

Is your organization truly prepared for the future of work? Sabbatical Leave in India is emerging as a powerful strategy to enhance employee well-being, retention, and productivity.
The rules of talent acquisition and retention have been rewritten. Today’s top performers aren’t just looking for a paycheck; they’re seeking purpose, balance, and growth. In a world where burnout is rampant and employee engagement is constantly challenged, forward-thinking organizations are exploring innovative solutions.
Sabbatical leave, once a fringe benefit, is now a strategic imperative—a powerful lever for attracting, retaining, and motivating a thriving workforce.
This blog post is your essential guide to understanding and implementing sabbatical leave in India, equipping HR professionals, both freshers and experienced, with the insights and frameworks to leverage this powerful tool for attracting, retaining, and motivating a thriving workforce.
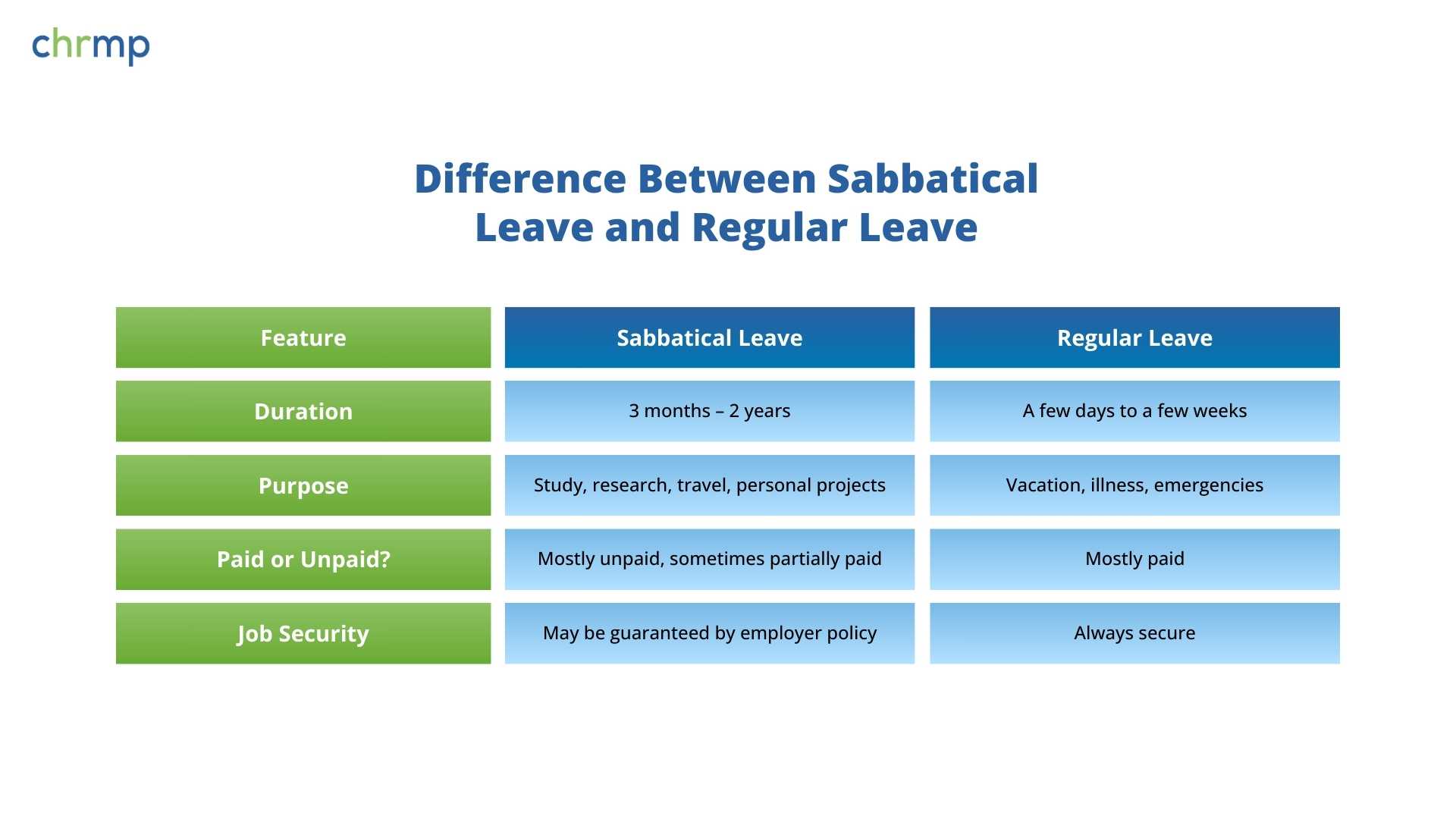
A sabbatical leave is an extended break from work granted by an employer for the purpose of personal or professional development. Unlike casual leave or earned leaves — which might be taken for immediate needs like medical rest, a family emergency, or a short vacation—a sabbatical is a longer-term absence and may be unpaid or partially paid, depending on the employer’s policy.
Historically, the concept of a “sabbatical” traces back to academia, where professors took extended leave to research, write, or refresh their knowledge. However, in modern corporate India, sabbaticals are no longer limited to academics alone. Companies offering sabbatical leave in India span various industries including IT, consulting, manufacturing, and even financial services.
In simplest terms, a sabbatical functions as a strategic pause. It differs from other leaves by its intentionality—employees usually plan their sabbaticals around personal or professional milestones such as pursuing higher education, engaging in community service, traveling, or focusing on personal projects. More importantly, sabbatical leave eligibility and benefits often require clear rules to ensure that employees know who can apply and under what conditions.
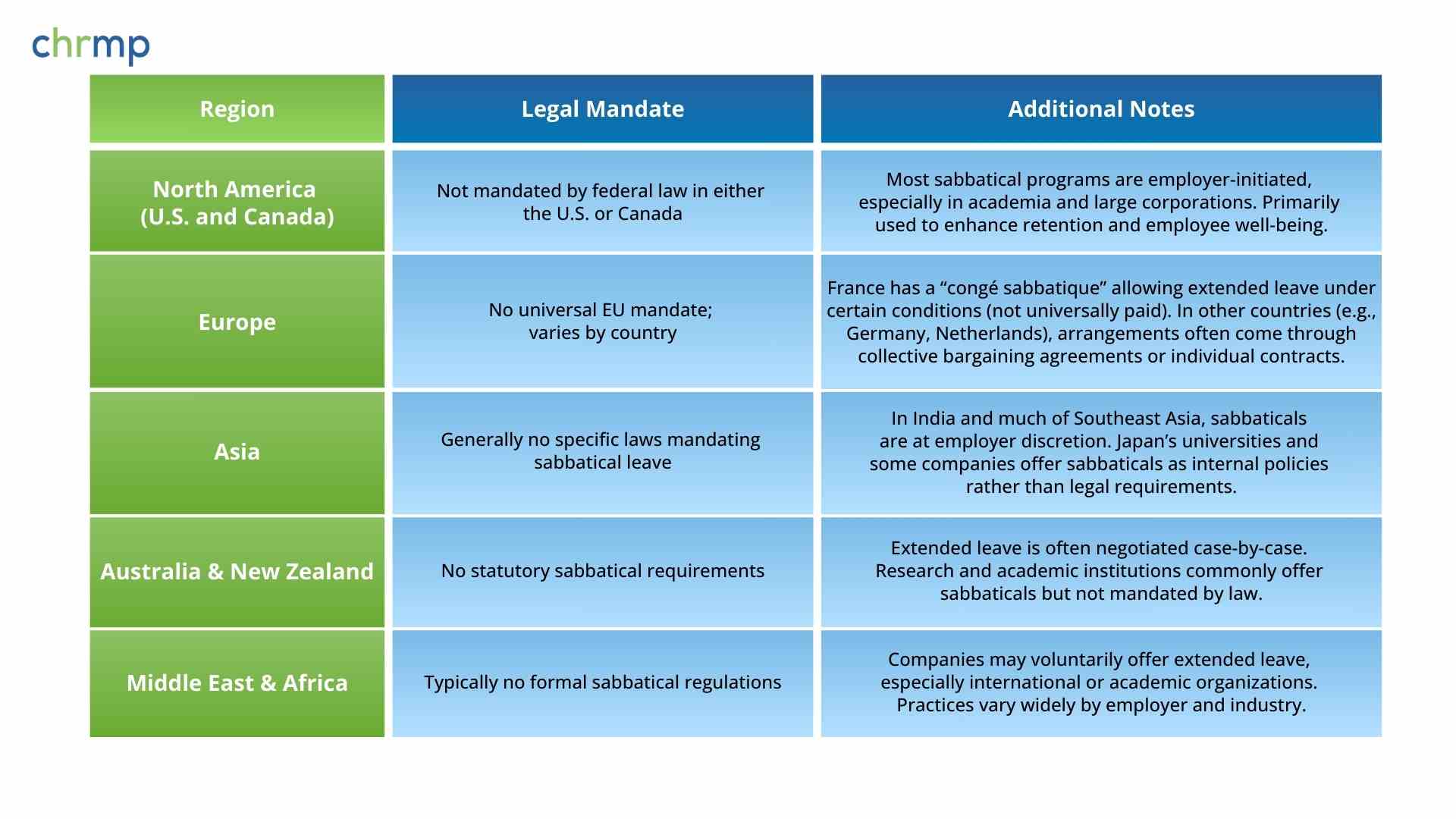
Generally, sabbatical leave is not mandated by law in most countries. While certain regions have statutory provisions for extended leave—such as parental or medical leave—dedicated sabbatical programs are typically left to the employer’s discretion allowing them to decide whether and how to offer extended leave.
Companies across the globe often include sabbatical leaves on a voluntary basis, recognizing them as a valuable method for improving staff loyalty, enhancing efficiency, and fostering overall employee well-being.
Below is a high-level look at how different regions approach sabbatical leave: (need a better looking table for this)
One of the most common questions HR professionals ask is whether Sabbatical Leave in India is mandated or recognized under labor law. This leave remains a discretionary benefit in India, shaped primarily by internal organizational policies rather than statutory requirements.
Indian labor statutes—such as the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, the Shops and Establishments Act, and the Factories Act—do not explicitly recognize or mandate sabbatical leave. Unlike maternity or paternity leave, there is no statutory provision that grants employees the legal right to take a sabbatical. Consequently, employers are not obligated to provide sabbaticals, and employees cannot demand them as a matter of law.
While sabbaticals lack legal backing, they are not prohibited. Employers have the freedom to create sabbatical policies that align with their organizational goals. Large multinationals, especially in the IT, consulting, and research sectors, often introduce sabbaticals to boost employee retention and well-being. However, the specifics—such as eligibility criteria, duration, and whether the leave is paid—vary widely among companies.
For private-sector employees, the availability and terms of a sabbatical usually depend on individual employment contracts, HR policies, and company culture. Some organizations may offer sabbaticals after a certain tenure or link them to performance records, while others may allow them only for educational or research purposes. Employees are advised to review their company handbook, offer letter, or employment agreement to determine whether a sabbatical option exists.
Public sector bodies and academic institutions often adopt more structured sabbatical frameworks. For instance, faculty at premier institutions (such as IITs and IIMs) can access paid or partially paid sabbaticals for research. Similarly, specific government departments permit extended leave for skill enhancement or higher studies. In contrast, many private corporations offer unpaid sabbaticals, often with clearly defined conditions.

Sabbatical leave serves multiple purposes, including:
Higher Education and Skill Development – Employees can pursue further studies, certifications, or research to enhance their professional growth.
Personal Well-being and Mental Health – Helps individuals recover from burnout, reduce stress, and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Family and Personal Commitments – Provides time to take care of family responsibilities, such as caregiving for elderly parents or spending quality time with loved ones.
Travel and Exploration – Allows employees to explore different cultures, experiences, and personal passions that contribute to overall growth.
Volunteering and Social Work – Enables employees to contribute to social causes, NGOs, or community service projects.
Creative and Entrepreneurial Pursuits – Offers employees the opportunity to work on personal projects, write a book, or even test new business ideas without quitting their job.
Criteria can vary depending on the organization. Common factors include:
For instance, a well-known Indian consulting firm offers sabbaticals after five years of continuous service, while an IT giant allows a sabbatical after three years, provided the employee has a robust performance track record.
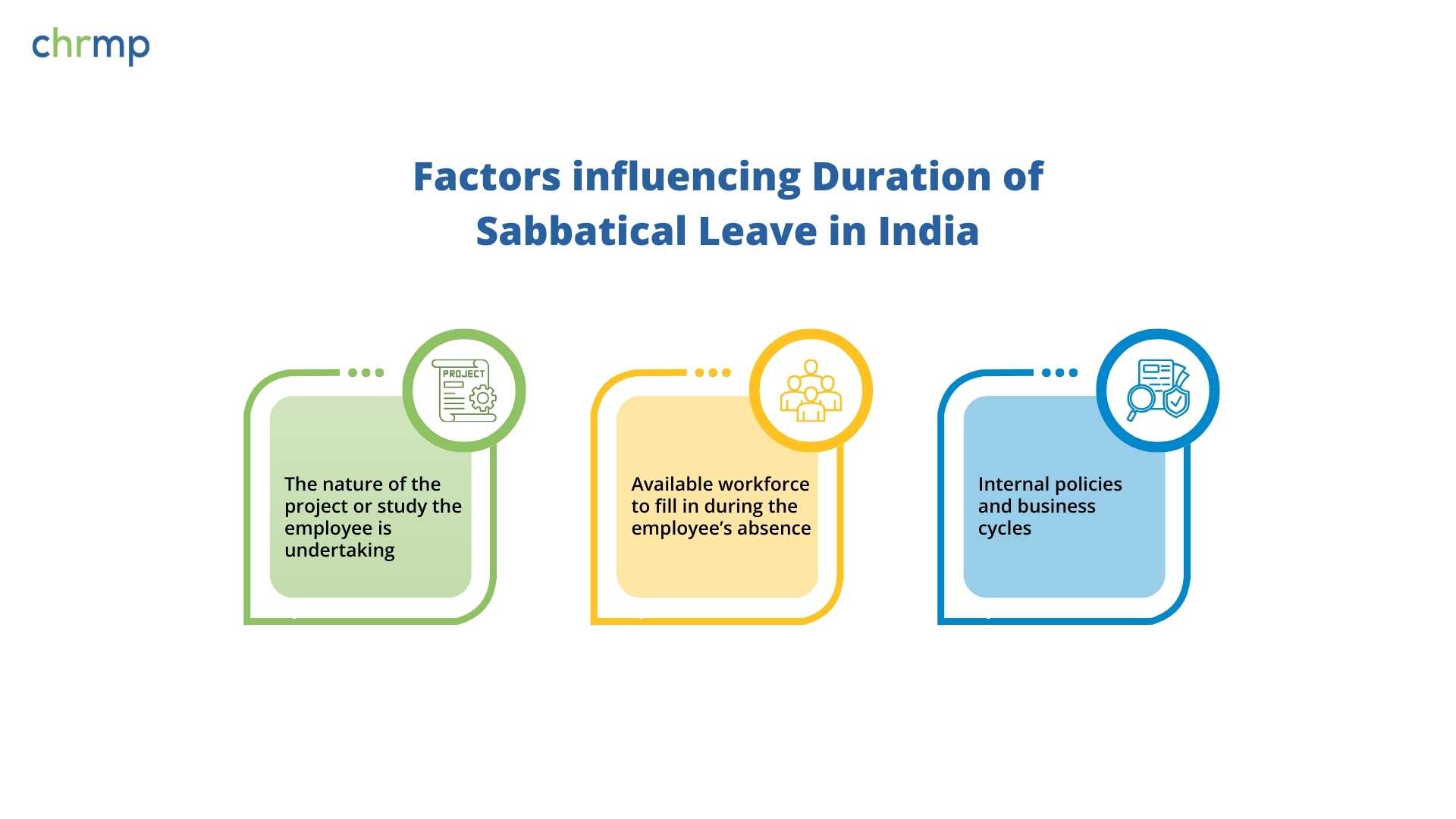
The duration typically ranges from three months to a year, although some companies allow even longer sabbaticals.
Factors influencing the duration may include
The nature of the project or study the employee is undertaking
Available workforce to fill in during the employee’s absence
Internal policies and business cycles
Extensions are usually possible but are subject to the employer’s discretion. Employees must provide valid reasons and must apply for extensions well in advance, making a strong case for why additional time is needed.
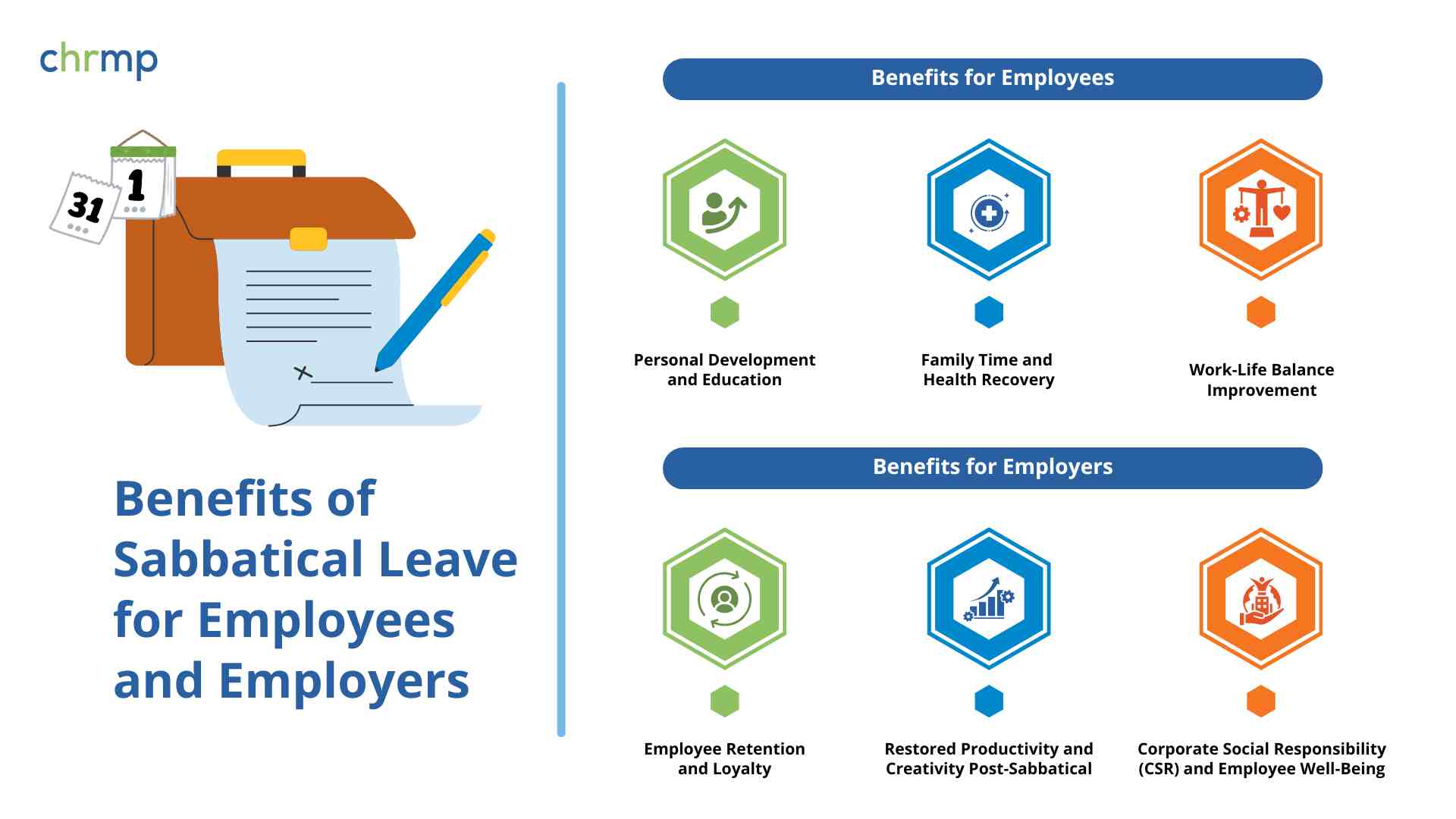
1. Personal Development and Education
Employees often use sabbaticals to pursue higher education, professional certifications, or research projects. This not only enhances their skill sets but can also increase their value to the organization upon their return.
2. Family Time and Health Recovery
Taking extended time off can be beneficial for personal well-being, whether it’s caring for a newborn, supporting an ailing family member, or focusing on mental and physical health.
3. Work-Life Balance Improvement
Prolonged stress can lead to burnout. Sabbatical leave offers a respite to recharge, reflect, and return with a renewed sense of purpose.
1. Employee Retention and Loyalty
Companies that offer Paid Sabbatical Leave in India or even unpaid but well-structured sabbatical leaves often see higher retention rates. Employees feel valued, which fosters loyalty and reduces turnover costs.
According to the Sabbatical Project, 80% of people who go on sabbatical ultimately return to their employers.
2. Restored Productivity and Creativity Post-Sabbatical
Employees returning from sabbatical frequently bring fresh perspectives, innovative ideas, and renewed motivation, all of which can significantly impact productivity and creativity.
3. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Employee Well-Being
Offering sabbatical leave is increasingly viewed as a socially responsible practice, showing the company’s commitment to employee welfare. This can strengthen the employer’s brand in the talent market.
Typically, the approval must come from both the employee’s reporting manager and the HR department. In some large organizations, final approval may also involve senior leadership if the role is critical.
In India, sabbatical leave policies vary widely. While Paid Sabbatical Leave in India exists in some organizations—particularly in academia and certain IT multinationals—most sabbaticals are unpaid or partially paid.
If the sabbatical is unpaid, the employee does not receive a regular salary during the sabbatical period. If it’s a paid or partially paid sabbatical, the salary may be disbursed according to agreed-upon terms—either a full salary for a limited period or a portion of the salary for the entire sabbatical.
For unpaid sabbaticals, PF contributions are usually paused because neither the employer nor the employee is contributing during the sabbatical. Upon returning, contributions typically resume as per the original PF arrangement. If the sabbatical is partially or fully paid, PF contributions may continue but could be recalculated based on the reduced salary.
Gratuity eligibility is generally tied to continuous years of service. Since many companies consider an approved sabbatical as continuous service, the employee’s gratuity is usually unaffected. However, it is advisable to confirm with your HR department, as policies differ. As for other retirement benefits—like superannuation or pension—employees should check the specific rules in their employment contracts or Sabbatical Leave Policies for Employers.
Theoretically, yes—if there are legitimate grounds such as misconduct, redundancy, or business closure. However, Employee Rights During Sabbatical Leave generally protect them from unfair termination. Termination of an employee on sabbatical without valid reason may be considered unlawful.
If an employee is terminated during an approved sabbatical without a fair reason, they can challenge the decision based on their employment contract and applicable labor laws. Employers should ensure due process is followed, which includes a proper notice period and a documented rationale.
Though Sabbatical Leave vs Maternity Leave are different in purpose, some employees choose sabbaticals to spend additional time with their newborn after exhausting statutory leave. However, this is entirely at the discretion of the employer and governed by the organization’s sabbatical policy.
Sabbatical leave policies in India provide employees with extended leave for personal or professional growth.
These policies typically outline eligibility criteria (such as minimum tenure), duration (ranging from a few months to a year), and compensation (paid, partially paid, or unpaid). Employers may specify acceptable reasons for a sabbatical, including higher education, research, volunteering, or personal commitments. The policy also includes application procedures, approval processes, and return-to-work guidelines to ensure smooth reintegration.
As companies increasingly focus on employee well-being and retention, structured sabbatical policies are becoming a valuable tool for work-life balance and professional development in India.
In today’s fast-changing business world, organizations must go beyond traditional leave policies to create a culture that prioritizes both productivity and employee well-being. Forward-thinking approaches to extended breaks and holistic wellness strategies can prevent burnout, inspire innovation, and build lasting loyalty. By fostering clarity, fairness, and flexibility in your HR practices, you cultivate a workforce that feels valued, engaged, and motivated to contribute their best.
Are you ready to create a workplace where employees thrive, innovate, and drive lasting success? Explore our certifications to take the next step in building a resilient, future-ready workforce. Let’s shape a culture of growth and excellence—together.
1. Who is eligible for sabbatical leave in India?
Employees who meet the minimum tenure requirement (commonly 3–5 years) and have a good performance record are typically eligible. However, the exact criteria vary by company.
2. What are the rules for sabbatical?
Rules can include minimum service duration, performance benchmarks, a formal application process, and an approval mechanism that considers the company’s business needs.
3. What is the policy for sabbatical leave?
Policies vary among organizations. Generally, they address eligibility criteria, duration, whether the leave is paid or unpaid, and the application and approval process.
4. What is the minimum duration of sabbatical leave?
Most companies have a minimum duration of 2–3 months. However, the norm in India ranges from 3 months to 12 months for a sabbatical.
5. What is sabbatical leave, and how is it different from other types of leave?
A sabbatical is an extended break for personal or professional development, lasting longer than typical annual or casual leaves. It’s not mandated by law, unlike maternity or sick leave.
6. Are sabbatical leaves legally mandated in India?
No, there is no specific legal mandate for sabbatical leaves in India. Organizations choose to offer them based on internal policies and strategic objectives.
7. Who is eligible to apply for sabbatical leave in Indian companies?
Eligibility usually hinges on tenure and performance. Some companies also have a “criticality of role” clause, limiting sabbaticals for certain job functions.
8. What are the common reasons for granting sabbatical leave?
Reasons include higher studies, skill enhancement, research, volunteer work, family obligations, and personal health recovery.
9. Is sabbatical leave paid or unpaid in India?
It varies. Some companies offer Paid Sabbatical Leave India, while others only offer unpaid sabbaticals. A few have hybrid models, providing partial pay or stipends.
10. How long can a sabbatical leave typically last?
It can last anywhere from a few months to a year. Some organizations allow extensions, subject to approval.
11. Are there any restrictions on how sabbatical leave can be utilized?
Generally, yes. Most companies require the leave to be used for constructive or genuine personal reasons. They may not allow employees to work for a competitor during this period.
12. Can employees retain their job role and benefits during sabbatical leave?
Employees typically retain their position, but the specifics regarding salary, PF, and other benefits depend on the employer’s policy. Some benefits may be paused or reduced during unpaid sabbaticals.
13. What is the procedure for applying for sabbatical leave in India?
Employees need to submit a formal application, outline the reasons and duration, and provide a transition plan. Approval generally involves discussions with both HR and senior management.

© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited
