

Human Resource Management (HRM) is the practice of strategically managing people to drive organizational success. Unlike traditional “personnel management,” which focuses on administrative tasks like payroll, modern HRM aligns employee skills, motivation, and well-being with business goals. For example, companies like Google use HRM to create flexible work policies and career development programs that retain top talent while fostering innovation.
According to CIPD, HRM involves designing policies that prioritize employee experience, such as mentorship programs or diversity initiatives. Deloitte’s 2023 Global Human Capital Trends highlights that HRM today is about balancing human needs (e.g., mental health support) with data-driven decisions (e.g., using analytics to predict turnover). In simple terms, HRM ensures employees are not just “resources” but partners in achieving business objectives.
HRM has evolved from a paperwork-focused role to a strategic business partner:
Key Drivers of Change:
Example:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, HRM rapidly adopted remote work tools (e.g., Zoom) and redesigned policies to support mental health, proving its adaptability.
Human Resource Management (HRM) plays a pivotal role in bridging employee needs with organizational goals. Below are its key objectives, explained in detail with real-world examples and actionable insights:
HRM ensures organizations hire skilled individuals who align with company values while retaining high performers through engagement and growth opportunities. Talent shortages and high turnover can cripple productivity, making this objective critical.
HRM safeguards organizations from legal risks by adhering to labor laws, ensuring workplace safety, and promoting ethical behavior. Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage.
Engaged employees are more productive, innovative, and loyal. HRM fosters this by creating a supportive environment and aligning individual goals with organizational outcomes.
HRM ensures the workforce has the skills and structure needed to achieve long-term business objectives, such as entering new markets or adopting AI.
Together, these objectives create a high-performance culture where employees thrive and businesses innovate. For instance, companies like Netflix combine competitive pay (retention), ethical practices (compliance), creative freedom (engagement), and agile workforce planning to dominate the streaming industry.
Human Resource Management (HRM) ensures organizations attract, develop, and retain talent while fostering compliance, engagement, and productivity. Core functions include recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, and employee relations. These pillars align workforce capabilities with business goals, creating a cohesive, motivated, and legally compliant workplace.
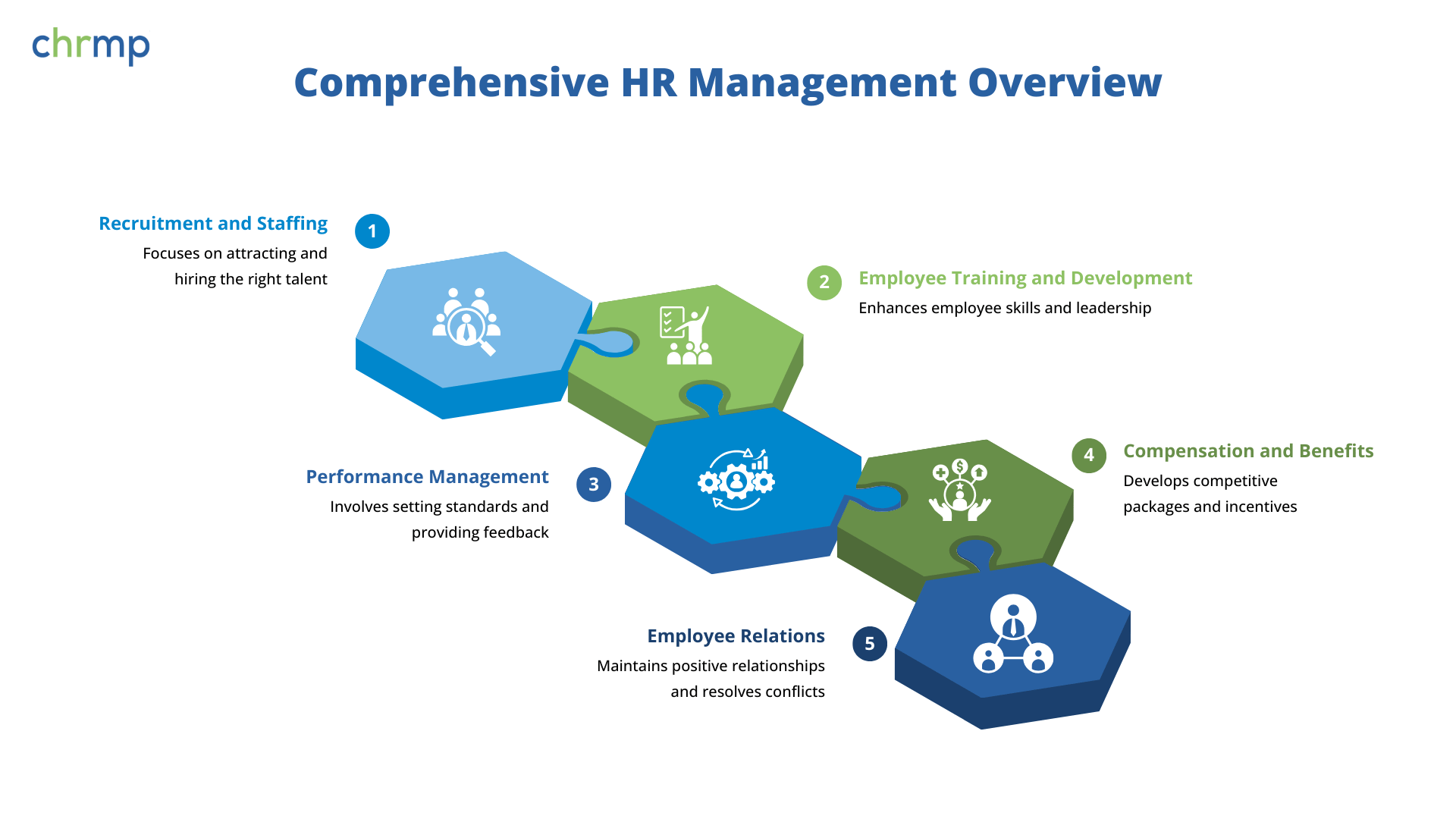
Recruitment and staffing involve identifying organizational talent needs, sourcing candidates, and hiring individuals who align with company goals and culture. This function ensures the right people are in the right roles, driving productivity and innovation. Effective staffing reduces turnover and builds a competitive workforce.
Attracting talent requires strategic employer branding, targeted job postings, and leveraging platforms like LinkedIn. Hiring involves structured interviews, skills assessments, and cultural fit evaluations. For example, Deloitte’s 2023 report highlights AI-driven tools that analyze candidate potential, reducing biased decisions and improving hiring accuracy by 40%.
Practical Insights:
Job descriptions outline roles, responsibilities, and expectations, while specifications detail required skills, education, and experience. Clear, inclusive language attracts diverse candidates. For instance, CIPD emphasizes avoiding gendered terms (e.g., “ninja” or “rockstar”) to boost applications from underrepresented groups by 30%.
Practical Insights:
Employee training and development ensure that organizations stay competitive by continuously enhancing workforce capabilities. HRM plays a crucial role in equipping employees with relevant skills, fostering innovation, and driving career growth. Effective training programs boost productivity, employee retention, and adaptability to evolving industry trends, ultimately contributing to long-term business success.
Skill enhancement programs help employees stay updated with industry advancements and emerging technologies. These initiatives include technical training, soft skills workshops, and cross-functional learning. For example, Amazon’s “Career Choice” program funds employee upskilling in high-demand fields, ensuring continuous learning and career growth while aligning talent development with business needs.
Practical Insights:
Leadership and career development initiatives prepare employees for future roles, fostering a strong internal talent pipeline. Programs like mentorship, coaching, and rotational assignments cultivate leadership skills. For instance, Google’s “g2g” (Googler-to-Googler) mentoring program empowers employees to learn from peers, supporting professional growth and succession planning within the organization.
Practical Insights:
Performance management ensures employees align with organizational goals through structured evaluations, continuous feedback, and improvement plans. Modern HRM shifts from annual reviews to ongoing performance tracking, leveraging data-driven insights for better decision-making. Effective performance management fosters motivation, enhances productivity, and helps employees grow while driving business success.
Setting clear performance standards and key metrics ensures employees understand expectations and contribute effectively to business objectives. Organizations use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Objectives and Key Results (OKRs), and competency models to measure success. For example, Google’s OKR framework aligns employee efforts with strategic goals, fostering accountability and innovation.
Practical Insights:
Appraisals and feedback mechanisms provide employees with structured evaluations, helping them understand strengths and areas for improvement. Organizations are moving from rigid annual reviews to real-time feedback models. For instance, Adobe replaced traditional performance reviews with its “Check-In” system, promoting continuous conversations between managers and employees.
Practical Insights:
Compensation and benefits play a crucial role in attracting, retaining, and motivating employees. A well-structured rewards system ensures fairness, boosts job satisfaction, and enhances organizational performance. Modern HRM emphasizes not just competitive salaries but also holistic benefits, including wellness programs and performance-based incentives, to create a thriving workplace.
Competitive compensation packages balance base salary, bonuses, and equity-based incentives to attract top talent and drive performance. Companies conduct market benchmarking and salary surveys to remain competitive. For example, Google offers stock options and performance bonuses to reward high-performing employees, ensuring long-term retention and motivation.
Practical Insights:
Beyond salaries, employee benefits and incentives enhance job satisfaction and well-being. Comprehensive benefits include health insurance, retirement plans, mental health support, and flexible work arrangements. Leading companies like Salesforce offer wellness stipends and paid volunteer time to foster employee engagement and work-life balance.
Practical Insights:
Employee relations focus on fostering a positive work environment through transparent communication, trust-building, and fair policies. Effective HRM ensures employees feel valued and heard, reducing workplace conflicts and enhancing engagement. A strong employee relations strategy leads to higher retention, increased productivity, and a more collaborative organizational culture.
Building positive employer-employee relationships requires open communication, mutual respect, and alignment of company values with employee expectations. Organizations that prioritize trust and transparency see improved morale and productivity. For instance, HubSpot’s “Culture Code” fosters an employee-first approach, emphasizing autonomy, inclusivity, and professional growth.
Practical Insights:
Workplace conflicts, if not managed effectively, can lead to decreased morale and productivity. HRM plays a critical role in resolving disputes through structured grievance mechanisms and mediation processes. For example, Microsoft uses conflict resolution training to equip managers with skills to handle disagreements constructively.
Practical Insights:
HRM is no longer just an administrative function—it is a strategic partner in driving business success. By aligning HR strategies with organizational objectives, companies ensure that workforce planning, talent management, and workplace culture contribute to long-term growth. Effective HRM fosters agility, innovation, and competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape.
HR goals should directly support an organization’s mission, values, and long-term objectives. This alignment ensures that recruitment, training, and retention strategies drive business success. For example, Tesla’s HR policies prioritize innovation and speed, ensuring employees are aligned with the company’s goal of revolutionizing the automotive industry.
Practical Insights:
HR plays a pivotal role in fostering an innovative and growth-driven workplace. By attracting top talent, upskilling employees, and creating a culture of experimentation, HRM fuels business expansion. For instance, Google’s “20% Time” initiative, allowing employees to work on passion projects, has led to groundbreaking innovations like Gmail.
Practical Insights:
Effective workforce planning and succession management ensure that organizations have the right talent in place to meet current and future business demands. HRM plays a critical role in forecasting workforce needs, identifying skill gaps, and developing leadership pipelines to maintain operational continuity and drive long-term success.
Strategic workforce planning involves analyzing future business goals, industry trends, and workforce demographics to ensure the organization remains competitive. Companies like IBM use AI-driven analytics to predict skill shortages and proactively upskill employees, ensuring a future-ready workforce.
Practical Insights:
Succession planning ensures business continuity by identifying and preparing employees for leadership roles. A well-structured plan minimizes disruptions when key executives or critical team members leave. For example, General Electric’s leadership pipeline focuses on internal promotions, reducing the risks of leadership gaps.
Practical Insights:
HRM plays a crucial role in ensuring organizations operate within legal frameworks while upholding ethical standards. Compliance with labor laws, fair treatment of employees, and ethical decision-making are essential for maintaining a positive workplace culture and avoiding legal repercussions. By integrating compliance with strategic HR functions, organizations build trust, promote equity, and foster a legally sound work environment.
Adhering to labor laws and industry regulations is fundamental to HRM. Compliance safeguards employees’ rights, protects organizations from legal risks, and ensures ethical employment practices. HR teams must stay updated on evolving regulations, from wage laws to workplace safety requirements, to prevent lawsuits and maintain operational integrity.
Employment laws govern areas such as wages, working hours, benefits, workplace safety, and employee rights. Non-compliance can result in penalties, reputational damage, and employee dissatisfaction. Companies like Uber have faced legal challenges over worker classification, highlighting the importance of understanding and adhering to labor laws.
Practical Insights:
A fair and inclusive workplace is not just an ethical requirement—it is a legal mandate under laws such as the Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Act and Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). HRM must actively prevent discrimination and bias in hiring, promotions, and workplace policies.
Practical Insights:
Ethical HRM practices foster trust, fairness, and accountability within an organization. HR professionals must ensure ethical hiring, fair treatment of employees, and transparent decision-making in areas like compensation and promotions. Ethical workplace practices enhance employer reputation, improve employee morale, and reduce risks related to discrimination, bias, and legal challenges.
Ethical hiring ensures fair and unbiased recruitment, preventing discrimination while promoting diversity and inclusion. Companies that prioritize integrity in hiring attract top talent and build a strong organizational culture. For instance, Accenture’s commitment to ethical hiring includes using AI to eliminate bias and ensuring fair evaluations.
Practical Insights:
Open and fair compensation and promotion policies are essential for building employee trust and ensuring equity. Lack of transparency can lead to dissatisfaction, disengagement, and legal challenges. Companies like Buffer have publicly shared their salary formulas to promote pay equity and accountability.
Practical Insights:
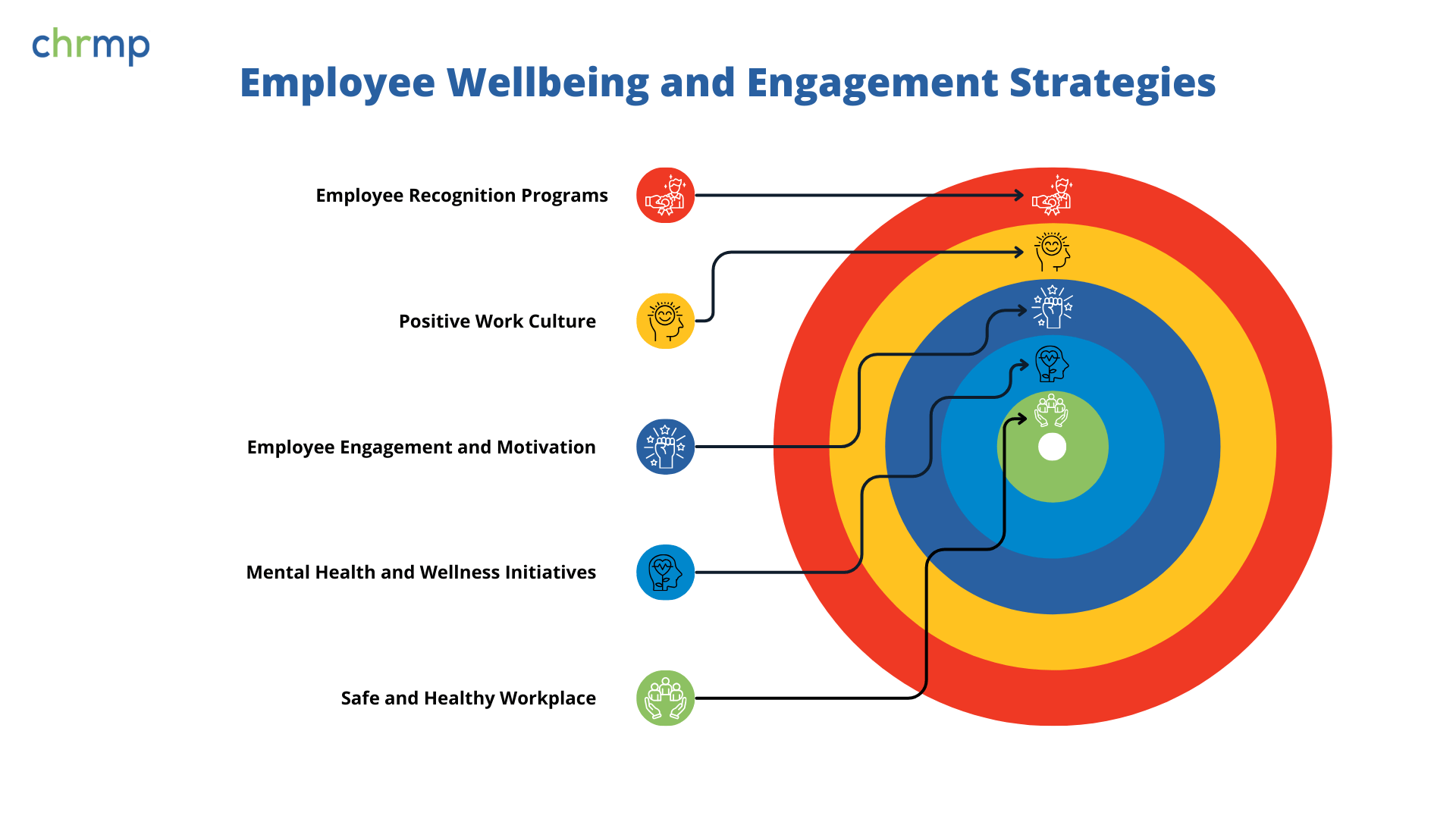
Employee wellbeing and engagement are critical factors in building a motivated and productive workforce. HRM plays a vital role in fostering a work environment that prioritizes physical health, mental wellness, and overall job satisfaction. Organizations that invest in employee wellbeing experience lower turnover, higher performance, and a more positive workplace culture.
Ensuring employee health and safety is a fundamental HR responsibility. A proactive approach to workplace safety minimizes accidents, enhances productivity, and boosts employee morale. Modern HRM integrates regulatory compliance with innovative wellness programs to create a secure and supportive work environment.
A safe workplace reduces risks, prevents injuries, and fosters a culture of care. Organizations must comply with workplace safety regulations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in the U.S. to maintain a hazard-free environment. Companies like Amazon invest in ergonomic workspaces and real-time safety tracking to prevent workplace incidents.
Practical Insights:
Work-related stress and mental health challenges can impact employee performance and job satisfaction. Forward-thinking organizations implement mental health initiatives to support employee well-being. For example, Microsoft provides free therapy sessions and mindfulness resources to promote a stress-free work environment.
Practical Insights:
Employee engagement and motivation drive productivity, innovation, and retention. HRM plays a crucial role in creating an environment where employees feel valued, connected, and aligned with organizational goals. Engaged employees are more likely to contribute their best efforts, leading to higher performance and a thriving workplace culture.
Recognition programs acknowledge employees’ hard work and achievements, boosting morale and motivation. Companies with strong recognition cultures see higher engagement and lower turnover rates. For instance, Salesforce’s “Thanks a Million” program allows employees to send peer-to-peer appreciation messages, fostering a culture of gratitude.
Practical Insights:
A positive work culture fosters collaboration, inclusivity, and job satisfaction. Organizations like HubSpot emphasize transparency and autonomy, creating an environment where employees feel empowered and valued. A strong workplace culture improves engagement, reduces burnout, and enhances overall job fulfillment.
Practical Insights:
The field of Human Resource Management (HRM) is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting workforce expectations, and global business trends. As HR moves beyond traditional administrative functions, the future of HRM will be defined by data-driven decision-making, automation, and employee-centric innovations. Organizations that embrace these trends will gain a competitive advantage in attracting, retaining, and engaging top talent.
Technology is revolutionizing HRM, making processes more efficient, data-driven, and personalized. From AI-powered recruitment tools to predictive analytics, HR professionals can leverage technology to enhance employee experience and drive business outcomes. Leading organizations like IBM and Google use AI-driven insights to optimize workforce planning and improve decision-making.
HR analytics empowers organizations to make strategic talent decisions based on real-time workforce data. By leveraging big data and predictive analytics, HR teams can anticipate talent shortages, improve employee engagement, and reduce turnover. For instance, Microsoft uses data analytics to predict employee attrition and proactively address workplace concerns.
Practical Insights:
Automation streamlines HR processes, reducing administrative burdens and improving efficiency. AI-driven recruitment tools enhance candidate screening, chatbots handle employee queries, and automated workflows simplify payroll and benefits administration. Companies like Unilever use AI-powered video assessments to analyze candidate responses, speeding up hiring while reducing bias.
Practical Insights:
The rise of remote and hybrid work models has transformed how organizations operate. HRM plays a crucial role in ensuring that remote work is productive, engaging, and sustainable. From managing virtual teams to supporting work-life balance, HR professionals must adopt strategies that foster flexibility while maintaining high performance. Companies like Spotify and Twitter have embraced “work from anywhere” policies, demonstrating the long-term viability of flexible work arrangements.
Managing a remote workforce requires clear communication, collaboration tools, and performance tracking mechanisms. Without physical office spaces, HR must implement virtual engagement strategies and ensure employees remain connected to company culture. For example, companies like GitLab, a fully remote organization, use asynchronous communication and project management tools to maintain efficiency.
Practical Insights:
Work-life balance has become a top priority for employees, with flexible work arrangements playing a key role in job satisfaction and productivity. HRM must design policies that support mental well-being, prevent burnout, and create boundaries between work and personal life. Companies like HubSpot offer unlimited vacation policies and flexible schedules, allowing employees to recharge and stay motivated.
Practical Insights:
Organizational change is inevitable in today’s fast-paced business environment, whether due to mergers, technological advancements, or market shifts. HRM plays a critical role in guiding employees through transitions, minimizing resistance, and ensuring smooth implementation of change initiatives. Companies that manage change effectively experience higher employee engagement, reduced turnover, and sustained business growth.
Successful change management requires a strategic approach that considers both business objectives and employee well-being. HRM ensures that transitions—whether restructuring, digital transformation, or cultural shifts—are implemented effectively with minimal disruption. For example, during Microsoft’s shift to a cloud-first strategy, HR played a key role in reskilling employees and fostering a growth mindset.
Change can be unsettling for employees, leading to uncertainty and resistance. HRM must proactively support employees by providing clear guidance, training, and emotional reassurance during transitions. For instance, companies like IBM invest in retraining programs when implementing new technologies, ensuring employees remain relevant in evolving roles.
Practical Insights:
Clear and transparent communication is crucial for successful change management. HRM must ensure that employees understand the reasons for change, its impact, and their role in the transformation process. Companies like Netflix emphasize open dialogue and continuous feedback loops to foster employee buy-in during major shifts.
Practical Insights:
Diversity and inclusion (D&I) are critical components of a thriving workplace, fostering innovation, collaboration, and employee satisfaction. HRM plays a vital role in implementing policies and initiatives that ensure equal opportunities for all employees, regardless of race, gender, age, disability, or background. Companies that prioritize D&I benefit from enhanced creativity, better decision-making, and a stronger employer brand.
Promoting workplace diversity involves more than just meeting hiring quotas—it requires a strategic approach to attracting, retaining, and developing a diverse talent pool. Organizations like Microsoft and Accenture lead the way in D&I by embedding inclusivity into their corporate values, recruitment strategies, and leadership development programs.
An inclusive hiring process ensures that job opportunities are accessible to candidates from diverse backgrounds, minimizing biases and promoting equal opportunities. Companies like LinkedIn have implemented AI-driven tools to eliminate gendered language from job descriptions, leading to a broader and more diverse applicant pool.
Practical Insights:
Diversity training helps employees and leaders recognize biases, develop cultural awareness, and create an inclusive workplace. Ongoing education and engagement are crucial to fostering an environment where all employees feel valued and respected. Companies like Google conduct unconscious bias training to help employees understand and mitigate workplace biases.
Practical Insights:
Creating an inclusive workplace culture goes beyond hiring diverse talent—it requires ongoing efforts to ensure every employee feels valued, respected, and empowered to contribute. HRM plays a key role in fostering inclusivity by implementing support systems, equitable policies, and cultural awareness initiatives. Companies like Salesforce and Deloitte have built strong inclusive cultures by embedding diversity into their leadership, training, and workplace policies.
Support systems for diverse employees enhance engagement, retention, and workplace satisfaction. Employee Resource Groups (ERGs), mentorship programs, and inclusive leadership initiatives provide underrepresented employees with a sense of belonging and career development opportunities. For example, Intel’s ERGs support women, LGBTQ+ employees, and racial minorities through networking and mentorship.
Practical Insights:
A diverse workforce leads to increased innovation, better decision-making, and stronger financial performance. Research from McKinsey shows that companies with high diversity levels outperform competitors in profitability and employee satisfaction. Organizations like Microsoft and Unilever have successfully leveraged diversity to enhance creativity, expand market reach, and improve customer relations.
Practical Insights:
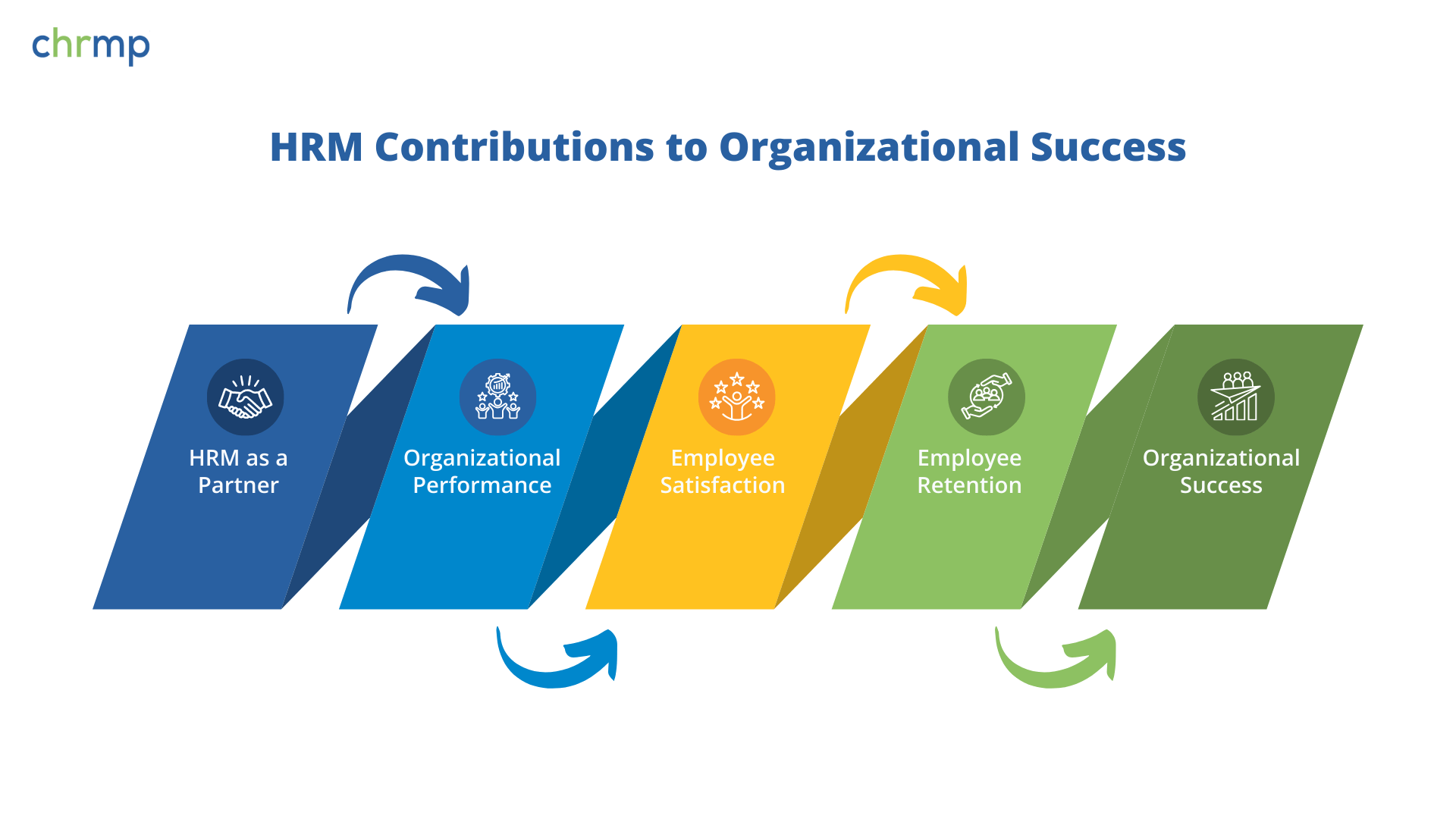
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a strategic function that directly impacts an organization’s success. By aligning HR initiatives with business objectives, HR professionals help create a high-performance culture, enhance employee engagement, and drive long-term growth. Organizations that invest in effective HRM strategies benefit from increased productivity, stronger employer branding, and sustained competitive advantage.
HRM plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the workforce is equipped, motivated, and aligned with company goals. From talent acquisition to leadership development, HR initiatives directly influence business performance. Companies like Amazon and Google use data-driven HR strategies to enhance productivity and innovation, proving that HR is a critical business partner.
Practical Insights:
Satisfied employees are more engaged, productive, and committed to their organizations. HRM enhances job satisfaction through competitive benefits, professional development opportunities, and a supportive work environment. For example, Salesforce’s “Ohana Culture” prioritizes employee well-being, resulting in high retention rates and strong employer branding.
Practical Insights:
Human Resource Management (HRM) has evolved into a critical function that shapes the success of organizations by fostering a skilled, engaged, and high-performing workforce. From talent acquisition and employee development to diversity, well-being, and organizational strategy, HRM plays a pivotal role in aligning people management with business goals.
By implementing best practices in HR strategy, compliance, and performance management, HR professionals create environments where employees thrive and businesses gain a competitive edge. The integration of HR analytics, AI-driven recruitment, and employee-centric policies further enhances HRM’s ability to drive innovation and long-term organizational growth.
As the workplace continues to evolve with remote work models, digital transformation, and shifting workforce expectations, HR leaders must embrace agility, ethical leadership, and strategic decision-making. Investing in HRM training and certifications, such as those offered by CHRMP, equips HR professionals with the expertise to navigate complex workforce challenges and implement effective HR strategies.
The future of HRM lies in its ability to adapt, innovate, and create workplaces that balance business objectives with employee well-being. Organizations that prioritize HRM as a strategic function will not only enhance productivity and retention but also cultivate a culture of continuous learning, inclusivity, and resilience in an ever-changing world of work.
Are you ready to elevate your HR career and drive meaningful change in your organization? Explore CHRMP’s HR Certification Programs to gain industry-recognized skills and stay ahead in the evolving world of Human Resource Management.

© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited
