

Are You Ready to Lead the Future of HR?
In today’s fast-changing business landscape, the role of HR directors is no longer just about being policy enforcers; they are strategic leaders shaping the future of work. Are your HR leadership skills evolving fast enough to keep up? As businesses grow more complex, the expectations from HR leaders expand beyond compliance and hiring—they now include business strategy, organizational change, workforce analytics, and leadership coaching.
Whether you’re an aspiring HR leader or an experienced HR director, understanding and mastering human resources competencies is crucial for staying ahead. This blog explores the key HR core competencies required for leadership in human resource management skills and competencies, offering insights that are both practical for freshers and valuable for experienced professionals.
HR directors are expected to drive company-wide transformation. Modern HR leadership is about aligning HR strategy with business goals, fostering innovation, and ensuring that employees thrive in a dynamic work environment.
Research from Harvard Business Review reveals that organizations with HR leaders who focus on strategic priorities (e.g., talent development, culture alignment) achieve higher profitability than those stuck in administrative roles. Similarly, Deloitte’s 2023 Human Capital Trends Report found that companies with agile, forward-thinking HR teams are more likely to lead innovation in their industries.
For HR professionals, this means transcending administrative tasks to become architects of organizational resilience and growth. You are no longer just the ‘policy police’ or the ‘hire-and-fire department’—you are the stewards of culture, the designers of employee experiences, and the catalysts for business transformation.
But what makes an HR leader truly effective? Let’s explore the HR competencies list that directly fuel organizational success and defines success in the modern workplace.
Effective HR leadership hinges on mastering two complementary dimensions: technical expertise—the functional competencies required to execute core HR functions—and strategic influence, which encompasses leadership, emotional intelligence, and the ability to drive impactful decisions. Together, these competencies transform HR from a support role into a powerhouse of organizational growth and innovation.
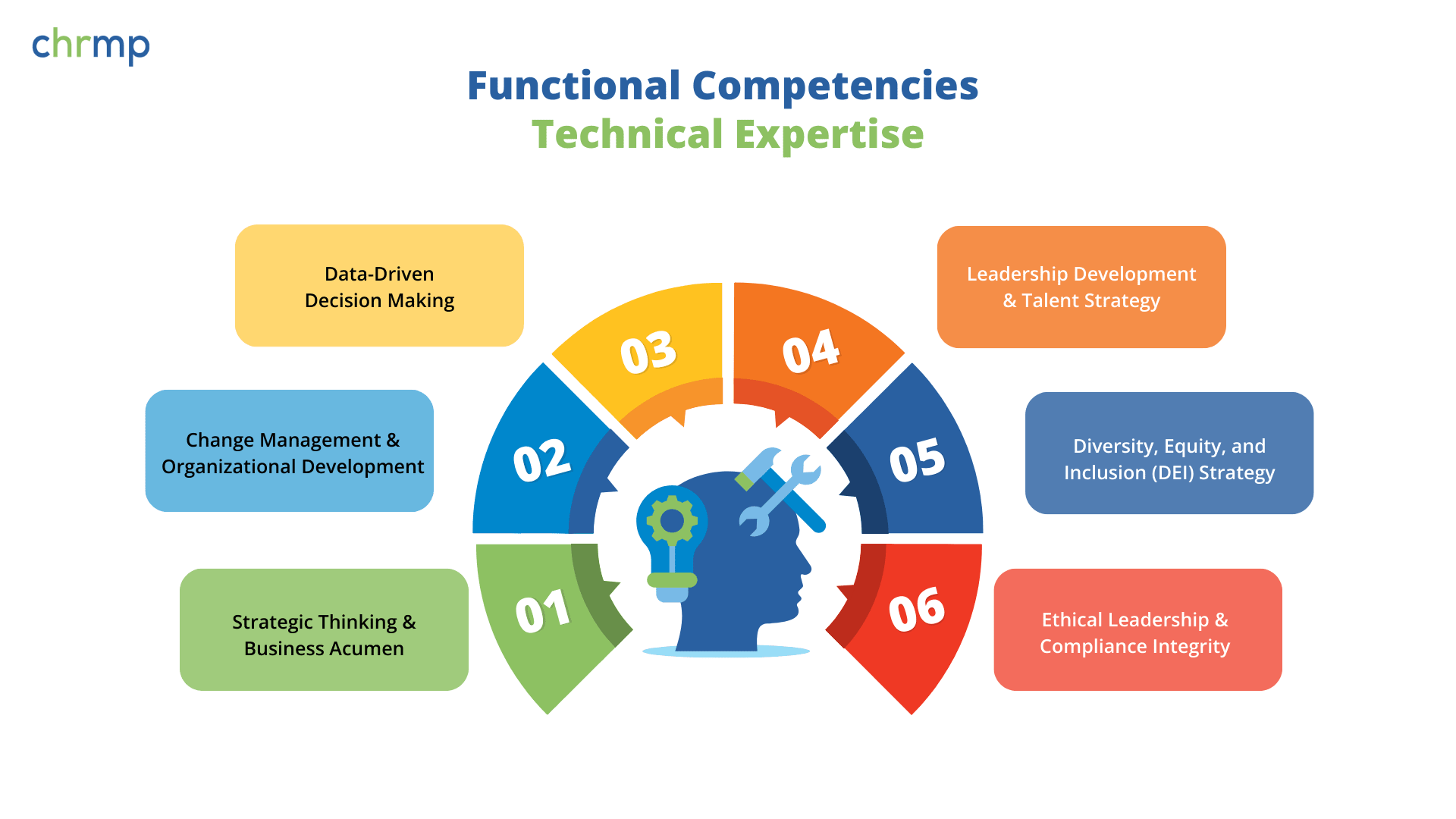
Strategic thinking is the ability to anticipate future trends, analyze business challenges, and develop forward-thinking HR strategies that align with corporate objectives. It involves proactive decision-making, problem-solving, and long-term workforce planning to ensure that HR contributes meaningfully to an organization’s success.
Business acumen refers to the ability to understand and apply business and financial insights to HR functions. HR leaders must grasp key business drivers, market dynamics, and financial indicators to align talent management with organizational performance. This competency ensures HR professionals can participate in high-level discussions and drive impactful change within their organizations.
Why it matters:
HR leaders are no longer confined to administrative tasks; they play a pivotal role in shaping business strategy. A deep understanding of financial metrics, industry trends, and organizational goals enables HR directors to align talent strategies with broader business objectives. By thinking strategically, HR can contribute to profitability, operational efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
Change management is the structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state. It involves planning, communication, and implementation strategies to ensure smooth transitions during organizational shifts. Effective change management reduces resistance, improves employee engagement, and enhances overall business performance.
Organizational development focuses on improving an organization’s effectiveness through planned interventions in processes, culture, and structure. It is a continuous process that fosters innovation, adaptability, and long-term growth by aligning HR strategies with business objectives.
Why it matters:
Leading HR professionals are change agents, driving workforce transformation and adaptability during mergers, restructuring, and industry shifts.
Organizations operate in an environment of constant evolution, from market shifts and digital transformation to mergers and restructuring. HR leaders must be adept at managing transitions, ensuring employees remain engaged and adaptable. Effective change management minimizes resistance, fosters innovation, and creates a culture of continuous improvement, positioning the organization for long-term success.
Data-driven decision-making refers to the process of utilizing HR analytics, metrics, and technology to make informed workforce decisions. It involves collecting and interpreting employee data to predict trends, measure productivity, and assess the impact of HR initiatives. This competency enables HR leaders to implement evidence-based strategies that enhance talent acquisition, retention, and overall business performance.
Why it matters:
The best HR directors don’t rely on gut feelings—they use people analytics and HR technology to make strategic workforce decisions.
Data-driven decision-making enables HR leaders to move beyond intuition and leverage analytics to shape workforce strategies. By utilizing HR technology and workforce data, HR leaders can proactively identify trends, optimize talent management, and align HR initiatives with business objectives. This competency ensures that HR is not only reactive but also a strategic force in achieving business outcomes, workforce efficiency, and long-term organizational growth.
Leadership development is the strategic approach to identifying, training, and nurturing future leaders within an organization. It ensures that employees have the skills, mindset, and support required to step into leadership roles effectively.
Talent strategy focuses on attracting, retaining, and managing high-potential employees. It involves aligning recruitment efforts with business objectives, fostering career growth, and ensuring continuous skill development to meet the company’s evolving needs.
Why it matters:
A great HR leader ensures succession planning and continuous leadership pipeline development.
As stewards of talent strategy, HR leaders must proactively identify, nurture, and retain future leaders who can drive business transformation. Effective leadership development not only strengthens the workforce but also mitigates succession risks, ensuring the organization remains resilient amid challenges.
Investing in talent development fosters innovation, enhances decision-making at all levels, and solidifies HR’s role as a key business partner in shaping the organization’s future success.
DEI strategy encompasses the policies and practices that ensure a diverse workforce, equitable opportunities, and an inclusive workplace culture. Diversity focuses on representation across demographics, equity ensures fair treatment and access to opportunities, and inclusion fosters an environment where all employees feel valued and respected.
Why it matters:
Modern HR leaders must ensure that organizations cultivate diverse talent and create inclusive work environments.
A diverse and inclusive workforce is not just a moral imperative but also a business advantage. Companies with strong DEI practices outperform competitors in terms of innovation, employee engagement, and customer satisfaction. HR leaders must champion equitable policies, remove biases in hiring and promotions, and cultivate an inclusive culture that values different perspectives.
Ethical leadership refers to the ability to make fair, transparent, and morally responsible decisions in the workplace. Compliance integrity involves adherence to laws, regulations, and corporate governance standards, ensuring that HR policies align with ethical and legal expectations.
Why it matters:
In an era of increased corporate scrutiny, HR leaders must uphold ethical business practices, regulatory compliance, and corporate governance.
HR must ensure that the organization adheres to legal requirements, ethical guidelines, and fair labor practices. Upholding integrity in decision-making fosters a culture of accountability, protects the company’s reputation, and mitigates legal risks.

Emotional intelligence (EQ) is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s emotions while effectively handling interpersonal relationships. It plays a crucial role in HR leadership by enabling professionals to navigate complex workplace dynamics, mediate conflicts, and foster strong relationships.
Executive presence is the ability to command attention, communicate confidently, and project credibility in high-stakes business settings. This competency is essential for HR leaders who need to influence key decision-makers and shape strategic initiatives.
Why it matters:
HR leaders operate at the intersection of business strategy and people management. They work closely with CEOs, stakeholders, and employees, requiring high EQ, executive communication skills, and strong leadership presence.
High emotional intelligence (EQ) allows HR directors to manage workplace relationships effectively, foster collaboration, and address conflicts with empathy. Additionally, executive presence—the ability to inspire confidence and communicate effectively—ensures that HR professionals influence key business decisions at the highest levels.
Crisis management involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from unexpected disruptions that impact business operations and employees. Workforce resilience refers to the organization’s ability to adapt to crises, maintain productivity, and support employee well-being during periods of uncertainty.
Why it matters:
Organizations will inevitably face crises—economic downturns, public relations challenges, cybersecurity threats, or global pandemics.
HR leaders must anticipate crises and develop workforce resilience strategies to keep employees engaged during uncertain times. Resilient HR leadership fosters a culture of adaptability, ensuring the organization thrives even in uncertain times.
Stakeholder management is the process of identifying, engaging, and building strong relationships with key individuals or groups who impact HR initiatives. Influence refers to the ability to advocate for HR policies, secure executive buy-in, and drive strategic HR decisions across different levels of an organization.
Why it matters:
HR leaders must navigate complex organizational structures and influence senior executives, board members, and employees to align HR initiatives with business goals.
The ability to navigate these relationships and advocate for HR initiatives is critical to securing buy-in and driving impactful change. Strong stakeholder management ensures HR remains a valued business partner rather than a support function.
Coaching is the practice of guiding employees toward achieving their professional goals through structured feedback and skill development. Mentorship involves long-term career guidance, knowledge sharing, and leadership development, fostering a culture of continuous learning and professional growth within an organization.
Why it matters:
Successful HR leaders invest in developing others, fostering a coaching culture where employees and managers continuously improve their skills and performance.
HR professionals who prioritize coaching and mentorship empower employees to grow in their careers, enhance performance, and contribute meaningfully to the organization. A culture of continuous learning strengthens workforce capabilities and prepares future leaders for greater responsibilities.
Conflict resolution is the ability to address and mediate disputes within the workplace in a fair, constructive manner. It involves active listening, problem-solving, and creating solutions that align with organizational objectives while maintaining positive employee relationships.
Negotiation is the ability to facilitate agreements between different parties, ensuring mutually beneficial outcomes. HR leaders use negotiation skills in employee relations, compensation discussions, and organizational decision-making.
Why it matters:
HR leaders often mediate disputes and ensure smooth workplace interactions. Effective conflict resolution skills help maintain a positive work culture and boost employee satisfaction.
Strong negotiation skills allow HR to advocate for employee well-being while balancing business priorities, fostering a work environment that is both collaborative and performance-driven
Innovation in HR refers to the ability to implement forward-thinking strategies, adopt new technologies, and drive creative solutions to workforce challenges. Agility involves adaptability, quick decision-making, and responsiveness to emerging business and workforce trends.
Why it matters:
The business world is evolving rapidly, and HR leaders must be adaptable and innovative to meet new challenges, whether through technology adoption or progressive policies.
HR leaders must be agile in their approach to talent management, policy creation, and employee engagement. Innovation in HR—whether through AI-driven hiring, flexible work policies, or cutting-edge training programs—ensures the organization remains competitive, adaptive, and responsive to emerging business challenges.

To maintain relevance and lead effectively, HR directors must prioritize continuous learning and professional development. Here’s how:
✅ Invest in Executive HR Certifications: Programs in competency human resource management, HR leadership, change management, and business strategy provide practical leadership training.
✅ Leverage HR Technology & Analytics: Upskill in HR manager skills and competencies, AI-driven talent acquisition, and digital workforce transformation.
✅ Develop Boardroom Influence: Gain executive communication and stakeholder management skills to drive HR strategy at the C-suite level.
✅ Foster Leadership Networks: Engage with HR leadership forums and executive coaching programs to stay connected with industry trends.
HR leadership is not just about managing people—it’s about leading organizational transformation. Whether you’re an HR manager aspiring for leadership or a current HR director refining your skills, the path to success lies in mastering the right competencies for HR leadership.
If you’re ready to take your HR career to the next level, explore and enrol in the right CHRMP Certification program that equips you with the strategic mindset, skills, and influence required to lead in today’s dynamic business environment.
If you’re ready to take your HR career to the next level, explore the various HR certification programs designed by CHRMP to enhance different leadership competencies. Identify the program that aligns with your career goals—whether it’s in strategic HR management, talent development, or workforce analytics—and take the step to enrol in the right certification to solidify your expertise and leadership in today’s dynamic business environment.
🚀 Step into HR leadership—your future as a transformative HR leader starts today! 🚀

© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited
