

A happy, satisfied workforce is key to building a successful business. A recent study concluded that happy employees are 13% more productive than employees with low satisfaction levels.
Similarly, if your employees are not satisfied at work, you’ll notice that, too, through low productivity and increased employee turnover rates.
Have your employees started leaving in droves? Do your employees stick around for the long run? If your answers to these questions are negative, you might want to consider your company’s attrition rate.
You’ve probably heard of the term ‘attrition rate,’ but what does it mean? In this blog, we shall look at the meaning of attrition rate, the formula to calculate it, and much more.
So without further ado, let’s get started.
The dictionary definition of attrition is “gradually making something weaker and destroying it, especially the strength or confidence of an enemy by repeatedly attacking it.”
But in the industrial world, the attrition rate is a metric used to calculate and analyze the rate at which employees in a company voluntarily leave. It also calculates the rate at which customers leave a business. The attrition rate is also known as the ‘churn rate.’

Keeping track of attrition rates has become extremely important, mainly due to the skyrocketing resignation rates and even higher number of job openings brought on by the pandemic-induced ‘Great Resignation.’ Experts believe that the Great Resignation isn’t just a short-term swing in the industrial landscape but rather the beginning of a trend that will stick around for a while.
Having a clear vision of your company’s attrition rate is vital to understanding where it stands in terms of retaining employees. A high attrition rate can indicate several underlying issues, such as the lack of a competitive benefits package or a healthy work environment.
By calculating and analyzing your company’s attrition rate, you will be able to address these underlying issues and ensure the retention of top-performing employees.
A high employee attrition rate indicates that your employees are not sticking with your company for long, while a low attrition rate means that your company has better employee retention.
Attrition rates vary due to several factors, such as:
A high attrition rate in the workplace can occur not just because employees leave but when a business can’t replace them quickly. Employees leaving for any reason, voluntarily or involuntarily, contribute to attrition.
A high employee attrition rate has become a top concern for companies today. In many instances, employees leaving the company faster than they are hired is out of the manager’s control.
But before we get into more details about attrition rate, let’s look at its five types.
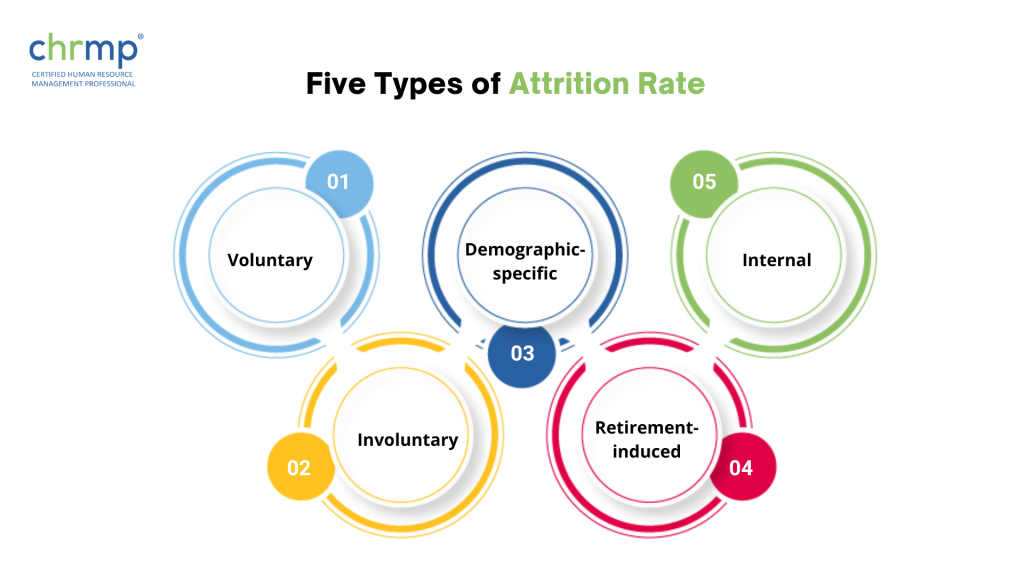
Let’s discuss these types in more detail.
Voluntary attrition is the most common type in which employees quit their current job to look for greener pastures elsewhere. There can be several reasons why this happens, but the most common ones include the following:
As evident, many of the reasons for voluntary attrition are under your control. Proactively curbing voluntary attrition among highly talented employees will go a long way in building a robust and success-driven workforce.
In this type of attrition, it is the organization that decides to lay off employees instead of employees leaving on their own accord. Factors such as mergers and acquisitions, structural reform, reduction in workforce or job position elimination are some of the reasons for involuntary attrition.
The company might sometimes dismiss an employee due to workplace misconduct. Keeping such employees might reflect poorly on the company’s image. Hence they are asked to leave.
Demographic-specific attrition indicates a specific group of employees: women, ethnic minorities, disabled people, veterans, or older professionals are leaving the company in large numbers.
This type of attrition is of particular concern for companies striving to create equal workplace opportunities. If you can identify a pattern of attrition among a specific demographic group, there is most likely a serious reason behind it.
In this type of attrition, employees within a department in a company switch their positions to gain a role in other departments. Even though internal attrition can redirect strong talent to vital functions in the company, it can also leave struggling departments even weaker.
If a department faces a high attrition rate, there might be several underlying causes, such as an inadequately skilled manager, failure to meet targets or an inconducive work environment.
It is natural for employees to retire and quit their jobs towards the end of their professional careers. Thus, it is statistically too insignificant to count under attrition in small groups.

However, it does not mean losing employees to retirement can be swept under the rug. Losing a sizable chunk of your employees at once due to retirement can add to your attrition rate.
Additionally, there might be several factors of retirement-induced attrition that have nothing to do with age. Some of your employees might retire for personal reasons such as illness or simply being able to afford to quit their jobs because they have substantial savings.
Another reason could be that your senior employee might want to become an independent consultant after acquiring decades of experience to have more career flexibility.
There can be several reasons for a high employee attrition rate, many of which might be outside your control. For example, employees might leave for personal reasons like family requirements or medical emergencies. The company itself induces other causes of attrition, like transfers, downsizing, organizational restructuring or termination.
But several causes of attrition can also be well under your control.
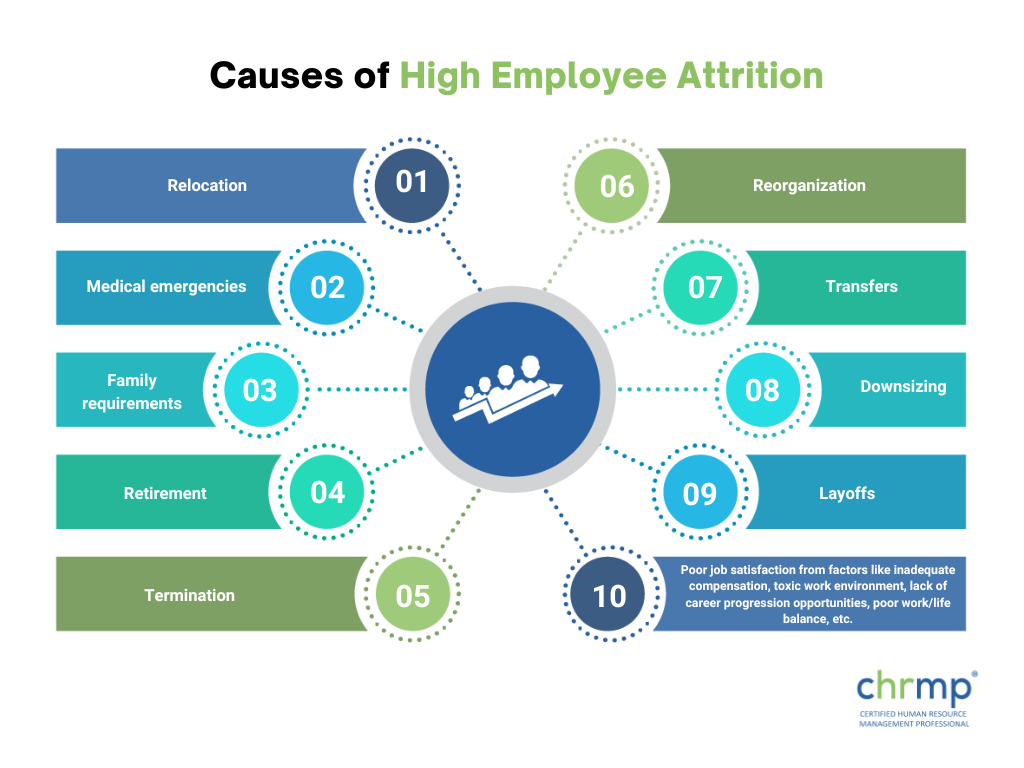
A common reason for employee attrition is poor job satisfaction; many other factors influence that. Pay is directly linked to job satisfaction, but this doesn’t mean employee satisfaction is just about the monthly money they take home. Other factors that add to a poor sense of job satisfaction include a lack of other financial benefits like bonuses and annual increments, a lack of career progression opportunities, a toxic work environment or poor work/life balance.
Another reason for employees quitting can be a lack of sense of belonging. We, as humans, are wired to fit in and be a valuable part of a community. Hence, it is only natural for employees to desire to fit in and feel valued by the company.
Understanding the attrition rate in your company can give you valuable insights into employee quitting trends and patterns, help identify what causes these patterns and eventually find a solution.
If attrition rates spike due to issues within the company, like inadequate pay and benefits or low job satisfaction, managers can focus on eliminating them. Here are some critical reasons to under attrition rate in your company.
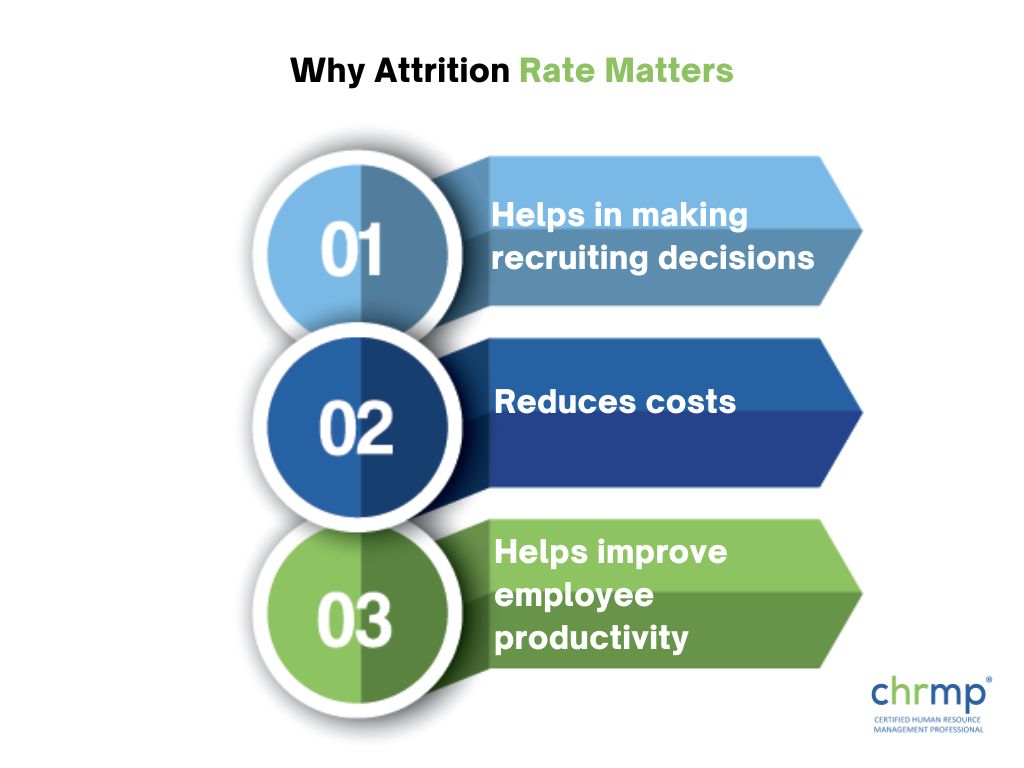
Understanding attrition and its causes in your company will help you better understand what employees expect from the company, resulting in a better recruitment process. It will also help you design better compensation and benefits packages to attract and retain highly talented candidates.
Hiring new employees can cost the company a lot of money. But suppose you have a good understanding of your company’s attrition rate. In that case, you’ll have a better idea of how many employees need to be hired within a specific period, which will prevent disruption in the workflow due to unfilled positions.
There are several ways in which understanding your company’s attrition rate can help you increase employee productivity, like reducing the time spent on training recruits. Another way to understand attrition can help identify and eliminate feelings of disgruntlement and low morale among employees due to underlying issues such as poor management or a lack of recognition, which boosts the overall productivity levels of the workforce.
The success of a company largely depends on unhindered contributions from its employees. It is vital to retain employees in whom you have invested precious time and resources. However, due to the many reasons discussed earlier, several employees leave the company to look for other options that can have far-reaching consequences.

A high attrition rate can heavily impact your company’s reputation, which indicates several unattended issues with your company. According to research, 50% of talented employees prefer not to work with a company with a negative reputation even when offered a higher salary.
The company’s progress is also negatively impacted due to a high attrition rate. How? Let’s assume that the average time for a new employee to settle and start adding to the profits is seven to eight months. That being said, if you constantly keep hiring new talents to replace leaving employees, a disruption in the workflow is inevitable, leading to a lag in your company’s progress.
To top it all, a high attrition rate results in a waste of training efforts and investment. It’s not just the company that gets impacted due to a high attrition rate; it affects the employees too. When employees see several of their colleagues leave the company, it takes a heavy toll on their morale and productivity.
There are several ways to manage your company’s attrition rate and prevent it from spiking. Some steps that you can take are:
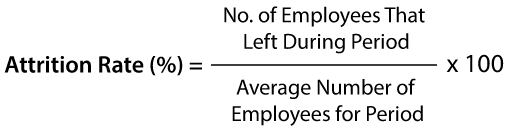
To determine the rate of attrition in your company, divide the average number of employees that quit over a specific time frame by the average number of employees in the company during that period and then multiply it by a hundred to obtain a percentage.
You can easily calculate the attrition rate of your company by using the formula,
Leadership is a vital factor in managing attrition rates within an organization. Good leaders create a positive work environment where employees feel valued, respected, and engaged.
They communicate clear expectations, provide regular feedback, and offer growth opportunities, helping employees understand their roles and responsibilities, set goals, and advance their careers.
Leaders who prioritize work-life balance and well-being can reduce burnout and stress, leading to higher employee satisfaction and retention. Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions boosts morale and motivation, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
Addressing employee concerns and grievances in a prompt and fair manner demonstrates commitment to employee well-being and satisfaction. Leading by example, with fairness, transparency, and integrity, can positively influence organizational culture and employee attitudes.
In conclusion, effective leadership is critical in managing attrition rates.
Leaders who create a positive work environment, foster engagement and satisfaction, offer growth opportunities, promote work-life balance, recognize and reward employees, address concerns and grievances, and lead by example can contribute to reducing attrition rates and retaining valuable talent within the organization.
Investing in strong leadership can yield significant benefits in employee retention, productivity, and overall organizational success.
What is ‘churn rate’?
Churn rate is another term for attrition rate and refers to the rate at which employees/customers leave a company/business over a specific period.
Are employee attrition and employee turnover the same?
Even though the terms’ employee attrition’ and ’employee turnover’ occur when employees leave a company, the two words have different meanings. The main distinction between employee attrition and employee turnover is that turnover includes all terminations, including refilled positions. On the other hand, employee attrition encompasses all long-term vacancies and position eliminations.
What is a good attrition rate for an organization?
A “good” attrition rate will depend on the company size, niche and the number of employees, among other factors. But most organizations should aim for a 10% attrition rate to keep the company running smoothly.
In conclusion, attrition rate is a critical metric for organizations to monitor and address in order to retain their valuable talent and maintain a healthy workforce.
High attrition rates can have detrimental effects on a company’s productivity, morale, and bottom line, while low attrition rates can indicate a positive work environment and employee satisfaction.
Through careful analysis of the causes of attrition, such as inadequate compensation, lack of career growth opportunities, poor work-life balance, and ineffective leadership, organizations can take proactive measures to reduce attrition and create a supportive and engaging work environment.
These measures may include conducting regular employee surveys, implementing competitive compensation and benefits packages, providing professional development opportunities, promoting work-life balance, and fostering a positive organizational culture.
© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited

Fill in the below details to get a CHRMP HR Analytics Program Plan.
