Introduction
The HR Generalist plays a pivotal role within any organization, providing comprehensive support across a range of human resources functions. Often considered the backbone of the HR department, HR Generalists handle an array of responsibilities, from recruitment to employee relations.
This blog will explore what an HR Generalist is, the typical roles and responsibilities associated with the position, and the key skills required to excel in this versatile role. Whether you are considering a career as an HR Generalist or looking to hire one, this guide will provide you with all the essential information.
What is an HR generalist?
An HR Generalist, also known as a Human Resources Generalist, is a professional who manages various HR functions within an organization. Unlike HR specialists who focus on specific areas like recruitment or benefits, HR Generalists cover a broad spectrum of HR activities.
They are responsible for ensuring that the organization’s HR policies and procedures are implemented effectively, aligning with overall business objectives. The role requires a versatile skill set, as HR Generalists deal with everything from employee onboarding to compliance with labor laws.
Roles and Responsibilities of an HR Generalist

HR Generalists play a multifaceted role in the organization, handling a variety of tasks that are essential for maintaining a healthy work environment. Here are some of the key roles and responsibilities:
Recruitment and Onboarding
HR Generalists are deeply involved in the recruitment process, which includes posting job openings, screening resumes, conducting interviews, and coordinating with hiring managers. They also manage the onboarding process, ensuring new employees are smoothly integrated into the company.
- Responsibilities:
- Creating and posting job advertisements.
- Screening and shortlisting candidates.
- Conducting interviews and background checks.
- Coordinating the onboarding process, including orientation and training.
Employee Relations
Maintaining positive employee relations is another crucial aspect of the HR Generalist’s role. They address employee grievances, mediate conflicts, and work towards fostering a positive work environment.
- Responsibilities:
- Handling employee complaints and grievances.
- Mediating conflicts between employees or between employees and management.
- Promoting a positive workplace culture.
- Ensuring compliance with company policies and procedures.
Compensation and Benefits
HR Generalists often manage employee compensation and benefits programs. This includes administering payroll, managing benefits packages, and ensuring that compensation practices are fair and competitive.
- Responsibilities:
- Administering payroll and benefits programs.
- Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations related to compensation.
- Conducting market research to ensure competitive compensation packages.
- Managing employee benefits enrollment and communication.
Performance Management
HR Generalists assist in the development and implementation of performance management systems. They help set performance standards, conduct evaluations, and provide feedback to employees.
- Responsibilities:
- Developing performance management processes and tools.
- Conducting performance appraisals and reviews.
- Providing feedback and coaching to employees.
- Identifying training and development needs.
Training and Development
Ensuring that employees have the necessary skills to perform their jobs is a key responsibility of HR Generalists. They identify training needs, organize training programs, and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Responsibilities:
- Assessing training needs within the organization.
- Developing and coordinating training programs.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of training initiatives.
- Supporting career development and succession planning.
Compliance and Legal
HR Generalists ensure that the organization complies with all relevant labor laws and regulations. They manage compliance-related documentation and processes, minimizing legal risks for the organization.
- Responsibilities:
- Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations.
- Maintaining accurate and up-to-date employee records.
- Conducting internal audits and ensuring adherence to company policies.
- Handling documentation and reporting for regulatory requirements.
What does an HR generalist do?
HR Generalists get involved in all aspects of the employee life cycle – from sourcing potential applicants to managing exits from the organization. Their main aim is to create and deliver people strategies that help organizations meet their goals.
On any given day, an HR Generalist might work with leadership teams on organization design models, or they might be dealing with specific disciplinary and grievance cases that have escalated. They draw from all parts of the specialist areas represented in the people profession, and their priorities are shaped by organizational needs. For example, an organization experiencing significant growth will need a heavy focus on resourcing and capability building, necessitating the broad expertise of an HR Generalist.
A key part of being an HR Generalist is the relationships you create across the organization. This helps you understand the wider priorities and create solutions that achieve the best organizational outcomes.
HR Generalist Roles and Job Titles
HR Generalist roles cover all levels of experience and seniority. The types of job titles you might find in general HR include:
- Human Resources Administrator
- Human Resources Officer
- Personnel Manager
- People Business Partner
- Human Resources Manager
- Head of People
- Director of People
Typical Activities for an HR Generalist
Here are some of the activities you can expect to be involved in as an HR Generalist:
- Designing people strategies and plans
- Creating employee engagement initiatives
- Developing people policies and procedures
- Setting up learning and development programs to meet organizational needs
- Designing organizational structures with business leaders
- Using HR information systems to gather people data and insights
- Creating an employer brand and recruiting for key positions
- Designing pay scales and benefits packages
- Identifying and retaining key talent across the organization
Skills and Competencies Required to Become a Successful HR Generalist
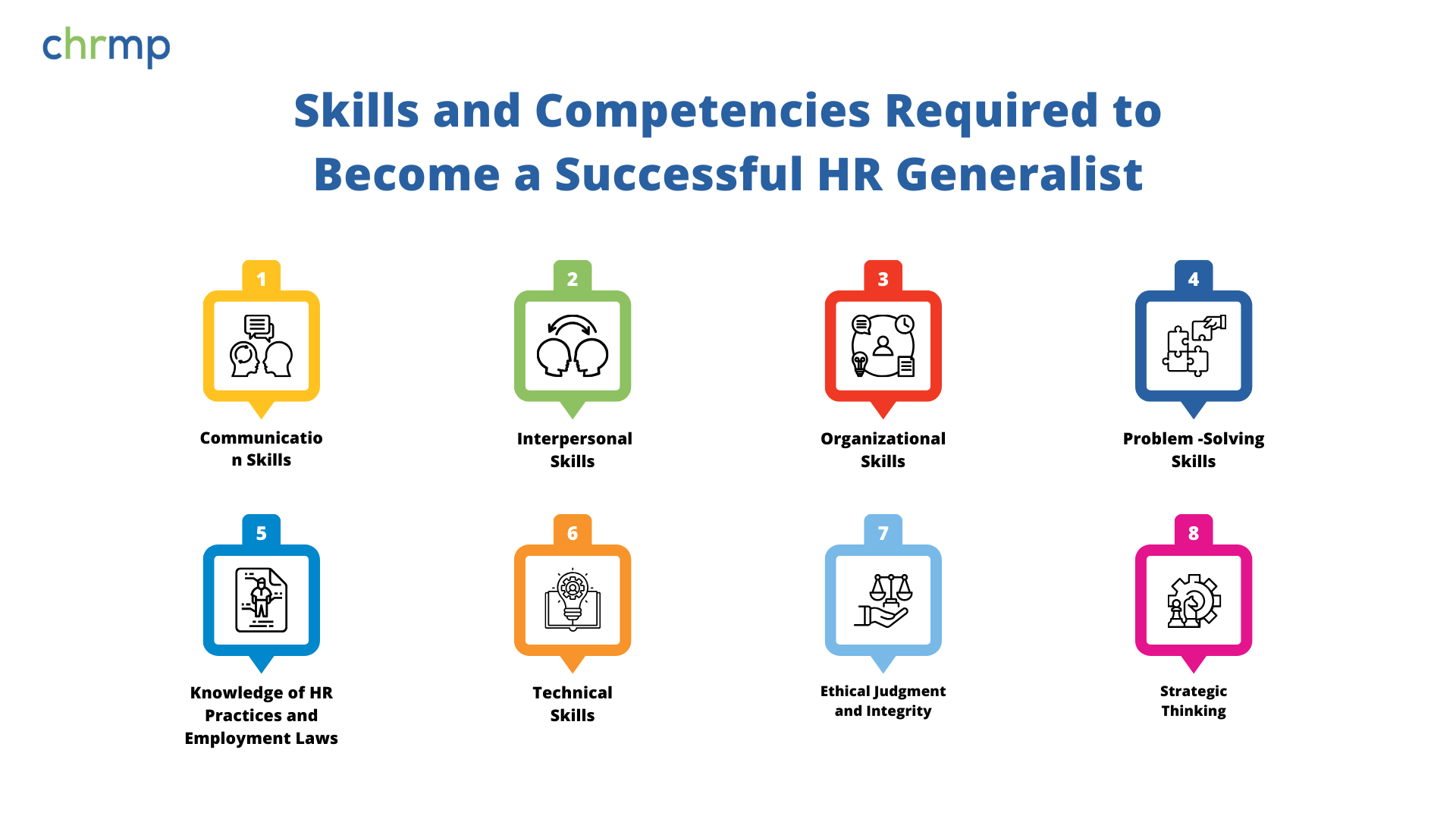
To excel as an HR Generalist, one must possess a diverse set of skills and competencies that enable them to handle the various facets of human resources management. Here are the key skills and competencies required to become a successful HR Generalist:
- Communication Skills
- Verbal Communication: Ability to articulate thoughts clearly in meetings, interviews, and presentations.
- Written Communication: Proficiency in drafting emails, reports, and HR policies.
- Active Listening: Engaging fully in conversations to understand issues and provide appropriate responses.
- Interpersonal Skills
- Empathy: Understanding and addressing the emotional needs of employees.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediating disputes and finding amicable solutions.
- Relationship Building: Developing trust and rapport with employees and management.
- Organizational Skills
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks to meet deadlines and handle urgent issues.
- Multitasking: Managing various HR functions simultaneously.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring accuracy in employee records, compliance documentation, and payroll processing.
- Problem-Solving Skills
- Analytical Thinking: Assessing problems and evaluating potential solutions.
- Decision-Making: Making informed decisions based on data and organizational policies.
- Creativity: Developing innovative solutions to improve HR processes and address employee concerns.
- Knowledge of HR Practices and Employment Laws
- HR Knowledge: Familiarity with recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management, and employee relations.
- Legal Compliance: Understanding labor laws, anti-discrimination regulations, and workplace safety standards.
- Continuous Learning: Keeping abreast of changes in HR practices and legislation.
- Technical Skills
- HRIS Proficiency: Managing employee records, benefits administration, and payroll using HR software.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing HR metrics to inform decision-making and improve HR strategies.
- Digital Literacy: Using technology to enhance recruitment, training, and employee engagement initiatives.
- Ethical Judgment and Integrity
- Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive employee information.
- Integrity: Upholding ethical standards and demonstrating honesty in all interactions.
- Fairness: Ensuring unbiased treatment of employees and adherence to organizational policies.
- Strategic Thinking
- Business Acumen: Understanding the organization’s goals and how HR can contribute to achieving them.
- Strategic Planning: Developing HR strategies that align with business needs.
- Change Management: Managing organizational changes and guiding employees through transitions.
By cultivating these skills and competencies, HR Generalists can effectively manage the diverse and dynamic aspects of human resources, contributing to the overall success and well-being of the organization.
HR Generalist vs. HR Manager: What’s the Difference?
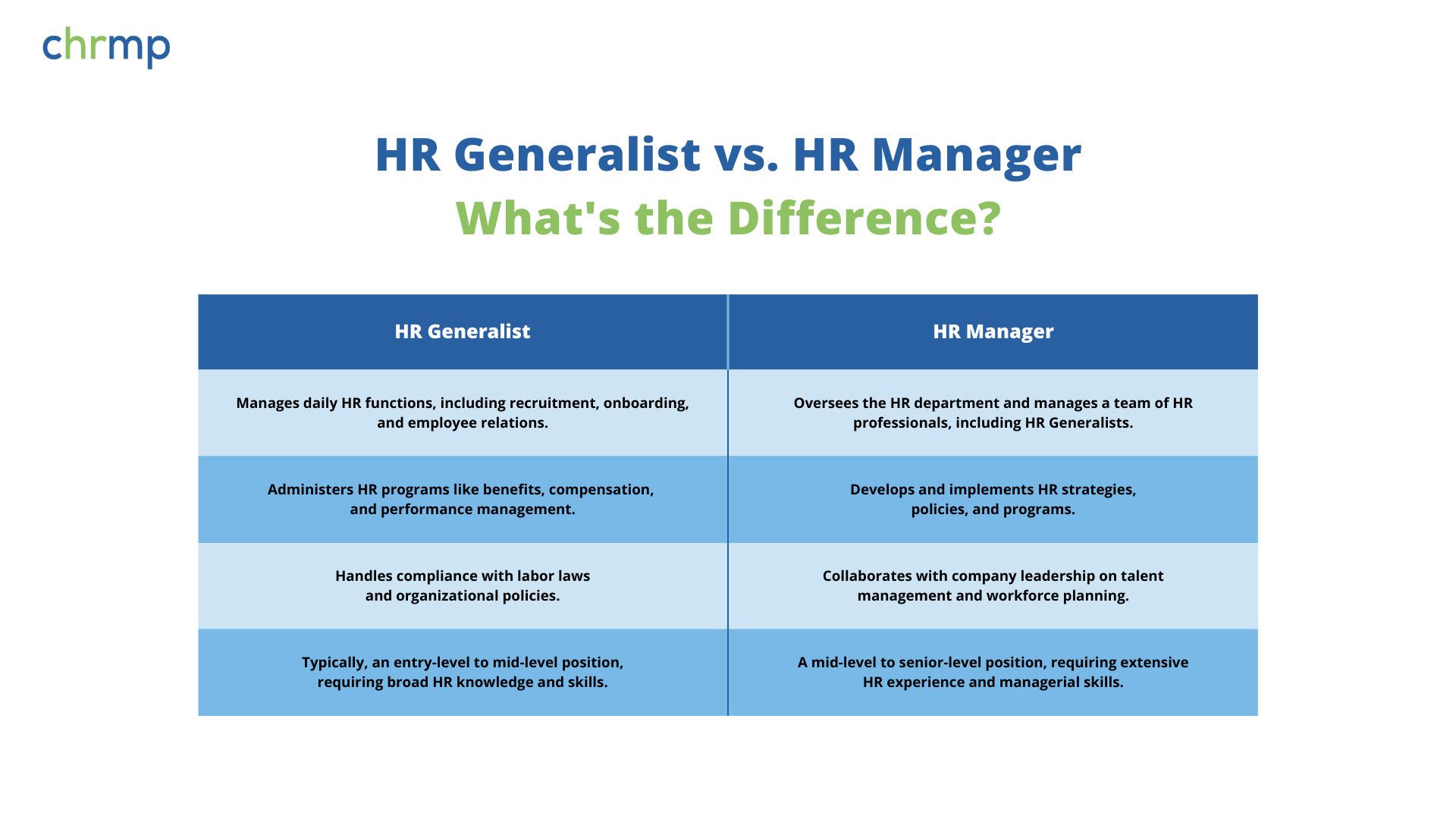
While both HR Generalists and HR Managers play crucial roles within the HR department, their responsibilities and focus areas differ significantly.
HR Generalist:
- Manages daily HR functions, including recruitment, onboarding, and employee relations.
- Administers HR programs like benefits, compensation, and performance management.
- Handles compliance with labor laws and organizational policies.
- Typically, an entry-level to mid-level position, requiring broad HR knowledge and skills.
HR Manager:
- Oversees the HR department and manages a team of HR professionals, including HR Generalists.
- Develops and implements HR strategies, policies, and programs.
- Collaborates with company leadership on talent management and workforce planning.
- A mid-level to senior-level position, requiring extensive HR experience and managerial skills.
Understanding the distinct roles and responsibilities of HR Generalists and HR Managers helps in appreciating how each contributes to the overall effectiveness of the HR department. HR Generalists handle the daily operational aspects of human resources, ensuring smooth HR processes and employee satisfaction. In contrast, HR Managers focus on strategic planning and overseeing the HR department to align with organizational goals and drive long-term success.
HR Generalist vs. HR Business Partner (HRBP): What’s the Difference?
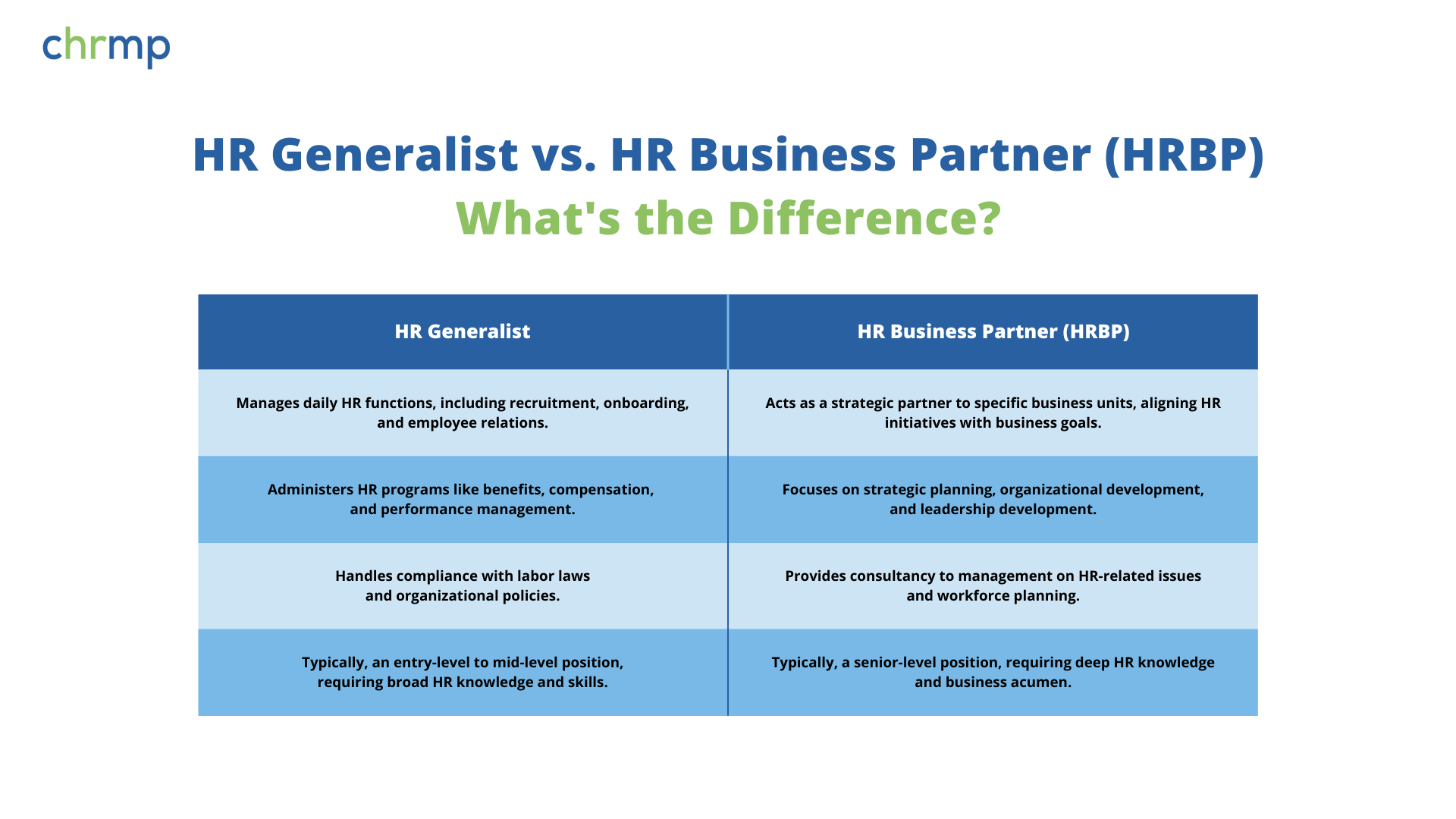
While both HR Generalists and HR Business Partners (HRBPs) play crucial roles within the HR department, their responsibilities and focus areas differ significantly.
HR Generalist:
- Manages daily HR functions, including recruitment, onboarding, and employee relations.
- Administers HR programs like benefits, compensation, and performance management.
- Handles compliance with labor laws and organizational policies.
- Typically, an entry-level to mid-level position, requiring broad HR knowledge and skills.
HR Business Partner (HRBP):
- Acts as a strategic partner to specific business units, aligning HR initiatives with business goals.
- Focuses on strategic planning, organizational development, and leadership development.
- Provides consultancy to management on HR-related issues and workforce planning.
- Typically, a senior-level position, requires deep HR knowledge and business acumen.
Understanding the distinct roles and responsibilities of HR Generalists and HR Business Partners (HRBPs) helps in appreciating how each contributes to the overall effectiveness of the HR department. HR Generalists handle the daily operational aspects of human resources, ensuring smooth HR processes and employee satisfaction. In contrast, HRBPs focus on strategic alignment of HR initiatives with business goals, partnering with business leaders to drive organizational success
How to Become an HR Generalist
- Pursue a Bachelor’s Degree in Human Resources: Complete a bachelor’s degree in human resources or a related field. This provides foundational knowledge in HR management, employment law, and business principles.
- Earn Certifications in Human Resources: Obtaining a CHRMP (Certified Human Resource Management Professional) certification can significantly enhance your qualifications and career prospects for an HR Generalist role. The CHRMP certification provides comprehensive training in HR principles and practices, equipping you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in an HR Generalist role.
- Gain Experience: Start with an entry-level HR job or internship to build your skills and gain practical experience. This helps you understand HR procedures and policies.
- Advance Your Career: Consider pursuing a master’s degree in human resources management or related fields to advance your career. Apply for higher-level positions as you gain experience.
Conclusion
The role of an HR Generalist is diverse and dynamic, requiring a broad skill set and the ability to handle various HR functions. HR Generalists are essential in creating and implementing HR strategies that help organizations meet their goals. By understanding their roles, responsibilities, and the skills needed to excel in this position, you can better appreciate the importance of HR Generalists in any organization.







