

HR must evaluate an employee’s contribution and future potential when evaluating employee performance or an individual’s value to an organisation.
To guarantee proper recognition and reward, the performance of an employee’s team is calibrated based on the appraisal of their present contribution.
Conversely, succession planning, which involves evaluating future potential, identifies top-performing employees who can advance into future leadership positions.
Organisations can boost work satisfaction and retention rates by enhancing employee performance and identifying team members for potential leadership positions.
The 9 box grid is one of the most often used frameworks for evaluating employee performance.
The 9 box grid is a talent management tool that managers frequently use to compare employee performance to potential and inform their staff development and succession plans.
The 9 box grid is a straightforward, cost-free exercise that divides employee performance into quadrants and guarantees that employees are treated consistently across various performance groupings.
The 9 box grid is a popular method for classifying talent that is meant to assist firms in understanding the types of talent they have on hand and deciding where to concentrate their development efforts and funding.
The 9 box grid is open to all users. However, HR professionals, leaders, and other development specialists frequently utilise it.
It is frequently used in succession planning procedures in addition to talent management.
A thorough succession plan, however, goes beyond simply recognising talent inside an organisation; as a result, there needs to be more than just employing the 9 box grid approach to produce such a plan.
The McKinsey management consulting firm developed the 9 box grid as an evaluation framework to assist General Electric (GE) in prioritising its investments across business units in the 1970s when the concept first emerged.
The growth share matrix from the Boston Consulting Group served as its first inspiration for what became known as the GE-McKinsey nine-box structure.
To help investors make decisions, the structure was a little different; it compared industry attractiveness versus competitive strength.
Since then, HR has modified the grid by altering the axial parameters according to their needs to cover recruitment and selection reasons.
A 9 box grid for succession planning in your company can be created in three steps:
1. Assessing employee performance
Each employee’s performance level is evaluated in the first phase.
Depending on an organisation’s requirements, the precise evaluation criteria for performance change.
But each worker needs to be put into one of these three categories:
Low performance: The employee does not meet the requirements of the job and does not meet the set objectives.
They exhibit a lack of drive and agreement with the company’s mission.
Moderate performance: They perform moderately and partially to meet their jobs’ needs and objectives.
High performance: These type of employees entails meeting all job criteria and personal goals while also exhibiting consistency across all duties.
2. Assessing employee potential
The next step is to evaluate each employee’s potential.
The future growth potential, openness to learning new things, and aptitude for applying the information to normal activities all contribute to an employee’s potential.
Evaluation of employee potential is less common for firms than evaluation of employee performance, as was highlighted in one of the problems.
In the most straightforward words possible, performance and potential can be separated as representing past conduct and expected future behaviour, respectively.
Potential frequently belongs to the following groups:
Low potential: The worker has either attained their potential or lacks the drive to advance.
Moderate Potential: The employee’s performance or knowledge in their current position can grow.
High potential: The employee goes above and beyond what is expected of them in their duties and job.
They embrace leadership roles with enthusiasm and a natural aptitude for taking on new challenges.
Note: Even if the processes appear to be the same, assessing potential differs from rating performance.
For instance, a worker with low potential can already exert the effort necessary for the job at hand, leaving them unfit to hold leadership positions in the future.
On the other hand, if an employee receives top-notch training and development, they can be considered for leadership positions in the following two to three years even if they have a high potential but a low or moderate performance scale.
3. Create a 3×3 grid by combining performance and potential:
The last step is to plot each person on a 33 grid to create your 9 box grid after all employees have been given low, moderate, or high performance and prospective scores.
The grid makes it evident to managers and HR where each employee stands.
The 9 box grid, an essential component of the performance management process, calls for HR and managers to collaborate to place people in the appropriate grid boxes based on their assessed levels of performance and potential.
Although the process is iterative, the discourse must be thorough because the insights gained evaluating one person may change the judgement of the other.
Perspectives on the future worth of present aptitude areas could also be affected by organisational goals or competitor behaviour.
The 9 box grid appears as follows:
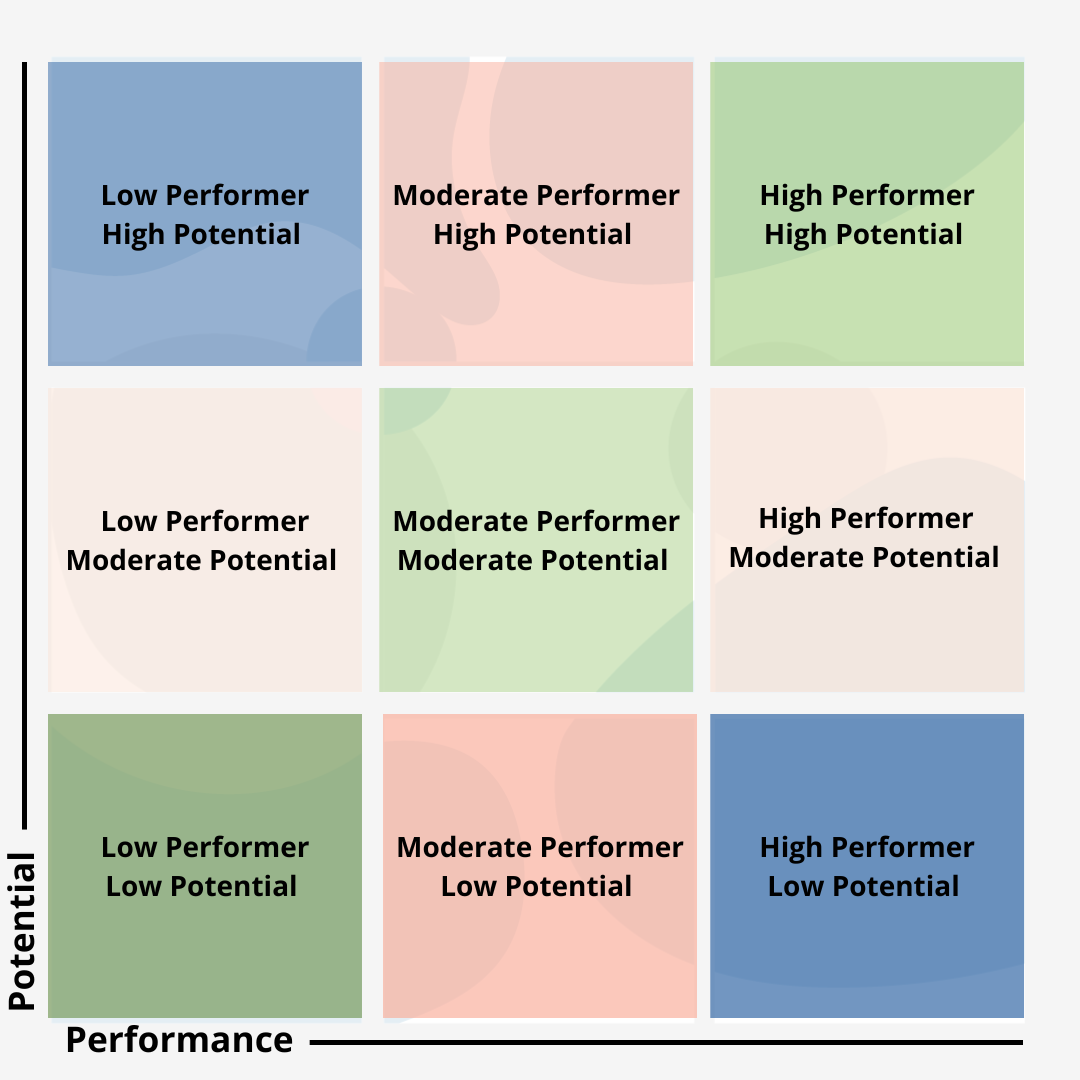
The 9 box grid is a divisive assessment instrument in human resources and people management.
While some consider it a simple concept, others consider it an old-fashioned strategy that places too much emphasis on labels.
But let’s go into more detail about both. The nine-box grid has the advantages and drawbacks listed below:
Let’s talk about the benefits of utilising the 9 box grid.
You may identify top achievers within the organisation who have a lot of potentials to become future leaders using the 9 box grid.
It aids in resource allocation and intelligent strategy development for including and fostering the growth of your organisation’s future leaders.
The 9 box grid also offers you an indication of the qualified people to take into consideration for these chances when internal promotions become available.
The lesser players, who aren’t currently qualified for their current position or lack particular skill sets, are also highlighted in the process of searching for high prospective leaders in the 9 box grid.
These insights give HR and managers the information they need to look into these workers further, give them the best support for achieving their next professional objective, and help these team members grow into stronger performers.
To evaluate the performance and potential of each employee, the leadership team must engage in open and honest communication.
These discussions aid in defining what the leaders anticipate from the staff in terms of contributing to the company’s objectives.
A 9 box grid model is a well-known tool with a relatively easy-to-understand structure.
When conducting an employee review, you must match the employee’s performance and potential to the appropriate box.
Even for people unfamiliar with this technique, the grid’s visual representation makes it simple to understand.
The 9 box grid offers a straightforward method of controlling talent and performance, but it is not without criticism.
Its most significant flaw is that it is linked to traditional performance management, which a manager’s annual, subjective evaluation characterises.
Continuous feedback has replaced annual performance assessments in several businesses, including Accenture and Deloitte.
This gives more options for performance improvement and more data points for precise performance evaluation.
We strongly advocate measuring performance with as many unbiased data points as possible.
Continuous feedback loops and goal-setting techniques like SMART goals or objectives and key results (OKRs) may be helpful in this situation.
Also important is transparency.
Without proper communication regarding talent management procedures, it may fall short of its intended outcome and lead to a “rank and yank” system in which workers are ranked against one another, and those at the bottom are fired (the yank).
The 9 box grid is not intended for this.
The 9 box grid should be used to develop and nurture talent instead, and through talent, the business may create a long-lasting competitive edge.
The 9 box grid has the following difficulties when used for talent and performance management:
It can be challenging to distinguish between potential and performance when both ideas have a clear definition and comprehension.
Organisations typically have a straightforward process for assessing performance; nevertheless, assessing potential is still less common, leading to incorrect assessments of potential in people.
Unconscious biases may also impact employee ratings without well-established procedures for selecting team members with high potential.
It may result in discouragement and poor employee morale if you are open and honest with your workers and provide performance information.
Being called a “poor performance” or “low potential” can cause unfavourable reactions in low-ranking employees, and with good reason.
The organisation’s teamwork and interpersonal relationships may be harmed by establishing a hierarchy among succession candidates due to sharing this information with the staff.
Your employees are limited to a single label by the 9 box grid, which impacts how management perceives them.
For example, A manager’s treatment and perception of an employee may vary if they are labelled as a low performance with low potential on the grid.

The 9 box grid has significant limits on its own, even though it can be a helpful tool for succession planning.
Combined with a performance value matrix, this method provides additional insights into the essential traits that all outstanding leaders possess.
The performance value matrix evaluates personnel across two dimensions: performance and culture values/behavioural alignment, in contrast to the 9 box grid, which scores performance and potential.
The performance value matrix provides insight into how employees get the best results if the 9 box grid identifies which employees do.
This primarily entails being aware of how successfully they collaborate with others to achieve their objectives.
Even if an employee excels in their team or area, they will only make good leaders if they use dishonest tactics and are tough to get along with.
The performance value matrix lists performance ratings from low to high on the y-axis and behavioural/value-based ratings on the x-axis. It is significantly more straightforward than the 9 box grid in its grid version.
It is possible to do succession planning that considers an employee’s capacity to produce results and how effectively they collaborate with others by connecting performance level to behavioural factors.

The holy grail of effective leadership succession planning, an article from Deloitte, emphasises how most organisations frequently fail to take the succession planning process seriously. Following a thorough investigation, they discovered that:
“More often than not, we found that companies were either avoiding succession planning altogether or were taking a dispassionate, process-oriented approach that minimises, or even ignores, the very real impact that it has on the people involved.”
The act of identifying and developing possible future leaders is essentially what succession planning entails.
It is crucial to the long-term success of a business in general.
When it comes to priorities, it can frequently be the case that a certain aspect of strategic planning is neglected and put on the back burner.
We are aware that well implemented succession planning enables businesses to make better long-term choices.
When properly implemented, it may be an effective tool for determining if team members are occupying the appropriate positions and for developing high-potential personnel for future advancement within the company.
The 9 box grid’s information can be utilised to find potential successors.
Leaders must consider current employees qualified to fill these responsibilities as soon as crucial roles have been identified.
Leaders should consider a number of people at various phases of their growth towards a role to have a strong succession bench.
Finding and developing individuals who can take over for successors as they advance in the firm is also crucial.
Leaders should concentrate on nurturing top talent while using the 9 box assessment for succession to prepare them for future roles.
This can be accomplished through leadership development, coaching, mentoring, and continuous 360-degree feedback.
A company’s succession plan is likely to include moderate performers and potential.
These people, in particular, can aid in filling vacancies left by elite talent who advance within the firm.
People with mediocre performance and high potential ratings may be candidates for succession if top talent is not readily available or suitable for particular essential tasks.
The 9 box grid is still a helpful talent management tool for promoting dialogue about employee performance and potential and facilitating organisational objectives.
The grid can be used effectively when the necessary criteria are discussed and defined clearly.
To ensure that the grid is worthwhile, deciding on the outcomes you want from the exercise before you begin is crucial.
Remember that assigning labels to your staff is not the real purpose of the 9 box grid.
Instead, it will be possible for you to review employees’ accomplishments during the assessment process and the talks that follow, ensuring that your company makes the appropriate development strategy investments.
As a result, be sure to be transparent about the talent and performance management strategies you use throughout the process.
To learn more about such interesting models visit, www.chrmp.com
1. What is a 9 box grid?
The 9 box grid is a talent management tool that managers frequently use to compare employee performance to potential and inform their staff development and succession plans.
2. How to create a 9 box grid?
To create the 9 box grid, you need to follow three steps: Assessing employee performance, Assessing employee potential and then combining these two.
3. What can you use a 9 box grid for?
The 9 box grid can be used for talent management and succession planning
4. How should I use the 9 box grid?
You can now map your employees onto the grid after you’ve done evaluating their performance and potential and bringing them all together.
Put them in the box that most closely matches their profile.
The results of your 9 box evaluation can then be used to implement particular coaching, talent management, and development methods for various personnel groupings.
© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited
