The Skill-Will Matrix is a powerful tool that helps you assess and categorize individuals based on their skill levels and willingness to perform a task or take on a particular responsibility.
By understanding where each team member falls on this matrix, you can make informed decisions about how to effectively manage and develop their talents.
Let’s look deeper into the Skill-Will Matrix to understand it better.
What is the Skill Will Matrix?
A skill will matrix is a visual tool for evaluating a person’s present abilities and willingness to learn new ones.
It enables people to recognize their areas of strength and growth, set priorities for their professional development objectives, and create plans for developing their talents.
The skill will matrix is divided into four quadrants, each representing a unique talent and readiness to learn that ability.
High Skill, High Will, High Skill, Low Will, Low Skill, High Will, and Low Skill, Low Will are the four quadrants.
Individuals may clearly understand which abilities they should concentrate on developing and how they can best do so by placing their skills in the relevant quadrant.
What’s the Difference Between Skill and Will?
Skill and will are two distinct aspects when assessing an individual’s potential and readiness to perform a task or take on a particular responsibility:
Skill refers to the level of proficiency, knowledge, and expertise an individual possesses in a specific area or task. It represents the person’s ability to perform the required job or activity effectively and efficiently. Skills can be developed through education, training, experience, and practice.

Examples of skills include technical expertise, problem-solving abilities, communication skills, or project management capabilities.
Will, on the other hand, pertains to an individual’s motivation, attitude, and willingness to engage in a task or take on new challenges. It reflects their level of commitment, enthusiasm, and initiative to accomplish a given goal.
Will is closely tied to factors such as personal drive, passion, interest, and work ethic. A person with high will demonstrates a proactive and positive attitude, embracing challenges and displaying a willingness to learn and grow.
While skill and will are separate dimensions, they often intersect and influence each other. A person may have high skill levels but lack the motivation or willingness to fully utilize their abilities.
On the other hand, someone with a strong will may exhibit enthusiasm and motivation, but their skill level may need further development to perform at their best.
Understanding the distinction between skill and will allows managers and leaders to assess individuals holistically, identify areas for growth and improvement, and design strategies to maximize their potential.
By leveraging this understanding, organizations can create tailored development plans, assign tasks effectively, and nurture a productive and engaged workforce.
Purpose of the Skill Will Matrix
The Skill Will Matrix was created to give people a framework for professional development and self-evaluation. It benefits people in the following ways:
1.Determine their areas of strength and need for development: People may determine their areas of strength and the skills they need to work on by examining their talents and willingness to learn new ones.
2.Prioritize their professional development goals: Organize and prioritize your professional development goals by putting your talents in the relevant quadrant.
Depending on your expertise and willingness, you may decide which skills you should work on most.
3.Create a plan for skill development: The Skill Will Matrix gives people a visual representation of their talents and willingness to learn more about them, enabling them to create a plan for improving their skills.
4.Increase their employability: People may raise their employability and competitiveness in the job market by consistently developing their abilities.
5.Promote job advancement: People can improve their career chances by concentrating on gaining talents in the High Skill, High Will quadrant.
The Skill Will Matrix is an effective tool for those who want to grow their professions and constantly develop their talents.
How to Use the Skill Will Matrix
The skill will matrix evaluates a person’s capacity and drive to perform a certain activity or job function.
The skill will matrix is often shown as a grid, with the vertical axis reflecting motivation and the horizontal axis representing ability.
An individual’s potential for success in a particular position may be inferred from the intersection of these two variables.
The steps below can be used to implement the skill will matrix:
1.Determine the job function or task you wish to evaluate: Choose the exact activity or job function for which you wish to assess a person’s likelihood of success.
2.Determine the person’s capacity: Determine the person’s current skill and knowledge level connected to the assignment or job function.
Determine the person’s interest, zeal, and dedication to the task or job function while evaluating their motivation.
3.Graph the outcomes on the matrix: Create a dot by placing the person’s ability level on the horizontal axis and their motivation level on the vertical axis.
4.Interpreting the outcomes: Your interpretation of the person’s potential for success in the task or job function will depend on where the dot is located on the matrix.
If the dot is located in the top-right quadrant, the person is capable and motivated, suggesting they are a good fit for the position.
If the dot is located in the bottom-left quadrant, the person may not be a good fit for the position since they lack competence and motivation.
Note: The skill will matrix should be used as one tool among many in a comprehensive evaluation of a person’s likelihood of success in a particular position.
It does not represent a clear-cut or exclusive indicator of a person’s fitness for a task or job function.
Knowing Your Capabilities and Willingness to Advance Them:
1.Listing your present abilities: This phase entails conducting a self-evaluation to discover the hard and soft skills (such as technical proficiency) you possess (such as communication and teamwork).
This can be accomplished by self-reflection, getting input from mentors and coworkers, or taking a skills assessment.
2.Assessing your willingness to learn each skill: This phase entails assessing your drive to develop each of your listed abilities.
Consider things like your degree of interest, its effect on your job, and how much work it will take to improve.
3.Appreciating the value of each talent in light of your professional objectives: This phase entails assessing how your skills correlate with your long-term career ambitions.
Think about the most important abilities for your chosen position, sector, or future objectives.
Steps of creating a skill will matrix:
1.Determine the competencies you wish to evaluate: List every talent you wish to evaluate.
2.Determine how well you are at each skill: Evaluate your present level of competence in each ability by giving yourself a score between 1 and 10. (1 being low proficiency, 10 being high proficiency).
3.Determine whether you are willing to learn each skill: Rate your level of motivation for mastering each skill on a scale from 1 to 10. (1 being low motivation, 10 being high motivation).
4.Draw a matrix showing the skills: The two axes of the grid should be ability and willingness. Plot each skill as a point on the matrix, with the ability score dictating the position horizontally and the willingness score dictating the position vertically.
The Four Quadrants of the Skill Will Matrix
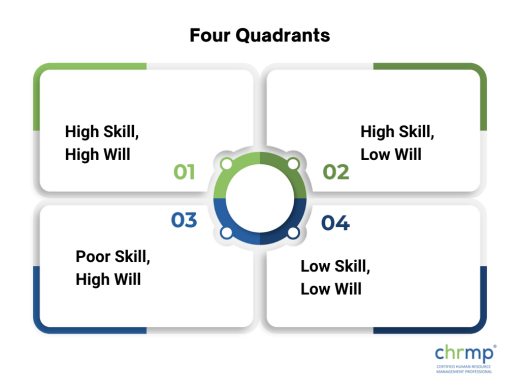
1.High Skill, High Will: Your abilities and desire to do better are high in this quadrant, represented by your skills.
You should prioritise these talents since they are probably essential to your success in your present position or your long-term professional objectives.
2.High Skill, Low Will: Skills in which you are highly skilled but lack the will to improve.
You could think about your lack of motivation and see if there are any methods to improve it.
Alternatively, you could prefer to concentrate on competencies in other quadrants that are more crucial for your professional objectives.
3.Poor Skill, High Will: This quadrant of skills represents your areas of low skill but high improvement motivation.
As your motivation may propel you to study and grow fast, these abilities should be prioritized for development because they may be crucial for your future job ambitions.
4.Low Skill, Low Will: The skills in this quadrant reflect your low ability as well as your lack of improvement drive.
If these talents aren’t critical for your present position or long-term professional objectives, you might want to think about whether it would be wise to acquire them.
Examples of Skills and Their Placement in the Skill Will Matrix:
It’s vital to understand that a skill’s placement in a particular quadrant just indicates its current degree of competence and readiness to grow. It says nothing about how excellent or poor a talent is.
The ideal quadrant is “High Skill, High Will” since it denotes a skill in which the person is already excellent and has a strong desire to keep improving.
Individuals should concentrate on improving their talents in this sector and look for opportunities to use them in their professional or personal lives.
The talent represented by the “High Skill, Low Will” quadrant is one in which the person is already skilled but has little desire to learn more.
In this quadrant, the person could think about the reasons for their lack of enthusiasm to keep learning the skill and whether it is still important to their objectives.
If it is unnecessary, they could decide to drop the talent.
If it is still applicable, they might want to look for ways to boost their motivation, such as coming up with a fresh challenge for the skill or coming up with a brand-new use for it.
The quadrant labelled “Low Skill, High Will” denotes a skill in which the person is not yet adept but has a great desire to learn.
The individual should concentrate on developing their talents in this quadrant through practice, instruction, or training.
In order to develop their confidence and mastery, they should also look for chances to put their new talents to use.
The skill that the person is not yet skilled in and has poor motivation to learn is represented by the “Low Skill, Low Will” quadrant.
The person may want to think about whether the talent is important to their goals in this quadrant, and if not, they may decide to let it go.
If the talent is still useful, they might wish to find a fresh challenge or use for it to boost their drive.
In conclusion, anyone wishing to further their professional growth may find the Skill Will Matrix to be a useful tool.
Individuals may prioritize their development efforts and choose the talents they wish to grow by analyzing their existing skills and willingness to develop them.
Using the Skill Will Matrix to Drive Professional Development
1.Prioritizing the Development of Skills Using the Skill Will Matrix
As these are the talents they are currently excellent in and have a strong desire to keep learning, they should give those in the “High Skill, High Will” quadrant priority.
These are the abilities that will most likely enable them to accomplish their professional objectives and bring them happiness and contentment.
2.Strategies for Developing Skills in the High Skill, High Will Quadrant
Those with skills in the “High Skill, High Will” quadrant should concentrate on honing and enhancing them. Among the tactics to take into account are:
3.Looking for new and more difficult challenges: Look for new opportunities to use the talent.
4.Finding a mentor or coach: Locate a subject-matter authority and ask for their advice and input.
5.Continuous learning: By enrolling in classes, going to seminars, or reading books and articles, you may keep up with the newest innovations and discoveries in the field.
6.Practising the skill regularly: Finding opportunities to use the skill in both professional and personal contexts consistently can help you maintain and advance your mastery of it.
Skills-Building Techniques for the High Skill, Low Will Quadrant:
Individuals may need to discover strategies to boost their drive to keep learning abilities in the “High Skill, Low Will” quadrant. Among the tactics to take into account are:
1.Reframing the skill: Finding a new challenge or application for the talent that is more enticing or meaningful to the individual is known as reframing the skill.
2.Pursuing fresh learning possibilities: Take classes or go to workshops that will help the person rediscover their enthusiasm for the skill and give them a new perspective on it.
3.Finding a coach or mentor: Work with someone who has a strong interest in the subject and who can offer direction and help.
Skills Development Strategies for the Low Skill, High Will Quadrant:
People should concentrate on developing their talents from the ground up for skills in the “Low Skill, High Will” quadrant. Among the tactics to take into account are:
1.Seeking out training or education: Enroll in classes or seminars to get a thorough grasp of the skill. Seeking training or education.
2.Practising the skill regularly: Regular practice will help you gain confidence and perfect your talent. Look for opportunities to use the skill in practical settings.
3.Seeking coaching or mentoring: Work with a person who is skilled in the area and who can offer direction and criticism.
4.Reading and gaining knowledge of the ability: To further comprehend the skill and keep up with the most recent advances, read books, articles, and webinars.
Skills Development Strategies for the Low Skill, Low Will Quadrant:
People may need to discover strategies to boost their ability level and drive to learn abilities that fall under the “Low Skill, Low Will” quadrant.
Among the tactics to take into account are:
1.Reframing the skills: Finding a new challenge or application for the talent that is more enticing or meaningful to the individual is known as reframing the skill.
2.Pursuing fresh educational possibilities: Take classes or go to workshops that will help the person rediscover their enthusiasm for the skill and give them a new perspective on it.
3.Finding a coach or mentor: Work with someone who has a strong interest in the subject and who can offer direction and help.
4.Considering the advantages of the skill: Think about the benefits that the skill adds to the person’s life and career and how to further improve the talent that could increase these advantages.
A useful tool for evaluating one’s talents and setting priorities for professional growth is the skill will matrix.
People can construct a growth plan that is in line with their professional objectives by assessing their present skill levels and willingness to learn each skill.
Bottom line
Individuals may adopt an organized approach to their professional growth by using the Skill Will Matrix, which will help them concentrate their efforts where they will have the biggest impact.
As people continue to learn and advance their abilities, they may return and update their matrix, making it a helpful tool for continual self-reflection.
The Skill Will Matrix is a flexible tool that may be applied to a person’s career.
Individuals may stay on track and advance in their professional development by periodically reviewing their matrix and making necessary adjustments to their growth strategy.
It is a helpful tool for people who are dedicated to ongoing personal development.
To know more about the skill will matrix, visit www.chrmp.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.How does the Skill Will Matrix function, and what is it?
The Skill Will Matrix is a tool for evaluating one’s present skill level and aptitude for learning new abilities. Displaying a person’s talents on a matrix with two axes—skill level and desire to learn—assists people in setting priorities for their professional growth.
The matrix is then split into four quadrants, each of which represents a particular skill and willingness combination, enabling people to pinpoint areas where they may concentrate their development efforts.
2.What do the four Skill Will Matrix quadrants represent, and what do they mean?
The High Skill, Low Will, Low Skill, High Will, and Low Skill, Low Will quadrants of the Skill Will Matrix are the four categories.
A talent’s quadrant placement reflects both a person’s present ability level and willingness to learn that skill.
For instance, the talents in the High Skill, High Will quadrant show areas in which the person has a solid foundation and a high level of willingness to learn more.
3.How much professional development be influenced by the Skill Will Matrix?
The Skill Will Matrix may be used to prioritize areas where a person has a high skill level and a high level of willingness in order to promote professional growth.
The greatest prospects for growth and development are found in these areas.
The matrix may also be used to pinpoint areas where a person has a high capacity for growth but a low degree of proficiency, highlighting areas where they may require further education or resources to strengthen their foundation.
The matrix may also assist people in coming up with plans for honing their talents in each of the four quadrants, enabling them to design an extensive development strategy that takes into consideration both their current abilities and their capacity for growth.







