Think about managing people without a plan—it’s like trying to build a house without a blueprint. Sure, you might end up with something, but will it stand strong? That’s where human resources models come in. They’re the well-thought-out frameworks that guide organizations in managing their most valuable asset—people.
At their core, HR models are structured approaches designed to make the complex world of people management easier to navigate. These models provide HR professionals with practical tools to address challenges like hiring, employee engagement, and performance management. They’re not just theories; they’re proven strategies that help organizations create workplaces where employees thrive, and business goals are met seamlessly.
Here’s why they matter: human resources models bring structure and clarity to HR practices. Think of them as a map for aligning employee needs with business objectives. They ensure every HR activity—whether it’s recruitment, training, or succession planning—is part of a bigger, purposeful strategy.
But it’s not just about processes; it’s about creating a workplace where people feel valued and motivated. HR frameworks help organizations design systems that support employees while driving company growth. They’re like a compass, pointing HR teams in the right direction when it comes to building strong, effective teams.
In short, HR management models are the secret sauce to turning a good workplace into a great one. Ready to uncover how these frameworks can simplify your HR strategy and elevate your people management? Let’s explore further!
Importance of Human Resources Models in 2025
Now that we understand what human resources models are, let’s delve into why they’re indispensable for modern organizations. Think of them as the backbone of your HR strategy—keeping everything aligned, efficient, and impactful. Here’s a detailed look at why these models are critical:
-
Ensuring HR Effectiveness Through Consistency
One of the greatest challenges in HR is maintaining consistency across processes, especially in large or fast-growing organizations. Without a structured approach, hiring practices, performance reviews, or employee engagement initiatives can vary wildly across teams or departments.
For instance, imagine a company with offices in multiple cities. Without a unified model, one location might prioritize quick hires while another takes a more strategic, culture-focused approach. The result? Misaligned teams and uneven outcomes. HR models act as a standardizing tool, ensuring everyone follows the same proven strategies. This consistency builds trust and ensures fairness across the organization, creating a more effective and unified workforce.
-
Aligning Workforce Goals with Business Objectives
It’s not enough for HR to manage people—they need to drive business success. HR models excel at aligning workforce strategies with the company’s larger objectives. By mapping out how talent acquisition, development, and retention contribute to business goals, HR teams can ensure that every initiative directly supports the organization’s growth.
Take, for example, a retail company preparing for peak holiday season. An HR model helps forecast staffing needs, align recruitment timelines, and train employees to deliver exceptional customer service—all while staying aligned with profitability targets. This alignment ensures that HR isn’t just a support function but a strategic driver of success.
-
Promoting Efficiency in HR Operations
Let’s face it—HR departments often juggle a lot. From managing payroll and benefits to handling employee relations and compliance, the workload can be overwhelming. HR models streamline these tasks by offering clear guidelines and workflows, reducing redundancy, and cutting down on inefficiencies.
Think about a manufacturing company with a complex hierarchy. An HR model can simplify processes like succession planning by clearly defining criteria for promotions, timelines for training, and evaluation metrics. This clarity not only saves time but also ensures the right people are in the right roles when they’re needed most.
-
Enhancing Employee Experience and Engagement
Employee satisfaction isn’t just a feel-good metric—it’s a business imperative. A robust HR model ensures that employee needs are met consistently, fostering a workplace where people feel valued and motivated. By integrating practices like regular feedback, growth opportunities, and fair policies, HR models create a thriving workplace culture.
For example, companies like Adobe use a feedback-driven HR model to replace traditional annual performance reviews with ongoing check-ins. This approach has boosted employee engagement and productivity while staying aligned with the company’s innovative spirit.
-
Preparing Organizations for the Future
The business landscape is ever-changing, and organizations need to be agile to survive. HR models provide the flexibility to adapt to new challenges like remote work, technological advancements, or shifting market demands.
Consider how the COVID-19 pandemic forced businesses to rethink their workforce strategies. Companies with adaptable HR models quickly pivoted to remote work, maintained employee morale, and even upskilled teams to meet changing needs. This ability to future-proof operations is a hallmark of effective HR frameworks.
In conclusion, the importance of HR models cannot be overstated. They ensure HR effectiveness, drive workforce alignment, and create a roadmap for tackling today’s challenges while preparing for tomorrow. Whether it’s improving efficiency, aligning with business goals, or enhancing employee satisfaction, HR models are the foundation of effective people management.
Ready to explore specific HR models and how they bring these benefits to life? Let’s dive deeper!
Popular Human Resources Models
To drive success in people management, HR professionals need structured approaches that address real-world challenges. The types of HR models discussed here are practical frameworks that can be applied directly to align HR strategies with organizational goals. Let’s explore two widely-used models—the Harvard Model and Ulrich’s HR Model—and how they can be used to create meaningful results.
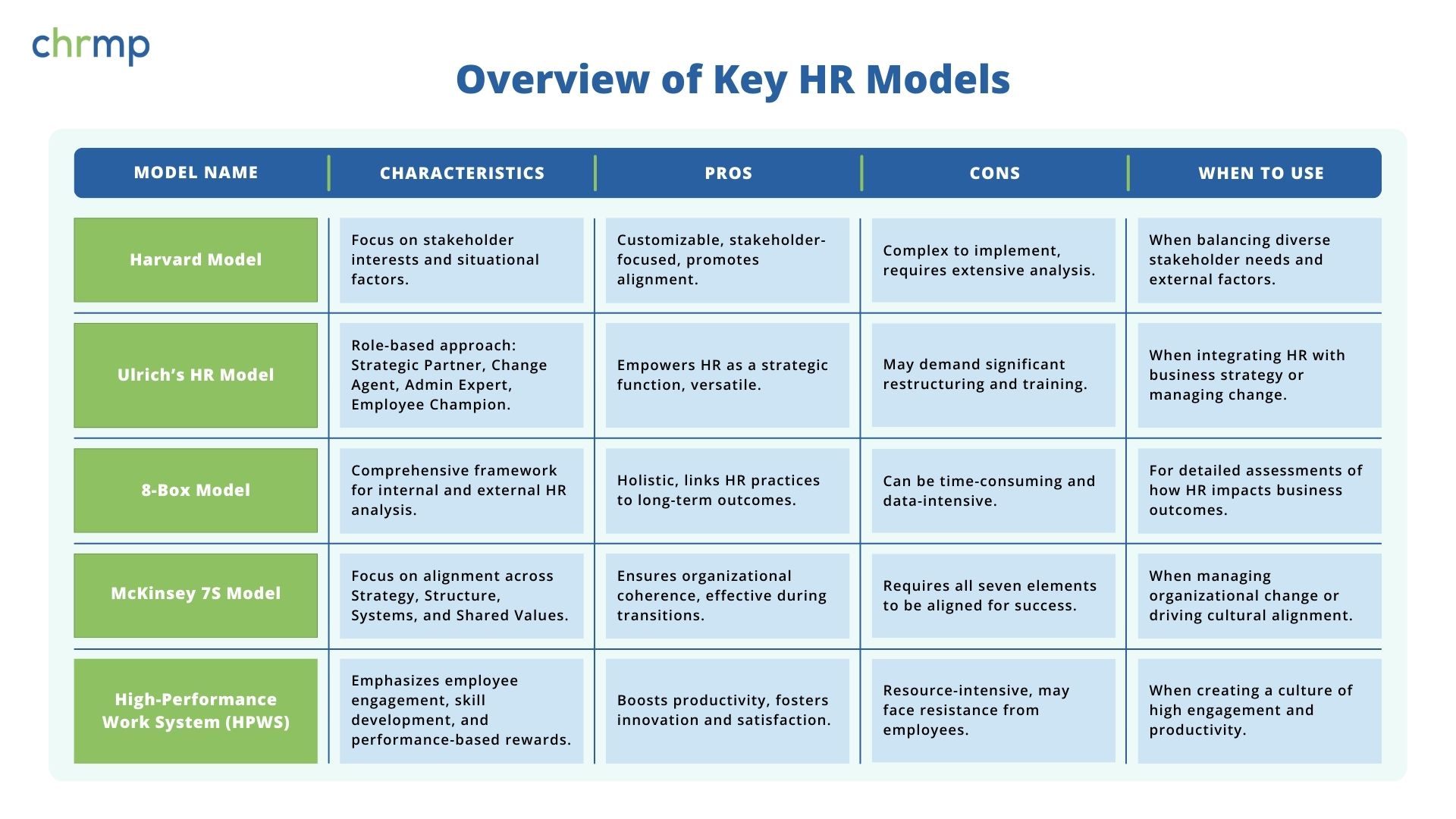
Overview of Key HR Models
The Harvard Model of HR Management
The Harvard Model focuses on understanding the bigger picture of human resource management. It’s not just about policies or processes; it’s about tailoring HR practices to fit the organization’s unique circumstances while balancing the needs of various stakeholders, such as employees, leadership, and external customers.
How It Works
The Harvard Model is built on two key pillars:
- Stakeholder Interests: HR must balance the priorities of employees, managers, shareholders, and customers. Each group has different expectations from HR practices.
- Situational Factors: Factors like organizational culture, economic conditions, and industry trends heavily influence HR decisions.
The outcomes of the model aim for:
- Employee Commitment: Creating a loyal and motivated workforce.
- Competence: Ensuring employees have the skills to meet organizational demands.
- Congruence: Aligning employee and organizational goals.
- Cost-effectiveness: Managing HR practices within budget constraints.
Applying the Harvard Model in Real Life
Let’s take an example of a mid-sized manufacturing firm experiencing high employee turnover. Using the Harvard Model, HR professionals can:
- Identify key stakeholders, such as employees (who seek better work-life balance) and managers (focused on maintaining production timelines).
- Analyze situational factors, like local labor market conditions or cultural barriers affecting retention.
- Design strategies to improve employee commitment—for instance, introducing flexible shifts or providing upskilling opportunities tailored to their needs.
The Harvard Model emphasizes customization. It reminds HR teams that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution and encourages thoughtful, strategic decision-making that balances all perspectives.
Ulrich’s HR Model
David Ulrich’s HR Model redefined HR by focusing on roles rather than functions. Instead of seeing HR as a purely administrative department, this model positions HR professionals as integral to the business’s success by taking on four distinct roles:
The Four Roles Explained
- Strategic Partner: Align HR practices directly with business objectives, ensuring HR actively supports company growth and innovation.
- Change Agent: Lead and manage change initiatives, helping employees and leaders adapt to shifting organizational needs.
- Administrative Expert: Optimize day-to-day HR processes to ensure smooth operations and compliance.
- Employee Champion: Represent employees’ interests, advocating for their well-being, engagement, and development.
How HR Professionals Can Apply Ulrich’s Model
Picture a fast-growing tech startup expanding into new markets. Here’s how the Ulrich Model can guide their HR strategy:
- As a Strategic Partner, HR can collaborate with leadership to design a talent acquisition strategy focused on hiring specialists for the new markets.
- Acting as a Change Agent, HR can guide the existing team through training programs to adapt to the new organizational structure.
- Taking on the Administrative Expert role, HR can streamline payroll and compliance systems to support a geographically dispersed workforce.
- Finally, as an Employee Champion, HR can establish mentoring programs to help employees manage the transition and feel supported.
Ulrich’s model empowers HR professionals to wear multiple hats, proving that HR isn’t just about managing policies but driving organizational success through active, strategic involvement.
The 8-Box Model by Paul Boselie
The 8-Box Model, developed by HR expert Paul Boselie, provides a comprehensive way to analyze and optimize human resource management. This model emphasizes the interplay between external influences, internal HR practices, and business outcomes, helping HR professionals create strategies that are balanced and effective.
The Eight Components of the Model
- External General Market Context: Includes broader economic, legal, and societal factors affecting the organization.
- External Population Market Context: Focuses on industry-specific factors, like competition and labor market conditions.
- Internal Organization Context: Covers the company’s culture, structure, and internal dynamics.
- HRM Configuration: Refers to the specific HR strategies and practices in place.
- Employee Contributions: Assesses the output of employees, such as skills, performance, and engagement levels.
- HR Outcomes: Measures the impact of HR practices, including job satisfaction, retention, and productivity.
- Strategic Outcomes: Evaluates how well HR outcomes align with organizational goals.
- Long-term Outcomes: Looks at sustainability, profitability, and the overall health of the organization.
How to Apply the 8-Box Model in Real Life
Imagine a retail company struggling with employee turnover during peak shopping seasons. Using the 8-Box Model, HR professionals can:
- Examine external factors, like the competitive labor market and economic conditions affecting retail hiring.
- Align HRM configurations by introducing flexible shift patterns or seasonal bonuses to attract talent.
- Measure HR outcomes, such as improved retention rates and higher job satisfaction.
- Link these improvements to strategic outcomes, like increased sales during peak periods, and eventually to long-term goals, such as maintaining a strong employer brand in the industry.
This model encourages HR professionals to think holistically, connecting day-to-day practices with long-term organizational success.
McKinsey 7S Model
The McKinsey 7S Model is a classic framework designed to ensure alignment across seven key elements of an organization. Originally created for business strategy, it’s also incredibly effective when applied to HR management. The 7S framework helps HR teams drive coherence between strategy, structure, and culture, which are critical for organizational effectiveness.
The Seven Elements
The model is divided into two categories:
- Hard Elements: Strategy, Structure, Systems.
- Soft Elements: Shared Values, Skills, Style, Staff.
How It Works
- Strategy: Ensure HR strategies align with the company’s overall goals. For instance, if the goal is to become an innovation leader, HR must prioritize hiring creative talent.
- Structure: Assess the organization’s hierarchy and reporting lines to support its strategy effectively.
- Systems: Refine processes like recruitment, performance management, and payroll to ensure efficiency.
- Shared Values: Foster a workplace culture that reflects the organization’s mission and values.
- Skills: Identify and develop key competencies required to achieve business objectives.
- Style: Ensure leadership styles promote collaboration and align with company values.
- Staff: Focus on hiring, retaining, and developing the right talent.
Applying the McKinsey 7S Model in Real Life
Consider a manufacturing company transitioning to automation. The HR team can use the McKinsey 7S Model to:
- Align their strategy by hiring experts in automation technologies.
- Adapt the structure by creating new roles and defining clear reporting lines for tech teams.
- Implement new systems for training employees to work alongside automation tools.
- Reinforce shared values by promoting innovation and adaptability as core principles.
By addressing each element of the model, HR ensures the organization is not only prepared for the transition but also thriving in the new operational landscape.
High-Performance Work System (HPWS)
The High-Performance Work System (HPWS) is a model that focuses on creating a culture where employees are empowered, engaged, and highly productive. This framework emphasizes the integration of HR practices to build an environment where both individuals and organizations thrive.
Key Features of HPWS
- Employee Involvement: Encourages employees to participate in decision-making processes, fostering ownership and accountability.
- Skill Development: Focuses on continuous learning through training and development programs to enhance employee competencies.
- Performance Management: Aligns employee objectives with organizational goals, ensuring everyone is working towards a shared vision.
- Reward Systems: Implements performance-based rewards to motivate employees and recognize achievements.
- Work Design: Structures jobs to encourage collaboration and innovation, ensuring that roles are meaningful and impactful.
How to Apply HPWS in Real Life
Consider a software company aiming to boost innovation and employee satisfaction. The HR team can use the HPWS model to:
- Create a feedback-driven performance management system that ties individual contributions to project milestones.
- Launch upskilling initiatives to help developers stay ahead of industry trends, fostering skill development.
- Offer performance-based incentives, like bonuses for delivering high-quality features ahead of deadlines.
- Design cross-functional teams to encourage knowledge-sharing and employee involvement in critical decisions.
By adopting HPWS, the company not only enhances productivity but also builds a motivated and engaged workforce, driving long-term success.
Conclusion | Human Resources Models?
Human resources models are not just theoretical concepts; they are practical tools that HR professionals can use to drive efficiency, alignment, and success. Each model has unique strengths tailored to different challenges:
- The Harvard Model emphasizes balancing stakeholder interests and situational factors, encouraging customized strategies.
- Ulrich’s HR Model redefines HR’s role, empowering professionals to be strategic partners, change agents, administrative experts, and employee champions.
- The 8-Box Model provides a comprehensive way to analyze internal and external factors influencing HR practices, ensuring balanced decision-making.
- The McKinsey 7S Model ensures alignment across strategy, systems, and values, making it ideal for managing transitions and fostering coherence.
- The High-Performance Work System (HPWS) focuses on creating a culture of engagement, productivity, and continuous improvement.
By understanding and applying these HR frameworks, HR professionals can tackle real-world challenges, align workforce strategies with organizational goals, and create thriving workplaces. Whether you’re navigating change, building a high-performance culture, or ensuring strategic alignment, these models provide the roadmap to success.
Take these frameworks, adapt them to your unique organization, and watch as your people management strategies evolve into powerful drivers of business growth.
Choosing the Right HR Model for Your Organization
Selecting the best HR model isn’t just about following trends—it’s about finding a framework that aligns with your organization’s unique needs and goals. With so many effective HR frameworks available, how do you make the right choice? The answer lies in evaluating key factors and customizing the model to suit your organization’s context. Let’s break it down into actionable steps:
1. Understand Your Organization’s Size and Structure
A small business with a lean team will have different HR needs than a multinational corporation with a complex hierarchy.
For startups, a model like HPWS might be ideal to build engagement and productivity early. Larger organizations may benefit from Ulrich’s HR Model, which assigns defined roles like strategic partner or administrative expert to HR professionals.
2. Analyze Your Industry Demands
Industry-specific challenges dictate HR priorities. For instance, tech companies need agility and innovation, while manufacturing may focus more on efficiency and compliance.
Use the 8-Box Model to assess external market factors and internal needs, ensuring your HR strategies reflect the realities of your industry.
3. Define Clear Organizational Goals
HR practices must directly support business objectives, whether it’s rapid growth, innovation, or workforce stabilization.
If your goal is cultural transformation, the McKinsey 7S Model can help align strategy, structure, and shared values. For improving talent retention, the Harvard Model offers a stakeholder-focused approach.
4. Consider Organizational Culture
HR models are most effective when they resonate with the company’s culture and values. A misaligned framework can create friction rather than cohesion.
Evaluate how the chosen model complements your existing culture. For example, HPWS works well in innovation-driven organizations, while the Harvard Model suits organizations emphasizing collaboration and inclusivity.
5. Customize the Framework
No model works out-of-the-box for every organization. Tailoring the framework ensures it addresses your specific challenges and leverages your strengths.
Take the principles of your chosen HR model and adapt them. For instance:
- Combine Ulrich’s HR roles with the cultural alignment focus of the McKinsey 7S Model.
- Use HPWS in tandem with the 8-Box Model to integrate external market realities with high-performance practices.
Taking Action
Once you’ve evaluated these factors, it’s time to put your plan into action:
- Pilot the Model: Start with a department or team to test how well the framework works in your context.
- Gather Feedback: Involve employees and leadership to identify what’s working and what needs adjustment.
- Refine and Scale: Make necessary changes based on feedback, then roll out the tailored model organization-wide.
Final Thought
Choosing the right HR model is less about picking the “best” one and more about finding the one that fits. By considering your organization’s size, industry, goals, and culture, and by tailoring the model to your specific needs, you can create an HR strategy that’s both practical and transformative. With the right framework in place, your HR team will be better equipped to drive business success and foster a thriving workforce.
Challenges in Implementing HR Models
Implementing HR models can transform an organization’s people management practices, but it’s not without its hurdles. Globally, HR professionals encounter several common HR implementation challenges, often stemming from resistance, resource limitations, or misalignment with organizational goals. Let’s explore these challenges and strategies to overcome them effectively.
1. Resistance to Change
Employees and managers often resist new HR frameworks, especially if they disrupt familiar processes or demand a shift in behavior. Change can be intimidating, leading to pushback or lack of buy-in.
This is a universal challenge across industries, from manufacturing to technology. Employees fear losing autonomy, while managers worry about increased workloads.
Mitigation strategies:
- Communicate Clearly: Share the purpose and benefits of the new HR model with all stakeholders.
- Involve Teams Early: Engage employees and managers during the planning stage to foster ownership and reduce resistance.
- Provide Training: Equip employees with the skills needed to adapt to new processes.
2. Lack of Resources
Implementing an HR model requires investments in technology, training, and skilled personnel. Many organizations, especially smaller ones, struggle to allocate sufficient resources.
Resource constraints are common in emerging markets or during economic downturns, where HR budgets are often among the first to be cut.
Mitigation strategies:
- Start Small: Pilot the model with a single team or department before scaling up.
- Leverage Technology: Use cost-effective HR software to automate processes and reduce administrative burdens.
- Seek Leadership Support: Present a clear ROI to leadership to secure additional funding.
3. Misalignment with Business Goals
When an HR model isn’t aligned with the company’s overall objectives, it creates disconnects, wasted effort, and limited impact on organizational success.
This challenge is prevalent in organizations with siloed departments, where HR and business leaders operate independently.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Collaborate with Leadership: Work closely with senior management to align HR strategies with business goals.
- Regular Reviews: Continuously assess the model’s effectiveness and make adjustments to ensure alignment.
- Focus on Metrics: Use data to demonstrate how HR outcomes support business objectives, fostering credibility and alignment.
4. Overly Complex Models
Some HR models are intricate, requiring significant expertise and time to implement. This complexity can overwhelm teams and stall progress.
In fast-paced industries like retail or startups, complex frameworks often clash with the need for agility and simplicity.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Simplify: Adapt the model to focus only on the most relevant elements for your organization.
- Phased Implementation: Break the process into manageable steps to avoid overwhelming HR teams.
- Use External Expertise: Consider hiring consultants or experts to streamline implementation.
5. Cultural Misfit
A one-size-fits-all HR model may not align with an organization’s unique culture, values, or employee expectations.
This is particularly evident in multinational organizations, where cultural differences can create friction in implementing standardized HR practices.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Customize: Tailor the model to reflect your company’s culture and employee needs.
- Localize: For global organizations, adapt the model to respect regional and cultural nuances.
- Engage Employees: Seek input from diverse teams to ensure the framework resonates across the board.
Emerging Trends in Human Resources Models
As workplaces evolve in response to technology and shifting employee expectations, future HR models are becoming more dynamic and adaptable. The integration of AI, HR analytics, and digital transformation is reshaping traditional approaches, while the focus on employee experience and inclusivity is driving the development of modern HR frameworks. Let’s explore these trends and how they’re redefining evolving HR strategies.
1. AI and Automation in HR Models
- What’s Happening: Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how HR processes are managed, from recruitment to employee engagement. Chatbots, predictive analytics, and automation tools are enabling HR teams to save time, reduce errors, and make data-driven decisions.
- How It’s Transforming HR Models:
- Recruitment models now leverage AI to screen resumes and identify top talent faster.
- Performance management frameworks use AI-powered insights to offer personalized feedback and development plans.
- AI simplifies administrative tasks, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
2. HR Analytics for Data-Driven Decision-Making
- What’s Happening: HR analytics is turning workforce data into actionable insights, helping organizations optimize their people strategies. Predictive analytics identifies trends like attrition risks or skill gaps, allowing HR teams to proactively address challenges.
- How It’s Transforming HR Models:
- Workforce planning models now integrate real-time data to predict staffing needs and optimize resource allocation.
- Engagement frameworks use analytics to track and improve employee satisfaction in measurable ways.
3. Digital Transformation in HR Frameworks
- What’s Happening: The shift to remote and hybrid work environments has accelerated digital adoption in HR. Cloud-based systems, collaboration platforms, and virtual onboarding tools are now integral to modern HR frameworks.
- How It’s Transforming HR Models:
- Remote-friendly HR models focus on virtual collaboration, performance tracking, and maintaining engagement across dispersed teams.
- Learning and development frameworks leverage e-learning platforms to make training accessible and scalable.
4. Focus on Employee Experience (EX)
- What’s Happening: Employee experience is now a central theme in modern HR frameworks. Companies are designing models that prioritize engagement, wellness, and career growth to attract and retain top talent.
- How It’s Transforming HR Models:
- HR models now include tools for continuous feedback, flexible work options, and well-being programs.
- Experience-driven frameworks are built to support employees throughout their lifecycle—from recruitment to retirement.
5. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
- What’s Happening: DEI is no longer an add-on—it’s a cornerstone of evolving HR strategies. Organizations are rethinking HR models to build more equitable workplaces that celebrate diversity.
- How It’s Transforming HR Models:
- Recruitment frameworks are being designed to eliminate bias and increase representation.
- Performance and development models now include metrics for equity and inclusivity.
The Road Ahead
The integration of technology and people-first approaches in HR models marks a new era for human resources. By leveraging AI, analytics, and digital tools, organizations can streamline operations and make smarter decisions. Meanwhile, the growing focus on employee experience, diversity, and inclusion ensures that HR strategies are not only effective but also human-centric.
To stay ahead, HR professionals must embrace these trends, continuously evolve their frameworks, and design strategies that meet the demands of the modern workforce. The future of HR models isn’t just about managing people—it’s about empowering them to thrive.
Conclusion | Human Resources Models?
Human resources models serve as the foundation for effective people management, providing organizations with structured frameworks to align HR strategies with business goals. From classic models like the Harvard Model and Ulrich’s HR Model to more dynamic frameworks like the 8-Box Model, McKinsey 7S, and High-Performance Work Systems, each offers unique insights into managing talent and driving organizational success.
However, the true power of these models lies in their adaptability. By considering factors such as organizational size, industry, culture, and goals, HR professionals can customize these frameworks to meet specific needs. Addressing challenges like resistance to change, resource constraints, and cultural misalignment is key to successful implementation.
As we look to the future, emerging trends in HR frameworks—like AI, HR analytics, digital transformation, and a focus on employee experience and inclusivity—are reshaping the way organizations approach HR strategy. These advancements highlight the evolving role of HR as not just a support function but a strategic driver of business success.
By embracing the right model, adapting it thoughtfully, and staying ahead of emerging trends, HR professionals can create workplaces where employees thrive, business goals are achieved, and innovation flourishes. The journey to effective HR begins with understanding these models and tailoring them to unleash the full potential of your organization’s greatest asset: its people.