbersome or complex.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do streamline the application process and make it mobile-friendly.
- Do provide clear instructions and required fields.
- Don’t include unnecessary steps or questions in the application.
- Don’t overlook the importance of a simple and efficient application process.
8. Interview-to-Hire Ratio
- Definition: The interview-to-hire ratio measures the number of interviews conducted before making a successful hire, indicating the selectiveness and efficiency of the interview process.
- Formula for Calculating: Interview to Hire Ratio=Total Number of HiresTotal Number of Interviews Conducted
- Data Required:
- Number of interviews conducted
- Number of hires made
- Impact on Organization: A lower ratio indicates an efficient interview process, while a higher ratio may suggest that the selection criteria or screening processes need refinement.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do ensure interviewers are trained and follow a consistent evaluation process.
- Do use structured interviews to improve consistency.
- Don’t conduct unnecessary interviews; refine your screening process.
- Don’t ignore the importance of feedback and calibration among interviewers.
9. Selection Ratio
- Definition: Selection ratio measures the proportion of applicants who are ultimately hired, reflecting the selectivity of the hiring process.
- Formula for Calculating: Selection Ratio = Total Number of Applicants Number of Hires
- Data Required:
- Number of applicants
- Number of hires
- Impact on Organization: A low selection ratio indicates a highly competitive hiring process, suggesting that the organization can attract a large number of qualified candidates. A high ratio might suggest a less selective process, which could affect the quality of hires.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do evaluate your selection criteria regularly to ensure they align with job requirements.
- Do use the selection ratio to assess the competitiveness of your hiring process.
- Don’t compromise on quality for the sake of filling positions quickly.
- Don’t ignore the potential need for additional sourcing or marketing efforts if the ratio is too high.
10. Applicants Per Opening
- Definition: Applicants per opening measures the average number of candidates applying for each job vacancy, providing insight into the position’s attractiveness and the effectiveness of job postings.
- Formula for Calculating: Applicants Per Opening=Total Number of OpeningsTotal Number of Applicants
- Data Required:
- Total number of applicants
- Total number of job openings
- Impact on Organization: High numbers indicate that the job posting is attractive and well-received by the candidate market. Low numbers may suggest issues with the job description, company reputation, or visibility of the job posting.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do review and optimize job postings for clarity and appeal.
- Do use various channels to increase job visibility.
- Don’t assume that a high number of applicants always equates to a high-quality pool.
- Don’t ignore feedback from candidates regarding the application process or job postings.
11. Percentage of Open Positions
- Definition: Percentage of open positions measures the proportion of vacant roles relative to the total number of positions within the organization.
- Formula for Calculating: Percentage of Open Positions=(Total Number of PositionsNumber of Open Positions)×100
- Data Required:
- Number of open positions
- Total number of positions
- Impact on Organization: A high percentage of open positions can indicate rapid growth, high turnover, or inefficiencies in the recruitment process. It can impact productivity and employee morale if roles remain unfilled for extended periods.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do regularly review staffing levels and identify critical vacancies.
- Do prioritize hiring for roles that have a significant impact on the business.
- Don’t let open positions linger without a clear plan for filling them.
- Don’t delay recruitment efforts due to budget constraints or other priorities.
12. Candidate Satisfaction
- Definition: Candidate satisfaction measures the level of satisfaction candidates feel about the recruitment process, regardless of whether they were hired.
- Formula for Calculating: Candidate Satisfaction Score=Average Survey Score
- Data Required:
- Feedback from candidates via surveys or interviews
- Impact on Organization: High candidate satisfaction enhances the company’s reputation and can lead to a larger and more qualified applicant pool in the future. Low satisfaction can deter candidates from applying or accepting offers and negatively affect the company’s employer brand.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do regularly collect and analyze feedback from candidates.
- Do make improvements based on candidate feedback.
- Don’t ignore negative feedback or trends indicating dissatisfaction.
- Don’t underestimate the impact of the candidate experience on the company’s reputation.
13. Click-Through Rate (CTR) for Emails to Candidates
- Definition: CTR for emails to candidates measures the effectiveness of email communications in encouraging candidates to engage further, such as clicking on links to job descriptions or application pages.
- Formula for Calculating: CTR=(Number of Emails DeliveredNumber of Clicks)×100
- Data Required:
- Number of emails delivered
- Number of clicks on links within the emails
- Impact on Organization: A high CTR indicates engaging and relevant email content, which can lead to more applications and greater interest in the company. A low CTR may suggest issues with the email content or the effectiveness of the communication strategy.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do use engaging and personalized content in your emails.
- Do experiment with different subject lines and content to improve engagement.
- Don’t overload emails with too much information or too many links.
- Don’t ignore the timing and frequency of your emails; these factors can significantly impact CTR.
14. Candidate Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Definition: Candidate NPS measures the likelihood that candidates will recommend your organization as a good place to work based on their recruitment experience.
- Formula for Calculating: {Candidate NPS} = {Promoters} – {Detractors}
- Data Required:
- Responses to NPS survey questions
- Impact on Organization: A high candidate NPS indicates a positive candidate experience, which can enhance the company’s reputation and attract top talent. A low NPS suggests areas for improvement in the recruitment process.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do use NPS as part of a broader feedback and improvement strategy.
- Do analyze the reasons behind scores to understand areas for improvement.
- Don’t ignore feedback from passives, as they can become promoters or detractors.
- Don’t overlook the importance of continuous improvement in the candidate experience.
15. Applicants/Candidates Per Hire
- Definition: This metric measures the average number of applicants or candidates needed to make one successful hire.
- Formula for Calculating: Applicants Per Hire=Total Number of HiresTotal Number of Applicants
- Data Required:
- Number of applicants
- Number of hires
- Impact on Organization: This metric provides insights into the recruitment process’s selectivity and effectiveness. A high number of applicants per hire suggests a competitive selection process, while a lower number may indicate a need for broader sourcing or marketing efforts.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do ensure that your sourcing strategies are effective and reach a broad audience.
- Do use this metric to evaluate the efficiency of your recruitment process.
- Don’t assume that a high number of applicants always leads to better quality hires.
- Don’t ignore the potential need for more targeted or specialized recruitment efforts.
16. Fill Rate
- Definition: Fill rate measures the percentage of open positions that have been successfully filled within a specific time frame.
- Formula for Calculating: Fill Rate=(Total Number of Open PositionsNumber of Positions Filled)×100
- Data Required:
- Number of positions filled
- Total number of open positions
- Impact on Organization: A high fill rate indicates an efficient recruitment process, while a low fill rate may highlight challenges in attracting or hiring candidates. This metric is crucial for maintaining business operations and meeting staffing needs.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do regularly review and adjust recruitment strategies to improve fill rates.
- Do prioritize critical roles and fill them promptly.
- Don’t compromise on candidate quality to improve fill rate metrics.
- Don’t neglect to investigate reasons for unfilled positions.
17. Candidate Engagement
- Definition: Candidate engagement measures the level of interaction and responsiveness from candidates throughout the recruitment process.
- Formula for Calculating:
Can be assessed using various metrics, such as
Candidate Engagement = Application Completion Rate, Response Rates, and Survey Feedback Scores
- Data Required:
- Application and response rates
- Survey feedback
- Website and email analytics
- Impact on Organization: High engagement indicates a strong employer brand and effective communication strategies, leading to a better candidate experience and a more qualified talent pool.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do maintain regular and transparent communication with candidates.
- Do use engaging and relevant content in job postings and communications.
- Don’t neglect to follow up with candidates promptly.
- Don’t ignore feedback indicating disengagement or dissatisfaction.
18. Hiring Manager Satisfaction
- Definition: Hiring manager satisfaction measures the satisfaction levels of hiring managers with the recruitment process and the quality of candidates they receive.
- Formula for Calculating: Typically gathered through survey scores: Hiring Manager Satisfaction Score = Average Survey Rating
- Data Required:
- Feedback from hiring managers via surveys or interviews
- Impact on Organization: High satisfaction indicates that the recruitment process meets the hiring managers’ expectations, leading to better collaboration and more successful hiring outcomes.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do regularly gather and analyze feedback from hiring managers.
- Do use feedback to improve the recruitment process and align it with department needs.
- Don’t ignore specific concerns or feedback from hiring managers.
- Don’t assume high satisfaction means no room for improvement.
19. Recruitment Funnel Effectiveness
- Definition: Recruitment funnel effectiveness assesses the efficiency of the various stages in the recruitment process, from sourcing to hiring.
- Formula for Calculating:
Recruitment Funnel Conversion Rate=Total Number of Candidates at Previous StageNumber of Candidates Moving to Next Stage×100
- Data Required:
- Number of candidates at each stage of the recruitment process
- Impact on Organization: This metric helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the recruitment funnel, improving overall hiring efficiency and candidate experience.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do monitor and analyze each stage of the recruitment funnel regularly.
- Do make data-driven adjustments to address bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Don’t focus only on the top of the funnel; consider the entire candidate journey.
- Don’t ignore the impact of each stage on the overall candidate experience.
20. Offer Decline Rate
- Definition: Offer decline rate measures the percentage of job offers that are declined by candidates.
- Formula for Calculating: Offer Decline Rate=(Number of Offers Declined/ Total Number of Offers Extended)×100
- Data Required:
- Number of offers extended
- Number of offers declined
- Impact on Organization: A high offer decline rate can indicate issues with the job offer package, company reputation, or the recruitment process. It affects the organization’s ability to secure top talent.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do collect feedback from candidates who decline offers to understand their reasons.
- Do evaluate the competitiveness of your compensation and benefits packages.
- Don’t assume that compensation is the only factor; consider other aspects such as job role clarity and company culture.
- Don’t ignore trends in offer declines; they may indicate deeper issues.
21. Candidate Screening Ratio
- Definition: Candidate screening ratio measures the proportion of candidates who pass the screening stage relative to those interviewed.
- Formula for Calculating: Candidate Screening Ratio=Number of Candidates Screened/Number of Candidates Interviewed
- Data Required:
- Number of candidates screened
- Number of candidates interviewed
- Impact on Organization: This metric helps evaluate the effectiveness of the initial screening process, ensuring that only qualified candidates proceed to the interview stage. It impacts the efficiency of the recruitment process and the quality of candidates interviewed.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do ensure that screening criteria are well-defined and aligned with job requirements.
- Do use technology and tools to streamline the screening process.
- Don’t rely solely on resumes; consider additional screening methods like assessments.
- Don’t overlook the importance of consistency in the screening process.
22. Hiring Velocity
- Definition: Hiring velocity measures the speed at which the organization can close job vacancies, indicating the responsiveness of the recruitment process.
- Formula for Calculating: Hiring Velocity = Total Hires / Total Time to Hire All Positions
- Data Required:
- Number of hires
- Total time taken to hire all positions
- Impact on Organization: A high hiring velocity allows the organization to quickly respond to staffing needs and market changes, maintaining operational efficiency and competitiveness.
- Do’s and Don’ts:
- Do set realistic timelines for hiring based on market conditions.
- Do continually review and optimize the hiring process for speed without compromising quality.
- Don’t prioritize speed over quality; ensure thorough vetting of candidates.
- Don’t overlook the importance of a comprehensive onboarding process.
Conclusion
Mastering these recruiting metrics is essential for optimizing your hiring process and enhancing the overall quality of your workforce. By understanding and utilizing these metrics, HR professionals can make data-driven decisions that improve recruitment efficiency, candidate experience, and organizational performance. Regularly monitoring these metrics will ensure that your recruitment strategies are aligned with your business goals and continuously improving.





